Preferences
The Available Preference Settings
The Preferences dialog is divided into the following sections:
|
General |
Settings for auto-saving and path substitutions. |
|
Project Defaults |
General project settings, and settings for color management. |
|
Performance |
Settings for caching, hardware, localization, and threads/processes. |
|
Behaviors |
Settings for start up, file handling, export options, scripting, node behaviors, and more. |
|
Panels |
Settings for the interface appearance, file browser, control panels, nodes, Viewers, script editors, and scopes. |
General
|
General |
|
|---|---|
|
Autosave |
|
|
force project autosave after <300> seconds |
Set the number of seconds after which to automatically save your project. Disable this by setting it to zero. |
|
Path Substitutions |
|
|
path substitutions |
Allows you to remap file paths in order to easily share projects across different operating systems. When the application encounters a file path, any text in the Mac/Linux column is replaced with the text in the Windows column, or vice versa. For example, if you enter /Volumes/networkmount in the Mac/Linux column and Z: in the Windows column: • On Mac and Linux, any file paths that start with Z: are converted to start with /Volumes/networkmount. • On Windows, any file paths that start with /Volumes/networkmount are converted to start with Z:. To be able to enter text in either column, you need to click on the + button below to add a row to the table. Note: Path substitution is invaluable for Sync Review sessions if you're using local source files rather than files from a central server. See Sync Review for more information. |
|
+ |
Adds a row under path substitutions. |
|
- |
Deletes the selected row(s) under path substitutions. |
|
Nuke |
|
|
Open In > New Hiero Session launches NukeX |
When enabled, new Hiero sessions are launched as NukeX. |
Project Defaults
Note: You must restart the application for changes to Project Defaults preferences to be applied.
|
Channel Management |
|
|---|---|
|
Channel Management |
|
|
Channel Warning Threshold |
Sets the total number of channels required in a script to trigger the Channel Warning. Hiero only supports 1023 uniquely named channels per script. The Channel Count is displayed in the bottom-right of the interface, next to the Localization Mode indicator. Note: Hiero does not remove unused channels until you close and reopen a script, so the Channel Count does not decrease when you remove Read nodes from the Node Graph. |
|
Color Management |
|
|---|---|
|
Default Color Management |
|
|
Default Color Management |
Sets the default color management system to use in new projects. |
|
OpenColorIO config |
|
|
OpenColorIO config file |
Sets the OpenColorIO configuration to use, if you don’t intend to use the nuke-default settings. |
|
If you select custom from the dropdown, enter the file path of the configuration file or click Choose to use the browser. Note: also includes an environment variable method for setting a config file. See Environment Variables in the Nuke Online Help for more information. |
|
|
Default Color Transforms |
|
|
working space |
Sets the colorspace files should be converted to, on import, and from, during render - it's the colorspace used by Hiero under the hood. |
|
viewer |
Sets the default LUT applied to Viewers. |
|
thumbnails |
Sets the default LUT applied to thumbnails when ever they are generated. |
|
Monitor Out |
Sets the default LUT applied to external monitors. |
|
8 bit files 16 bit files log files floating point files |
Sets the default LUT applied to the specified ingested file type. |
|
OCIO Roles |
|
|
Allow OCIO Roles in Colorspace Knobs |
When enabled, OCIO roles are available in all colorspace controls. |
|
Prioritize OCIO Roles |
When enabled, OCIO roles are created in the main menu of cascading dropdowns, with Colorspaces in a sub-menu. When disabled, roles are demoted to a sub-menu called Roles. You can also control this preference using an environment variable. See Hiero Environment Variables for more information. |
|
HDR (macOS only) |
|
|
Enable macOS HDR Color Profile (Display P3) (Beta) |
When enabled, running under macOS with a screen capable of displaying values greater than 1 allows you to display HDR images in the Display P3 colorspace correctly. |
|
Hiero Script Project Settings |
|
|
color management |
Sets whether Hiero uses the LUTs read from the configuration specified or the Nuke native LUTs during export. Selecting OCIO makes the relevant OCIO LUTs available to the Read and Write nodes in scripts on a per project basis. All configurations except nuke-default automatically switch this control to OCIO. |
|
General - these preferences only apply to new scripts and projects. To affect the current project, use the Project Settings. |
|
|---|---|
|
Project |
|
|
project directory |
Sets the project directory used by new projects. You can change the project directory for the current project in the Project Settings. |
|
Hrox Directory |
Click to set the project directory to the location of the .hrox file using the [python {nuke.script_directory()}] expression. |
|
export directory |
Sets the directory used by timeline exports: • Use Project Directory - use the directory specified by the project directory preference. • Use Custom Directory - use the directory specified by the custom export directory control. |
|
custom export directory |
Sets the export directory used by new projects when the export directory control is set to Use Custom Directory. |
|
Sequence |
|
|
output resolution |
Use this to set the output resolution in the Timeline environment for new projects. By default, clips in the sequence are not reformatted to fit this format, they retain the source clip resolution. You can adjust the reformatting for new clips added to a sequence using the Clip settings below or by selecting clips in the timeline and adjusting the settings in the Properties tab. |
|
frame rate |
Select the frame rate for new projects in the Timeline environment. |
|
start timecode |
Use this to define the start timecode for new projects. For shots, this overrides the timecode defined in the media. |
|
time display |
You can use this to select the display format for times. You can select either Timecode or Frames. |
|
drop frame |
Use this to choose whether timecodes from this sequence are displayed in drop frame times or not. Drop Frame is a timecode display option that leaves out two frames from the 30 fps timecode sequence every minute (except every 10th minute) so that long running NTSC sequences are accurate to a real-time clock (NTSC frame rate is 3000/1001, or approximately 0.01% slower than 30fps). Note: Enabling Drop Frame is a Timecode display feature only - the source media remains a continuous stream of frames. |
|
Clip |
|
|
clip reformat |
Sets how new clips added to a sequence are formatted. The default, None, displays shots at the source clip resolution, whereas To Sequence Resolution reformats the shot to the output resolution using the resize type control. |
|
resize type |
When clip reformat is To Sequence Resolution, determines how the shot is resized to fit the output resolution. This control is disabled when clip reformat is set to None. |
|
center |
When clip reformat is To Sequence Resolution, disabling center places the clip at the bottom-left of the output resolution, rather than the center. |
|
Link bin and track item versions |
When enabled, selecting a new version for a clip in a bin or a shot on the timeline updates all instances of that media. When disabled, you can version clips and shots independently, even if they reference the same media. |
|
Poster Frame |
|
|
poster frame |
Sets a preset poster frame for all new source clips or select Custom to select a relative frame offset as the poster frame: • First - new source clips display the first frame of the file on disk as the poster frame. • Middle - new source clips display the middle frame of the file(s) on disk as the poster frame. • Last - new source clips display the last frame of the file(s) on disk as the poster frame. • Custom - the poster frame number is derived from the number of frames in the clip starting at 0. Use the frame offset control to set the relative offset. |
|
frame offset |
When poster frame is set to Custom, enter the relative frame offset from the first available frame in the file(s) on disk. |
|
Sync Session (Beta) |
|
|---|---|
|
Default Appearance |
|
|
name |
Sets the name and color you want to display on participant sessions. Click the color swatch to open the color picker. |
|
Default Behavior |
|
|
open sync panel on sync session startup |
When enabled, automatically open the Sync Session panel when a session is started. |
|
Project Saving |
|
|
save directory |
Sets the default directory where all Sync Session projects are saved. |
|
Views - these preferences only apply to new scripts and projects. To affect the current project, use the Project Settings. |
|
|---|---|
|
Views |
|
|
+/- |
Click to add and remove views from the views list. |
|
↑ ↓ |
Click to move views up and down the views list. Moving a view changes the position of the corresponding Viewer button. |
|
View |
Lists the views in the script or project and the color associated with the view when Use color in UI is enabled. |
|
hero |
Sets the principal view selected on script or project load. |
|
Set up views for stereo |
Click to automatically add left and right views to scripts or projects. |
|
Use colors in UI? |
When enabled, the colors specified in the views matrix are applied to the interface. For example, if you click Set up views for stereo and enable this control, any UI items representing the left and right views are colored red and green. |
Performance
|
Caching |
|
|---|---|
|
Timeline Disk Caching |
|
|
directory path |
The directory where all .exr files from timeline disk caching are stored by default. The caching directory should be on a local disk, preferably with the fastest access time available. It’s also important to leave enough space for the maximum disk cache size (defined below). |
|
limit to (GB) |
This allows you to set the maximum amount of space (in GB) to use for the timeline disk cache. Set to zero for unlimited size. Values lower than zero, leave that amount of space free. The currently in use and currently free fields display how much free cache remains from the total specified. If this limit is reached during caching, a dialog displays options to free up disk space. |
|
EXR compression |
Sets the type of compression applied when writing files to the disk cache: • DWAB • Zip (1 scanline) Note: DWAB compression produces smaller cache files more quickly, but can be lossy compared to Zip compression. |
|
clear cache |
Clear All removes all cached files from the root directory specified in the directory path control. A dialog displays a list of files for confirmation before the files are deleted. |
|
Comp Disk Caching |
|
|
temp directory |
The comp disk cache saves all recent images displayed in the Viewer for fast playback. Using this control, you can specify where you want Hiero to save these images. Select a local disk (for example, C:/temp), preferably with the fastest access time available. It’s also important to leave enough space for the maximum disk cache size (defined below). |
|
Memory Caching |
|
|
playback cache size (% of system RAM) |
Specifies the percentage of system RAM used for the timeline Viewer playback cache. The entire amount is allocated, even if you've only got a few frames in the Viewer. Recently used frames are retained in the memory to avoid relying on the disk buffering system. The cache is freed when you switch to the compositing Viewer and reallocated when you switch back to the timeline Viewer. Tip: On low-end machines, minimizing this may improve application responsiveness at the expense of smooth playback. |
|
free timeline playback RAM cache when switching to the node graph |
When enabled, any frames cached to RAM (the white bar in the timeline Viewer) are discarded when you switch to the Node Graph within Nuke Studio, freeing the RAM for use in Hiero. Note: When you switch back to the timeline, the cached files are re-cached, which can be time consuming. |
|
Audio Waveforms |
|
|
waveform memory (MB) |
Sets the amount of memory available for storing timeline audio waveforms. |
|
Application in Background |
|
|
pause timeline Viewer when the application goes to the background |
When enabled, pause timeline Viewer caching when the application is in the background. |
|
clear timeline Viewer cache when the application goes to the background |
When enabled, the timeline Viewer cache is cleared when the application goes into the background. Note: This preference is only available when pause timeline Viewer when the application goes to the background is enabled. |
|
Undo Caching |
|
|
undo history size |
Allows you to set the amount of RAM, in MB, to use for the undo history. If this limit is exceeded, older items are discarded. |
|
minimum undo events |
Use this to set the amount of undo events. This setting always applies, even if it breaches the undo history size limit. |
|
Hardware |
|
|---|---|
|
Audio |
|
|
audio device |
The audio device control allows you to select an existing audio device for playout from a list of automatically detected devices. You can disable playout on a device by selecting Disabled. |
|
RED Rocket |
|
|
use red rocket |
You can select the use red rocket checkbox to speed up decoding RED media. If you’re using R3D Rocket graphics card, note that using it is likely to only be considerably faster when you’re reading in at full resolution. If you’re reading in at half resolution, for instance, using without the R3D Rocket card enabled may be faster. This is because the R3D Rocket graphics card is designed to be fast when reading in multiple frames at the same time. This is not how it works internally, and therefore reads with the R3D Rocket card disabled may sometimes be faster when working in lower resolutions (< 4K widths). Also, note that the R3D Rocket card always produces better results than when downsampling. Also, the R3D Rocket card can only be used by one application at a time, so if you are viewing multiple scripts at once, you may only be able to use the R3D Rocket card in one. |
|
GPU |
|
|
expand 3 to 4 channels |
You can use this to expand images cached for playback from 3 to 4 color channels per pixel. Some graphics hardware performs better at loading images to video memory with 4 channels per pixel, than it does with 3. Enabling this option improves playback performance on such hardware, at the expense of reducing the number of frames that it's possible to cache. If you are seeing poor playback performance, enabling this option may help. However, if you are seeing acceptable playback performance with this option disabled, then leaving it disabled increases the number of frames that may be cached for smooth playback. Note: You must restart Hiero for this option to take effect. |
|
enable vsync |
When enabled, synchronize new timeline Viewer's playback frame rate with the refresh rate of the monitor. Enabling vsync limits the playback fps to the monitor refresh rate and may reduce performance. When disabled, timeline Viewer performance is unaffected but you may see tearing in timeline Viewers. Note: This preference is only shown in Nuke Studio and Hiero sessions and only affects new timeline Viewers. Close and reopen any existing Viewers after enabling this option. |
|
Localization |
|
|---|---|
|
System |
|
|
mode |
Sets the overall localization mode: • on - checks for updates to source clips and Read nodes with localization policy set to On or From auto-localize path and localizes those files automatically. • manual - checks for updates to source clips and Read nodes with localization policy set to On Demand and prompts you to update them manually. • off - no source clips or Read nodes are localized, regardless of the their localization policy. Note: The current localization mode is displayed in the status bar at the bottom-right of the interface. |
|
read source files when localized files are out of date |
When enabled, source clips and Read nodes referencing out of date localized files automatically revert to reading the entire sequence from the original source files. Source files are read in the following circumstances: • With Localization mode set to on: • A localized source clip or Read node with localization policy set to on demand is detected to be out of date. • A localized source clip or Read node with localization policy set to on or from auto-localize path is detected to be out of date and it is queuing to be automatically localized. • With Localization mode set to manual: • A localized source clip or Read node with localization policy set to on, on demand, or from auto-localize path is detected to be out of date. When disabled, the out of date localized files are read until you update them manually. |
|
hide out of date progress bar |
When read source files when localized files are out of date is enabled, you can enable this control to hide the progress/status bar on Read nodes that are reading from the original source files. |
|
pause localization on script/project open |
When enabled, localization does not start automatically when you open a script or project. Enabling this option can help to open scripts and projects more quickly. |
|
Inputs |
|
|
localization policy |
Sets the localization policy for all new source clips and Read nodes: • on - always localize source clips and Read nodes with this policy automatically. • from auto-localize path - localize these source clips and Read nodes automatically if they reside in the auto-localize from directory. • on demand - only localize these source clips and Read nodes when you manually update them. • off - never localize these source clips or Read nodes. |
|
Paths |
|
|
auto-localize from |
Enter the location of the files you need automatically localized, unless otherwise specified in the Read node’s cache locally control |
|
localize to |
Enter the file path where all the localized files are automatically stored. Localizing files allows for faster reloading for files that are stored in a location that is slow to access (such as a network drive). On Windows, files saved to the localize to directory replace \\ (double back slashes) and : (colon drive signifiers) with underscores so that the file path works as expected between operating systems. For example: \\windowspath\to\my\network\file.dpx is saved as __windowspath\to\my\network\file.dpx |
|
Storage |
|
|
limit to (GB) |
This allows you to set the maximum amount of space (in GB) to use for localized files. Set to zero for unlimited size. Values lower than zero, leave that amount of space free. The currently in use and currently free fields display how much free storage remains from the total specified. If this limit is reached during localization, a dialog displays options to free up storage space. |
|
Network |
|
|
check for updated files every |
When files are localized, specifies the time interval (in minutes) before Hiero checks for updated versions of the files. |
| Appearance | |
|
progress bar |
Sets the colors used to represent the localization states of source clips and Read nodes. |
|
Threads/Processes |
|
|---|---|
|
Playback |
|
|
default number of threads per reader |
Sets the number of threads to use per reader. If your source files are located on high performance local drives, increasing the number threads can significantly improve read times. CPU intensive operations, such as .jpg decoding, can also be improved by increasing the number of threads per reader. |
|
override number of threads per reader |
Allows you to override the default number of decode threads used, dependent on file format. Use the plus button to add an entry to the table and then select the file format using the dropdown menu. Double click the Number of threads column to set the required number of decode threads for that format. |
|
OpenEXR helper threads to use |
Sets the number of helper threads to use for OpenEXR only. The default, zero, automatically sets the number of helper threads used. |
|
Arri helper threads to use |
Sets the number of helper threads to use for ARRI only. The default, zero, automatically sets the number of helper threads used. |
|
Note: The OpenEXR and ARRI helper thread preferences are independent of the threads per reader and override table per format settings. |
|
|
QuickTime decoders to use |
Sets the number of background processes available to handle QuickTime file I/O. You must restart the application for this preference change to take effect. Note: Using too many decoders can affect performance, depending on the available hardware. Note: You must restart Hiero for this setting to take effect. |
|
Rendering |
|
|
frame server render timeout |
Allows you to increase the number of minutes a render process can stay unresponsive before ending. If you're experiencing Render application timed out messages with process-heavy scripts, you can try increasing this value. |
|
focus background renders |
When enabled, rendering using the Frame Server automatically opens the Background Renders panel, or if it is already open, shifts focus to the panel. |
|
frame server processes to run |
Set the number of worker Hiero processes to run for the frame server. Note: You must restart Hiero for this setting to take effect. |
|
export renders |
You can select from several render options: • limit renderer (more responsive ui) – Select this option to make the user interface more responsive during transcodes. It tells Hiero to use 2 threads to transcode and to use 25% of RAM to cache. Using this option is likely to result in slower transcodes. • no renderer limits (fastest transcoding) – Select this option to ensure that transcodes happen as quickly as possible. This option may result in a less responsive user interface during transcodes. • customize render limits – Select this option to manually configure the number of threads used and cache memory available when transcoding files. Note: You must restart Hiero for this setting to take effect. |
|
number of threads |
Sets the number of threads that Hiero uses when transcoding. Lower numbers allow the Timeline environment's interface to be more responsive. Higher numbers allow faster transcodes. This setting is passed to Hiero using the -m option. |
|
cache memory (GB) |
Use this to set the number of gigabytes of RAM that Hiero uses for its cache settings. Lower numbers may improve the Timeline environment's interface responsiveness, while higher numbers may improve the speed of the transcodes. This setting is passed to Hiero with the -c option. |
|
Downsize Filtering |
|
|
8-bit images 10-, 12- and 16-bit integer images 16-bit float images 32-bit images |
Customizes the downsize filtering behavior by bit-depth. The default (1x) retains the original image size. You can select 2x to halve the image size, or 4x to quarter the image size. The Viewer image quality dropdown affects the decode rate and resolution of clips displayed in the Viewer. Lower resolutions decode faster and vice versa. |
Behaviors
|
Documentation |
|
|---|---|
|
documentation source |
Sets the help source for the Properties ? button: • local – use Hiero's built-in HTML help server. Hiero's local help server also searches the NUKE_PATH, .nuke, and .nuke/Documentation directories for HTML files with the same name as the requested node, such as Blur.html. • foundry – This uses Foundry's Online Help, the most up-to-date version of the documentation. • custom – Select this to point to your own help server. |
|
auto port |
When enabled, assign a free port automatically. |
|
local port |
Specify a local documentation server port manually. This is usually >= 1024. You can also set this to 0 to automatically assign the port. |
|
range |
Specify a range of ports to attempt with the local documentation server. |
|
File Handling |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
scan for file sequence range on drop into Bin view |
When enabled, identify and import the file range of media that is dropped into the bin. When disabled, no range is detected and only a single frame is ingested. (This does not affect container formats, such .mov and .r3d.) |
||||||
|
automatically rescan versions when moving off end of the version list |
When enabled, incrementing a source clip or shot’s version past the end of the previously discovered versions list, forces a rescan to update the versions list. See Using Versions for more information. |
||||||
|
frame number style |
Sets the sequence display mode to be used in the file browser. |
||||||
|
assume fixed width frame numbers in file sequences |
When enabled, assume frames have a fixed width number. With this selected, frame numbers need to be padded with zeros to a fixed length, otherwise frame numbers without preceding zeros are assumed to belong to sequences with no padding. This is important as the sequence identifier specifies a unique file name for each and every frame. For example:
|
||||||
|
default red clip video decode mode |
Sets the default red clip decode mode for new projects. You can choose from FullPremium, HalfPremium, HalfGood, QuarterGood, EighthGood, or SixteenthGood. Note: Changing this preference does not change the default decode setting for existing projects. |
||||||
|
Positions |
|
|---|---|
|
show menus with previous item under the cursor |
When enabled, opening contextual menus positions them with the most recently used item under the pointer. |
|
Startup |
|
|---|---|
|
startup workspace |
Sets which workspace to display on startup. You can choose from Compositing, Conforming, Editing, Finishing, Reviewing, and Timeline. You can also choose to save a customized workspace, which would also be available from this list. |
|
show splash screen at startup |
When enabled, display the splash screen on startup. |
|
show startup dialog |
When enabled, display the dialog on startup. |
|
restore workspace when opening projects |
When enabled, restore the selected saved workspace when opening projects. |
|
Analytics |
|
|
submit usage statistics |
When enabled, certain usage statistics are collected from the machine on which you license Hiero, NukeX, Nuke Studio, Hiero, and HieroPlayer. When disabled, we don't collect any usage data from your machine. Note: The port number used to communicate with Foundry is 443, the same one used for uploading crash reports. |
|
Timecode |
|
|---|---|
|
R3D file timecode |
Sets the source timecode for RED files. You can choose from Default From File, Absolute Timecode, or Edge Timecode. |
|
other media timecode |
Sets the timecode source for file-per-frame media (such as .dpx). You can choose from File Header or Frame Number. If File Header is selected and a timecode exists, then the timecode is used. Otherwise it defaults back to using the frame number from the file name. |
|
max valid timebase (fps) |
Sets the maximum image header timebase above which the value is clamped. Image files are often created with application specific timebase values in the header description. This can lead to reading in spuriously high frame rates and the clamp aims to prevent this from happening. If your clips do have extremely high frame rates, increase this value as necessary to avoid clamping. |
|
EDL style spreadsheet timecodes |
When disabled, the srcOut and dstOut values in the spreadsheet use the film convention, representing the last frame of the cut. When enabled, the srcOut and dstOut values in the spreadsheet use the video convention, representing the frame directly after the cut. |
|
UI Scaling |
|
|---|---|
|
Note: You must restart the application to apply changes to UI Scaling preferences. |
|
|
UI Scaling Mode |
Sets the scaling mode for the UI on Windows and Linux. macOS handles UI scaling automatically. • off - no scaling is applied to the UI, regardless of screen resolution. • auto - the UI attempts to scale appropriately dependent on screen resolution. • all - enables the Scale All dropdown, which allows you to scale all screens by the selected factor. • per display - enables the Per Display table, which allows you to set the scaling applied per screen. |
| Scale All | When UI Scaling Mode is set to all, allows you to scale all screens by the selected factor. |
| Per Display | When UI Scaling Mode is set to per display, allows you to set the scaling applied per screen. |
Panels
|
Appearance |
|
|---|---|
|
Font |
Change the type, weight, angle, and size of the font used on Hiero’s user interface. |
|
UI Colors - right-click on any color button and select Set color to default to revert changes. |
|
|
Background |
Change the background color of most user interface elements (menus, toolbars, panes, properties panels, Viewers, and pop-up dialogs). |
|
Base |
Change the color of input fields, the input pane of the Script Editor, and the left side of the Curve Editor. |
|
Highlight |
Change the color of the highlighting that appears when you hover the cursor over a control, select a file or folder in the File Browser, or scrub to a new frame on the timeline. |
|
Highlighted Text |
Change the color of any highlighted text (for example, text you select in node properties). |
|
Label |
Change the color of labels and text on the application interface. Note that this does not set the color of the labels on nodes in the Node Graph. |
|
Button |
Change the color of buttons and dropdown menus. |
|
Animated |
Change the color that indicates a control has been animated. |
|
Keyframe |
Change the color that indicates a keyframe has been set. |
|
Disk cached frames |
Change the color of the disk cached frames on the Viewer timeline. |
|
RAM cached frames |
Change the color of the RAM cached frames on the Viewer timeline. |
|
Playhead |
Change the color of the frame marker on the Viewer timeline. |
|
In/Out Markers |
Change the color of the in and out frame markers on the Viewer timeline. |
|
Curve Editor / Dope Sheet - right-click on any color button and select Set color to default to revert changes. |
|
|
no. of curves visible |
Sets the maximum number of curves visible in the Curve Editor. |
|
background |
Change the background color of the Dope Sheet tab. |
|
unselected key |
Change the color used for an unselected key on the Dope Sheet. |
|
part-selected key |
Change the color used for a part-selected key on the Dope Sheet. |
|
selected key |
Change the color used for a selected key on the Dope Sheet. |
|
timeline |
Change the color used for the timeline on the Dope Sheet. |
|
control text |
Change the color used for the control text on the Dope Sheet. These indicate the frame number of a key when you select one. |
|
control text shadow |
Change the color used for the shadow of the control text on the Dope Sheet. |
|
time label |
Change the color used for the time labels on the Dope Sheet. These indicate frame numbers. |
|
current frame |
Change the color used for the current frame on the Dope Sheet. This is a vertical line that indicates the current frame on the timeline. |
|
project frame range |
Change the color used for the project frame range on the Dope Sheet. These are two vertical lines indicate your frame range. |
|
Control Panels |
|
|---|---|
|
max nodes in properties bin |
Use this to set the maximum number of panels that can be open in the Properties pane. |
|
reopen acts like new panel |
When this is enabled, double-clicking a node that has been open before, places the panel in the same place as a new panel. If this is disabled, the panel appears in its previous position. |
|
expand / collapse panels in Properties bin to match selection |
If this is enabled, the node selection in the Node Graph determines which control panels are expanded (all unselected nodes automatically have their panels collapsed). This does not apply to floating control panels. |
|
Color Panel |
|
|
color picker button opens |
Sets the type of color picker displayed when you click a color picker button in the properties panel: • in-panel color picker - opens a color wheel and sliders in the properties panel. • floating color picker - opens a color wheel and sliders in a floating panel. Tip: Holding Ctrl/Cmd and clicking the color picker button opens the alternate color picker to the one specified in the Preferences. |
|
File Browser |
|
|---|---|
|
start file browser from most recently used directory |
When enabled, new file browsers open at the last location used. When disabled, new file browsers open at the current working directory. |
|
Node Colors |
|
|---|---|
|
autocolor |
Deselect this checkbox to ignore individual soft effect color settings and, instead always use the All Others color. |
|
<node name or type> |
The
|
|
All Others |
Use this to select the color to use as default for all |
|
Project Items |
|
|---|---|
|
shade project items |
When enabled, additional shading is applied to source clips and shots in the Project bin and timeline. |
|
Item Labels |
|
|
project bin |
Click to change the color of labels in the Project and timeline panels. A color wheel displays allowing you to select the required color. |
|
timeline |
|
|
auto-adjust contrast |
When enabled, label colors are automatically adjusted if a potential color-clash is detected. |
|
Item States |
|
|
offline |
Click the buttons to change the color of shots and comps in the timeline panel. A color wheel displays allowing you to select the required color. |
|
error |
|
|
freeze |
|
|
comp not rendered |
|
|
comp out of date |
|
|
comp rendered |
|
|
Item Colors |
|
|
display in project panel |
When enabled, the specified item colors, or defaults, are displayed in the Project panel. |
|
display in sequence panel |
When enabled, the specified item colors, or defaults, are displayed in the timeline panel. |
|
spreadsheet color rows |
When enabled, the specified item colors applied to rows in the spreadsheet. |
|
project |
Click the buttons to change the color of items in the Project and timeline panels. A color wheel displays allowing you to select the required color. |
|
bin |
|
|
sequence |
|
|
source |
|
|
audio |
|
|
comp |
|
|
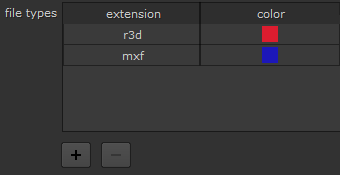
file types |
Allows you to add custom color-coding by file extension. Click the Any source clip or shot with that extension is then colored accordingly in the interface.
|
|
Scopes |
|
|---|---|
|
black point |
Use the slider or the entry box to select the black point value. |
|
white point |
Use the slider or the entry box to select the white point value. |
|
luma/chroma encoding |
Use this to select the video standard to use when converting from RGB to luma and chroma for scope display. |
|
Include viewer color transforms |
Select this checkbox to include applied Viewer color transforms (gain, gamma, and LUT) in scope data. If this checkbox is disabled, all Viewer transforms are ignored. Note: If disabled, rendering may become slow as image calculation may be needed. |
|
Force full frame |
Select this checkbox so that the Viewer always requests full frame data when a scope is displaying data for that Viewer. If this checkbox is disabled, the scopes only display data for the current area requested by the Viewer, rather than the whole image. |
|
Script Editor |
|
|---|---|
|
font |
Use this to select the font to use in the Script Editor. Note: This control also changes the font in the BlinkScript Kernel Source field. |
|
indent |
You can use this control to set the indent value to use when scripting. |
|
save and restore script editor history |
Disable this checkbox if you prefer that the contents of the Script Editor is not saved and restored between sessions of Hiero. |
|
clear input window on successful script execution |
Disable this checkbox if you want the most recent script to remain in the input window after execution. |
|
Timeline |
|
|---|---|
|
show frame end marker |
When enabled, an extra line is drawn on the timeline to the right of the playhead, indicating the end of the current frame. |
|
visible range follows playhead |
When enabled, the timeline scrolls with the playhead, constantly updating the view. When disabled, the playhead is allowed to move off screen. |
|
Audio Tracks |
|
|
half waveforms |
When enabled, audio tracks on the timeline display only the rectified waveform. When disabled, the full waveform is displayed. |
|
Viewer (Monitor Out) |
|
|---|---|
|
use video legal range for monitor out |
When enabled, automatically limit monitor out to the legal range when swapping between the Timeline environment and Compositing environment. |
|
always keep the floating window on top |
When enabled, Hiero's internal floating monitor out window always remains on top of other open application windows. |
|
Enable support for HMD devices |
When enabled, VR headsets such as the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive are added to the Monitor Out > Device dropdown. Choose the required headset from the dropdown to pass the monitor out to the selected device. |
|
background |
Sets the background color used to fill Hiero's floating window when the output is not full-frame: • black • gray - use the slider to the right to set the brightness of the plain background. • checkerboard - use the slider to the right to set the brightness of the checkerboard background. |
|
Viewer |
|
|---|---|
|
default flipbook |
Sets the default flipbook mode, Hiero's Flipbook Viewer or HeiroPlayer. • Flipbook Viewer opens a new Viewer inside Hiero containing the flipbooked content. • HieroPlayer launches an instance of the application containing the flipbooked content, but requires either a Nuke Studio or HieroPlayer license. |
|
playback mode |
Use this to set the Viewer playback mode: • Play All Frames - the default setting, plays all frames in real-time (dependent on hardware). • Skip Frames - plays frames in real-time skipping where necessary to maintain the frame rate. • Play All Frames, Buffering - plays all frames by buffering and playing frames back as they become available. |
|
guides |
You can use this to choose to show overlays in the image area. You can choose from: • Title Safe – Indicates where text should be entered to be visible. • Action Safe – Indicates the area in which to place actions so that they are visible. • Format – Displays the size of the format over the Viewer. |
|
fullscreen display |
Use this to select which display to use for fullscreen mode. This setting takes effect the next time fullscreen mode is entered. |
|
see through missing media |
Select this checkbox to see through missing media in the timeline, displaying the first displayable media in the underlying tracks. |
|
background |
Use this to select the Viewer background. You can select black, or gray (using the slider to determine the grayscale), or checkerboard (using the slider to determine the brightness). |
|
frame increment |
Use this to set the default number of frames skipped by the Viewer skip controls, and the timeline Nudge More commands. |
|
filtering mode |
Use this to determine the filtering used during rendering in the Timeline environment. You can select Auto, Nearest neighbour, or Linear. Auto uses ths same automatic selection as in the Compositing environment. This does not affect exports or rendering in the Compositing environment. |
|
Audio |
|
|
default latency adjustment (ms) |
Use this to adjust the default timing offset (in milliseconds) between audio and video to apply to new Viewers. Positive values make audio play earlier relative to video; negative values make audio play later. To convert from video frames to ms, divide 1000 ms by the video frame rate. For example: • at 25fps, a video frame is 1000/25 = 40ms, or • a 1.5 video frame delay = 1.5 * 40ms = 60ms. |
|
default volume |
Use the slider or numeric field to set the default volume. |
|
Viewer Handles |
|
|---|---|
|
Controls |
|
|
2D handle size |
Adjust the size of the square control handles that appear on the Viewer for some operations, such as transformations, warps, and Bezier and B-spline shapes.
By default, this value is set to 5. You can also set the pickable area size of the square control handles in the numeric field or slider to the right of the 2D handle size control. |