Cook Interface (C++)¶
C++ Reference¶
- group FnGeolibOp
The Op API offers a unified interface for manipulating the scene graph and modifying attributes, something that was previously only possible through a combination of SGGs and AMPs. All of Katana’s shipped Ops are written with the Op API.
The Op API also provides a number of utility functions for a number of common tasks such as obtaining frequently used attributes (such as bounding boxes) and reporting errors to the scene graph. The majority of the utility functions are designed to be used within the context of an Op’s
cook()function and require a reference to the GeolibCookInterface that has been passed to thecook()function.- Utility Functions
Functions
-
std::string GetInputLocationType(const GeolibCookInterface &interface, FnPlatform::StringView location = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Returns the location type for specified location on the corresponding GeolibCookInterfaces’s input.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
location – The scene graph location path.
inputIndex – The input index on which to retrieve the specified scene graph location path.
- Returns
The location’s
'type'attribute. If type attribute is invalid an empty string will be returned, if it is not set thengroupwill be returned by default.
-
std::string GetAbsOutputLocationPath(const GeolibCookInterface &interface, const std::string &outputLocationPath)¶
Resolves a relative output scene graph location path to an absolute path.
This method cannot be used to query input locations (such as those used with methods such as GeolibCookInterface::getAttr()) but those methods that operate on the Op’s output such as GeolibCookInterface::createChild(). If you require the absolute scene graph location path for an input location you should use GetAbsInputLocationPath().
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
outputLocationPath – The relative output scene graph location path.
- Returns
The corresponding absolute location path.
-
std::string GetAbsInputLocationPath(const GeolibCookInterface &interface, const std::string &inputLocationPath)¶
Resolves a relative input scene graph location path to an absolute path.
This method cannot be used to query output locations (such as those used with methods such as GeolibCookInterface::createChild()) but those methods that operate on the Op’s output such as GeolibCookInterface::getAttr(). If you require the absolute scene graph location path for an output location you should use GetAbsOutputLocationPath().
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
inputLocationPath – The relative input scene graph location path.
- Returns
The corresponding absolute location path.
-
void RenameChild(GeolibCookInterface &interface, FnPlatform::StringView src, FnPlatform::StringView dst)¶
Renames the specified child.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
src – The name of the child to rename.
dst – The new name of the child.
-
FnAttribute::Attribute GetGlobalAttr(const GeolibCookInterface &interface, FnPlatform::StringView name, FnPlatform::StringView location = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Returns attribute from the input scene, including inherited attributes.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
name – The name of the attribute.
location – The location at which the attribute should be found.
inputIndex – The input index of which to search for the input scene graph location.
- Returns
The specified attribute at the given location including inherited attributes.
-
void ReportError(GeolibCookInterface &interface, const std::string &message)¶
Reports the specified error message to the scene graph at the current scene graph location.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
message – The error message.
-
void ReportWarning(GeolibCookInterface &interface, const std::string &message)¶
Reports the specified warning message to the scene graph at the current scene graph location.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
message – The warning message.
-
FnAttribute::GroupAttribute MergeImmediateGroupChildren(const std::vector<FnAttribute::GroupAttribute> &attrs)¶
Merges the unique children of the specified GroupAttribute.
The left-most definition for a child attribute “wins”, and the left-most attribute ordering is preserved.
Note
This matches the combination logic used in Merge for
lightList,renderSettings.outputs,relativeScopedCoordinateSystems,collections, etc.- Parameters
attrs – A vector of GroupAttribute to be merged.
- Returns
A GroupAttribute containing the merged GroupAttributes.
-
FnAttribute::GroupAttribute GetGlobalXFormGroup(const GeolibCookInterface &interface, const std::string &inputLocationPath = std::string(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Returns the global transform as a GroupAttribute, where the immediate children represent all the entries from
/rootto the leaf which have an'xform'attribute present.Note
If a collapsed 4x4 transform matrix is required pass the result of this function to the
FnGeolibServices::FnXFormUtil::CalcTransformMatrix..() functions.- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
inputLocationPath – The input scene graph location to retrieve the global transform from.
inputIndex – The input index from which to retrieve the scene graph location.
- Returns
The global transform at the specified location.
-
float GetCurrentTime(const GeolibCookInterface &interface)¶
Returns the current time from the current Graph State.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
- Returns
The current time.
-
float GetShutterOpen(const GeolibCookInterface &interface)¶
Returns the shutter open time from the current Graph State.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
- Returns
The shutter open time.
-
float GetShutterClose(const GeolibCookInterface &interface)¶
Returns the shutter close time from the current Graph State.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
- Returns
The shutter close time.
-
int GetNumSamples(const GeolibCookInterface &interface)¶
Returns the number of time samples from the current Graph State.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
- Returns
The number of time samples.
-
FnAttribute::Attribute GetGraphStateVariable(const GeolibCookInterface &interface, FnPlatform::StringView variableName)¶
Returns the specified variable from the current Graph State.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
variableName – The name of the graph state variable.
- Returns
The Graph State Variable specified by
variableName.
-
FnAttribute::DoubleAttribute GetBoundAttr(const GeolibCookInterface &interface, FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Returns the bound attribute at the specified input scene graph location.
- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
inputLocationPath – The scene graph location to obtain the bound attribute from.
inputIndex – The input index on which to find the scene graph location.
- Returns
A 6-element DoubleAttribute containing the bound attribute or an invalid DoubleAttribute if bounds do not exist at the specified location.
-
void GetBoundAttrValue(double outMinBound[3], double outMaxBound[3], const FnAttribute::DoubleAttribute &boundAttr, float sampleTime)¶
Fills the array’s
outMinBoundandoutMaxBoundwith the values stored in the DoubleAttributeboundAttr.- Parameters
outMinBound – A 3-element array that will contain x-min, y-min, z-min.
outMaxBound – A 3-element array that will contain x-max, y-max, z-max.
boundAttr – The bounds attribute to process.
sampleTime – The sample time that the bounds attribute
boundAttrshould be sampled at.
-
void GetTransformedBoundAttrValue(std::vector<BoundPoint> &outPoints, const FnAttribute::DoubleAttribute &boundAttr, float sampleTime, const double xform[16])¶
Returns the bounding box specified by the bound attribute
boundAttrafter being transformed by the 4x4 transform matrixxform.- See
- Parameters
outPoints – [out] An empty vector that will filled with the 8 points of the transformed bounding box.
boundAttr – A 6-element DoubleAttribute specifying the bounding box to be transformed.
sampleTime – The sample time that the bounds attribute
boundAttrshould be sampled at.xform – A 4x4 transform matrix by which
boundAttrwill be transformed.
-
void GetTransformedBoundAttrValue(double outMinBound[3], double outMaxBound[3], const FnAttribute::DoubleAttribute &boundAttr, float sampleTime, const double xform[16])¶
Returns the axis-aligned bounding box specified by the bound attribute
boundAttrafter being transformed by the 4 x 4 transform matrixxform.- Parameters
outMinBound – [out] A 3-element array that will contain the transformed x-min, y-min, z-min.
outMaxBound – [out] A 3-element array that will contain the transformed x-max, y-max, z-max.
boundAttr – A 6-element DoubleAttribute specifying the bounding box to be transformed.
sampleTime – The sample time that the bounds attribute
boundAttrshould be sampled at.xform – A 4x4 transform matrix by which
boundAttrwill be transformed.
-
FnAttribute::DoubleAttribute MergeLocalBoundAttrs(const std::vector<FnAttribute::DoubleAttribute> &boundAttrs)¶
Returns a single bound attribute, given a vector of bounds in the same local coordinate system.
If any of the bounds are multi-sampled the result will promoted to a multi-sampled attribute. The resulting time samples will be the union of the supplied sample times. Missing values will be synthesized using either DoubleAttribute::fillInterpSample(). This is the same combination logic used by Merge Op’s
sumBoundsoption.- Parameters
boundAttrs – A vector of 6-element bound attributes in the same local coordinate system to be merged.
- Returns
The merged bound attributes.
-
FnAttribute::GroupAttribute FilterNullAttributes(const FnAttribute::GroupAttribute &groupAttr)¶
Returns a newly constructed GroupAttribute based on
groupAttrwith all NullAttribute removed.- Parameters
groupAttr – The GroupAttribute to filter.
- Returns
A new instance of type GroupAttribute which contains all values in
groupAttrexcept NullAttributes.
-
FnAttribute::GroupAttribute ResolveReferentialInheritance(const FnGeolibOp::GeolibCookInterface &interface, FnPlatform::StringView keyAttrName, FnPlatform::StringView attrName, const std::string &inputLocationPath = std::string(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Returns a GroupAttribute which contains the attributes stored at the location contained in the specified attribute
"keyAttrName".Note
Currently
attrNameis ignored.- Parameters
interface – A reference to a valid GeolibCookInterface object.
keyAttrName – The attribute name on the input scene graph location that contains the reference location(s).
attrName – The attribute(s) that will be merged with those at the referenced location. If an empty string is specified then all attributes will be used.
inputLocationPath – The input scene graph location path at which
attrNamewill be found.inputIndex – The input index on which
inputLocationPathcan be found.
- Returns
A GroupAttribute which is a combination of those attributes at the location specified in
keyAttrNameand those attributes stored under the attribute specified atattrName.
-
class Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface¶
- #include <FnGeolibCookInterface.h>
Provides a unified interface for querying and manipulating the scene graph.
A reference to an instance of GeolibCookInterface is passed to your Op’s
cook()each time it is called by the Runtime.Its methods can broadly be divided into two categories:
Methods which query the incoming, or upstream, scene graph. These methods provide read-only access to the incoming scene graph.
Methods which modify the output scene graph, observable after executing this Op. This involves creating new scene graph locations, modifying attributes of incoming scene graph locations, or entirely deleting locations.
Query Input
The following functions refer to queries on the connected input scene graph. Client code is free to do scattered queries of the incoming scene graph as required to express the desired processing.
If your Op makes multiple scattered queries in a single cook() call, it is recommended that prefetch() is used.
Note
Input scene graph locations which have not been cooked at the time of the query may throw an internal exception, aborting execution of the requesting Op. Client code should not catch these exceptions, they are a signal to the the runtime to recook the Op when the inputs are ready.
-
FnAttribute::Attribute getAttr(FnPlatform::StringView attrName, FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput) const¶
Returns the specified attribute on the Op’s input.
It is often necessary to perform some action or compute a value based on the result stored in another attribute. The getAttr() function allows you to interrogate any part of the incoming scene graph by providing the attribute name and a scene graph location path (either absolute or relative).
By default getAttr() will return the specified attribute on the Op’s default input. In most cases where the Op only has one input branch this will suffice. If the Op has multiple inputs (e.g. the Merge node) the
inputIndexparameter can be used to specify a particular branch. When specified,inputIndexmust satisfy 0 <= inputIndex < getNumInputs().Note
It is important to remember that getAttr() will only interrogate the Op’s input scene graph. Calls made to setAttr() will not be visible to getAttr(). If you need to see what attributes have been set during an Op’s execution you should call getOutputAttr().
- Parameters
attrName – The name of the attribute.
inputLocationPath – The input location path the attribute should be retrieved from.
inputIndex – The input index the attribute should be retrieved from.
- Returns
The attribute at the specified location path and input index.
-
bool doesLocationExist(FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput) const¶
Returns true if the specified location exists on the Op’s input.
- Parameters
inputLocationPath – The scene graph location path.
inputIndex – The input index that should be searched.
- Returns
trueif the location exists at the specified location and index otherwise false.
-
FnAttribute::StringAttribute getPotentialChildren(FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput) const¶
Returns a StringAttribute containing list of names of potential children on input.
The ability for Ops, via deleteSelf(), to delete themselves gives rise to a subtle behavior. When an upstream Op is evaluated and creates children, if downstream Ops have the ability to delete them, the upstream Op can only go so far as to state that the children it creates may potentially exist after a downstream Op has been evaluated at those child locations. This is because the Op has no knowledge of what a downstream Op may do when evaluated at such a location. To that extent, getPotentialChildren() returns a list of all the children of a given location on the input of an Op.
- Parameters
inputLocationPath – The input location path to obtain the potential children for.
inputIndex – The input index to be used.
- Returns
A StringAttribute containing the potential children at the specified input location.
-
void *getPrivateData() const¶
Returns a raw pointer to the private data stored in this Op or
NULL.- Returns
Raw void pointer or NULL if no private data has been set.
-
void prefetch(FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput) const¶
Indicates to the Runtime that the caller depends on the specified location.
Calling the
prefetch()function within an Op’scook()function instructs the Runtime that the specified location is required for the Op’s processing task.The
prefetch()function will return immediately, scheduling the computation of the requested location to be cooked concurrently or at some point in the future.prefetch()is recommended if your Op makes multiple scattered queries during a cook. Note that it is not necessary to prefetch parent locations of your default input.The use of a prefetch creates a data flow dependency, so do not prefetch locations or inputs you do not need.
- Parameters
inputLocationPath – The scene graph location path to be prefetched.
inputIndex – The input index from which to request the specified
inputLocationPath. In common cases the default input will suffice, however if your Op has multiple input branches (like a Merge Op) you will need to specify a particular input index.
-
FnAttribute::Attribute getOutputAttr(FnPlatform::StringView attrName) const¶
Returns the specified attribute (if set) on the Op’s output for the current location.
This is useful for inspecting the output attributes set during an execOp() that may potentially require further processing after the exec’d Op has returned.
Note
This is not recommended for normal usage.
- Parameters
attrName – The name of the attribute to query.
- Returns
The attribute set on the Op’s output. If not set an invalid attribute will be returned.
Modify Output
-
void setAttr(FnPlatform::StringView attrName, const FnAttribute::Attribute &value, const bool groupInherit = true)¶
Sets the specified attribute on the Op’s output.
attrNamecan be specified in dot-delimited form e.g.attr1.attr2.attr3, in which case a new GroupAttribute is created for each level required and the value ofgroupInheritwill determine the GroupAttribute’s inheritance state.Note
Calls to setAttr() made in the current Op will not be reflected in subsequent calls to getAttr(). This is because functions which mutate the scene graph only affect the output of this Op. Methods such as getAttr() and doesLocationExist() query the input to this Op. This is also true for non-local queries i.e., when an Op queries attributes of its parent. In this case it will be querying the input at its parent, and thus does see the results of its own processing. If you need to see the attributes set during a cook call you should use getOutputAttr().
- Parameters
attrName – The name of the attribute to create. This can be specified in dot-delimited form.
value – The FnAttribute instance to be associated with
attrName.groupInherit – The group inheritance state for newly created GroupAttributes.
-
void copyAttr(FnPlatform::StringView dstAttrName, FnPlatform::StringView srcAttrName, const bool groupInherit = true, FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Copies the specified source attribute to the specified destination attribute.
The specified source attribute (determined by
inputLocationPathandinputIndex) will be copied to the output of this Op asdstAttrName. If the source attribute or location does not exist this call is equivalent to calling deleteAttr() with the destination attribute.- Parameters
dstAttrName – The name of the attribute to copy the attribute at
srcAttrNameto.srcAttrName – The name of the attribute to copy to
dstAttrName.groupInherit – The group inheritance state of the destination attribute.
inputLocationPath – The scene graph location path on this Op’s input to copy from.
inputIndex – The input index to copy from (where multiple branches in the Op tree exist).
-
void extendAttr(FnPlatform::StringView dstAttrName, const FnAttribute::Attribute &value, FnPlatform::StringView srcAttrName = FnPlatform::StringView(), const bool groupInherit = true, FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Extends the existing input attribute with additional values if the types match.
If no input attribute exists with the specified name then this call is equivalent to setAttr().
Multi-sampling is supported; the new attribute is constructed as the union of all incoming and new time samples, leveraging the FnAttribute’s existing interpolation.
If there is a type mismatch, it will be reported as a scene graph error. If more sophisticated or fine-grained type mismatch handling is required it is recommended to instead manually call getAttr() / setAttr()
Incoming NullAttribute’s are equivalent to the attribute not being set in the incoming scene.
- Parameters
dstAttrName – The name of the attribute to be extended.
value – The Attributes that will extend the specified attribute.
srcAttrName – The name of the attribute a specified location to be extended, if empty string is used this is the equivalent of setAttr().
groupInherit – The value of the group inheritance flag.
inputLocationPath – The input location path from which
srcAttrNameshould be sourced from.inputIndex – The input index to search for
inputLocationPathon.
-
void deleteAttr(FnPlatform::StringView attrName)¶
Deletes the attribute specified by
attrNameso it will no longer on this Ops output.- Parameters
attrName – The name of the attribute to delete from the Op’s output.
-
void deleteAttrs()¶
Deletes all attributes on this Op’s output.
-
void replaceAttrs(FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Replaces the attributes on this Op’s output with those specified by the input scene graph location path.
- Parameters
inputLocationPath – The attributes at inputLocationPath will replace those on this Op’s output.
inputIndex – The input index to use where multiple input branches exist for this Op.
Change the Output Topology
-
typedef void (*FnDeletePrivateDataFunc)(void *privateData)¶
A function pointer of the form
void (*deletePrivateData)(void* privateData)that will be called to delete the givenprivateData.- Parameters
privateData – The private data to delete by the function.
-
void createChild(FnPlatform::StringView name, FnPlatform::StringView opType = FnPlatform::StringView(), const FnAttribute::Attribute &opArgs = FnAttribute::Attribute(), ResetRoot resetRoot = ResetRootAuto, void *privateData = NULL, FnDeletePrivateDataFunc deletePrivateData = NULL)¶
Creates a new child at the specified location if one didn’t already exist.
If the child already exists in the incoming scene then the Op will be run and previously created attribute values and children will be preserved. To ensure the child will not have any pre-existing attributes or children it is recommended to first call deleteChild(), doing so will maintain the original child index ordering.
If the Op type is not specified or is an empty string the calling Op’s type will be inherited by the child.
To modify the result of getRelativeOutputLocationPath() in calls beneath this location the
resetRootargument can be set. If ResetRootAuto is specified then the child’s root location will be reset if and only if the Op’s type differs from the parent’s.- See
Note
Multiple calls to createChild() for the same named child location causes the last specified
opTypeto be used, that is to say, successive calls to createChild() mask prior calls.- Parameters
name – The name of the child to create.
opType – The type of the Op that will be evaluated at the child location. If an empty string or nothing is specified then the current Op’s type will be used.
opArgs – The Op arguments that will be passed to the Op when run at the child location.
resetRoot – Specifies what the root location for Ops run at child location should be.
privateData – A pointer to user data that can be used inside the Op.
deletePrivateData – A function pointer of the form
void (*deletePrivateData)(void* privateData)that will be called to delete the givenprivateData.
-
void replaceChildren(FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput)¶
Replaces the children under the Op’s current scene graph location with children from an alternate input location and/or input index.
- Parameters
inputLocationPath – The input scene graph location whose children will replace this location’s children.
inputIndex – The input index on which the where the input location path should be retrieved.
-
void deleteChildren()¶
Deletes all children on this Op’s output, both newly created by the current Op and any incoming children.
-
void deleteChild(FnPlatform::StringView name)¶
Deletes the specified child location on the Op’s output.
Note
Calling deleteChild() is more efficient than allowing the child location to delete itself. Where possible you should prefer deleteChild() over deleteSelf().
- Parameters
name – The name of the child location to delete.
-
void deleteSelf()¶
Deletes the current output location.
It is common to return from cook() immediately following this call.
Note
Calls to deleteSelf() will not remove the location from the location’s parent
getPotentialChildren()list. Thus, if there is a way to structure code to usedeleteChild()instead, it is generally preferable.
-
void copyLocationToChild(FnPlatform::StringView child, FnPlatform::StringView inputLocationPath = FnPlatform::StringView(), int inputIndex = kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput, FnPlatform::StringView orderBefore = FnPlatform::StringView())¶
Copies the specified location in the input scene, to the specified child location.
The specified
inputLocationPathwill not be evaluated until the new child location is traversed. At this time, if the input does not exist, neither will the new child.copyLocationToChild()can be used to rename a child location:rename(dst, src) { copyLocationToChild(dst, src, kFnKatGeolibDefaultInput, src); deleteChild(src); }
The
inputLocationPathalways refers to the input name, andchildrefers to output name, so multiplecopyLocationToChild()calls are unambiguous.- Parameters
child – The name of the child to be copied to the output of this Op.
inputLocationPath – The input scene graph location path to copy.
inputIndex – The input index to copy the
inputLocationPathfrom.orderBefore – The child that this should be precede in the scene graph ordering.
-
void replaceChildTraversalOp(FnPlatform::StringView opType, const FnAttribute::GroupAttribute &opArgs, void *privateData = NULL, FnDeletePrivateDataFunc deletePrivateData = NULL)¶
Replaces the Op type and Op arguments for child locations of this Op.
Newly created child locations (created with createChild()) only have access to the Op arguments / type and private data they were created with originally. Conceptually, this is the type and Op arguments used when traversing locations in the incoming scene.
- Parameters
opType – The Op type that will be evaluated at child locations.
opArgs – The arguments that will be passed to the Op when run at the child locations.
privateData – A pointer to user data that can be used inside the Op.
deletePrivateData – A function pointer of the form
void (*deletePrivateData)(void* privateData)that will be called to delete the givenprivateData.
-
void stopChildTraversal()¶
Stops this Op from running at descendants of the current location.
-
void execOp(FnPlatform::StringView opType, const FnAttribute::GroupAttribute &opArgs, void *privateData = NULL, FnDeletePrivateDataFunc deletePrivateData = NULL)¶
Runs the specified Op with the provided arguments at the current location.
Children created as a result of the execOp() call will behave as expected in such that they will retain the type and Op arguments of the exec’d Op.
- Parameters
opType – The type of Op to be run.
opArgs – A GroupAttribute describing the arguments that will be passed to the Op when run.
privateData – A pointer to user data that can be used inside the Op.
deletePrivateData – A function pointer of the form
void (*deletePrivateData)(void* privateData)that will be called to delete the givenprivateData.
-
void resetRoot()¶
Marks this location as the new root location in the Op’s traversal.
Subsequent calls to getRelativeOutputLocationPath() at child locations will return paths relative to this one.
Note
Calls to getRelativeOutputLocationPath() at the current location will remain unaffected by this function.
Public Types
-
enum ResetRoot¶
The values of
ResetRootcontrol which root scene graph location will be used for Ops when run at child locations.Values:
-
enumerator ResetRootFalse¶
The root location of the Op evaluated at the new location is inherited from the Op that called
createChild().
-
enumerator ResetRootTrue¶
The root location of the Op evaluated at the new location is reset to the new location path.
-
enumerator ResetRootAuto¶
The root location is reset only if
opTypeis different to the Op callingcreateChild()(the default).
-
enumerator ResetRootFalse¶
Public Functions
-
GeolibCookInterface(FnGeolibCookInterfaceHandle interfaceHandle, FnGeolibCookInterfaceSuite_v1 *interfaceSuite)¶
-
std::string getOutputName() const¶
Returns the leaf name for the output location.
For example:
"/root/world/geo" returns "geo"
- Returns
The leaf name of the output location.
-
std::string getInputName() const¶
Returns the leaf name for the input location.
This will typically match getOutputName(), but may differ when copyLocationToChild() is used.
- See
copyLocationToChild(FnPlatform::StringView, FnPlatform::StringView, int inputIndex, FnPlatform::StringView)
- Returns
The leaf name for the input location.
-
std::string getOutputLocationPath() const¶
Returns the output scene graph location path in its absolute form.
The output scene graph location path is the scene graph location that is currently being cooked. For example:
"/root/world/geo"- Returns
The absolute output scene graph location path.
-
std::string getInputLocationPath() const¶
Returns the scene graph location path corresponding to the input scene graph location that is currently being traversed.
- Returns
The input scene graph location that is currently being traversed.
-
std::string getRelativeOutputLocationPath() const¶
Returns the location path relative to the root execution location currently being traversed.
For Ops instantiated at document level:
”/root” returns “”
”/root/world” returns “world”
”/root/world/geo” returns “world/geo”
For an Op first executed at /root/world/geo (producing “a/b”)
”/root/world/geo” returns “”
”/root/world/geo/a” returns “a”
”/root/world/geo/a/b” returns “a/b”
- Returns
The location path relative to the root execution location currently being traversed
-
std::string getRelativeInputLocationPath() const¶
Returns the relative location path corresponding to the input scene graph location that is currently being traversed.
- Returns
The relative location path corresponding to the input scene graph location that is currently being traversed.
-
std::string getRootLocationPath() const¶
Returns the scene graph location corresponding to the root of the Op’s execution.
This may or may not be
/root, specifically in the case where execOp() is called beneath/root.- See
- Returns
The root of the Op’s execution.
-
bool atRoot() const¶
Returns true if we are at the topmost location this Op has been cooked at.
This is often, but not always
/root. It is equivalent to the expression:getRootLocationPath() == getOutputLocationPath()
- Returns
true if we are at the topmost location this Op has been cooked at, otherwise false.
-
int getInputIndex() const¶
Returns the input index this scene graph location was created in.
In most cases getInputIndex() will return 0, this reflects the fact that most Ops operate on the default input or branch.
In specific cases, such as in a Merge Op, getInputIndex() may return an index > 0: Certain locations may be present only in additional input scenes, but not in the first (connected) input scene. Those locations are created in the output scene, and are then cooked by subsequent cook() calls of the Merge Op. For those locations, the Runtime keeps track of the index of the scene in which they were contained. That index is accessible using getInputIndex(). This allows the Merge Op to know which input scene a particular location came from, and is used for performance optimizations when certain circumstances apply.
- Returns
The input index this location was created on.
-
int getNumInputs() const¶
Returns the number of input branches this Op has.
An Op can have the output from multiple other Ops as its input. Obvious use cases for this are instances where you wish to merge multiple scene graphs produced by different OpTrees into a single scene graph, comparing attribute values in two scene graph states, or copying one scene graph into another one. The getNumInputs() function allows you to determine how many Ops you have as inputs, which is a precursor to interrogating different branches of the OpTree for scene graph data.
- Returns
The number of inputs this Op has.
-
std::string getOpType() const¶
Returns the type of this Op.
For user supplied Ops this will be the string that was used to register the Op in the
REGISTER_PLUGIN()macro.- Returns
A string containing the Op’s type.
-
FnAttribute::Attribute getOpArg(FnPlatform::StringView specificArgName = FnPlatform::StringView()) const¶
Returns the specified Op argument or all Op arguments if an empty string is provided.
Op arguments are passed to the Op to configure how it should run. Op arguments are stored in a GroupAttribute. This method allows you to interrogate the Op arguments available to this Op.
If you supply an argument name this can be in the dot-delimited form i.e.
a.b.cor the single name form.- Parameters
specificArgName – The dot-delimited name of the Op argument.
- Returns
An instance of Attribute containing the Op argument.
-
inline FnGeolibCookInterfaceHandle getHandle() const¶
-
inline FnGeolibCookInterfaceSuite_v1 *getSuite() const¶
-
class QueryAbortException¶
- #include <FnGeolibCookInterface.h>
Thrown by the Runtime to abort the current.
call.cook()
This exception type will be thrown by methods on GeolibCookInterface and should never be caught by client code, consequently, you should avoid the use of in your code
-
class Foundry::Katana::GeolibPrivateData¶
- #include <FnGeolibCookInterface.h>
Convenience base class that can be derived from to allow users who require private data in their Ops.
This class is typically inherited by classes that are used with GeolibCookInterface::createChild(), GeolibCookInterface::replaceChildTraversalOp(), or GeolibCookInterface::execOp().
Public Static Functions
-
static inline void Delete(void *data)¶
Utility function for deleting a GeolibPrivateData instance.
- Parameters
data – Pointer to the private data that will be deleted. This should be a valid address to an object of type GeolibPrivateData (or derived type), or else it will cause undefined behavior.
-
static inline void Delete(void *data)¶
-
struct Foundry::Katana::BoundPoint¶
- #include <FnGeolibCookInterface.h>
Utility structure that can be used to represent a point in 3D space. Multiple points can be used to describe a bounding box.
-
class GeolibOp¶
-
class Foundry::Katana::GeolibSetupInterface¶
- #include <FnGeolibSetupInterface.h>
Provides functions to allow an Op to configure how it’s scheduled and evaluated by the Runtime.
Public Types
-
enum ThreadMode¶
By default an Op can potentially be evaluated by the Runtime in multiple threads concurrently. The
ThreadModeenumeration provides a means to specify to the Runtime the concurrency requirements of an Op.Values:
-
enumerator ThreadModeConcurrent¶
The Op can be evaluated concurrently with any other Op in the Op tree, In addition, the same op type can be evaluated by more than one thread concurrently. Ops which declare themselves
ThreadModeConcurrentmay be run at anytime, even duringGlobalUnsafeexecution.Considerations for marking an Op as
ThreadModeConcurrent:Does the Op contain global static data? If yes, is it properly guarded against race conditions?
Does the Op make use of third-party libraries and are these libraries thread-safe?
Does the Op pass or share the same private data instances amongst its children? If so, is that data structure also appropriately guarded for concurrent access and is its means of destruction thread-safe?
-
enumerator ThreadModeGlobalUnsafe¶
The Op will run in a single thread, only one
GlobalUnsafeOp will be scheduled to run within the entire process at any one time even across multiple Runtime instantiations.Use this if the Op makes calls to unknown code, unknown libraries, or code known to be thread-unsafe.
Note
GlobalUnsafeOps do not prevent the concurrent execution of those explicitly white-listed as Concurrent.
-
enumerator ThreadModeConcurrent¶
Public Functions
-
GeolibSetupInterface(FnGeolibSetupInterfaceHandle interfaceHandle, FnGeolibSetupInterfaceSuite_v1 *interfaceSuite)¶
-
void setThreading(ThreadMode threadmode)¶
Sets the concurrency constraints the Runtime must adhere to when evaluating this Op.
- See
- Parameters
threadmode – The thread mode (see ThreadMode) appropriate for this Op.
-
void setOpsCollapsible(const FnAttribute::StringAttribute &collapsedOpArgsGroupName)¶
Allows Geolib3 to collapse Ops of this type and make a single cook() call passing the accumulated Op Args as a group under the name specified by collapsedOpArgsGroupName.
- Parameters
collapsedOpArgsGroupName – The name of the attribute under which the batch will be stored.
-
enum ThreadMode¶
Geolib Op Private Data¶
Private Data Overview¶
When creating child locations, developers of Ops can pass user-defined data to the created child locations in one of two ways:
Using Op Args: If you wish to pass data to child locations, the best way to do this is through their Op Args. The Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface::getOpArg() function gives all arguments as a GroupAttribute.
Using private data: If you need to pass more complex data down to children that is not representable as attributes, then you can additionally use the private data pointer. For instance:
Associative maps
Modifiable data
Thread-safe data accessors
Performance-critical data
Other raw data
Private data can be passed as a void pointer to the following functions:
Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface::createChild()Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface::replaceChildTraversalOp()Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface::execOp()
A utility class is defined; Foundry::Katana::GeolibPrivateData; that can be used as a base class for custom private data classes.
For example, the class is used in the AlembicIn Op for its own private data type:
class AlembicInPrivateData : public Foundry::Katana::GeolibPrivateData
To retrieve the private data, the Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface::getPrivateData() function can be used.
Example Op that uses private data¶
The following example shows how private data can be used to pass complex information to the created child locations.
The first time the Op runs at a specific location, a file reader is created in order to open a file. Because this operation is usually expensive, we want to reuse the file reader to retrieve the required information for all the locations. However, the file reader is not suitable for being stored in a FnAttribute, therefore, it will need to be wrapped into a private data container (derived from Foundry::Katana::GeolibPrivateData in this case), then to be passed down to the created child locations.
/// Example class that reads a metaphorical custom format file and converts its
/// data into FnAttributes.
class CustomFormatFileReader final
{
public:
CustomFormatFileReader(const std::string& filepath) { ... }
~CustomFormatFileReader() { ... }
std::vector<std::string> getChildren(const std::string& parent) { ... }
FnAttribute::GroupAttribute getAttrs(const std::string& location) { ... }
private:
...
};
/// Private data container to pass data to child locations.
class PrivateData : public Foundry::Katana::GeolibPrivateData
{
public:
PrivateData(const std::shared_ptr<CustomFormatFileReader>& fileReader)
: m_fileReader(fileReader) {}
std::shared_ptr<CustomFormatFileReader> m_fileReader;
};
/// Example Op that reads a custom format file and creates the hierarchy in
/// Katana along with all its attributes.
class CustomFormatIn : public Foundry::Katana::GeolibOp
{
public:
static void setup(Foundry::Katana::GeolibSetupInterface& interface)
{
interface.setThreading(
Foundry::Katana::GeolibSetupInterface::ThreadModeConcurrent);
}
static void cook(Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface& interface)
{
std::shared_ptr<CustomFormatFileReader> fileReader;
if (interface.atRoot())
{
// Open file only when at root.
const FnAttribute::StringAttribute filepathAttr(
interface.getOpArg("filepath"));
const std::string filepath = filepathAttr.getValue("", false);
fileReader = std::make_shared<CustomFormatFileReader>(filepath);
}
else
{
// Get previously opened file from private data.
const PrivateData* const privateData =
static_cast<const PrivateData*>(interface.getPrivateData());
assert(privateData && "Private data not found where it should");
if (!privateData)
return;
fileReader = privateData->m_fileReader;
}
const std::string relativeOutputPath =
interface.getRelativeOutputLocationPath();
// Set attributes for this relative location.
const auto attrs = fileReader->getAttrs(relativeOutputPath);
const int64_t attrCount = attrs.getNumberOfChildren();
for (int64_t i = 0; i < attrCount; ++i)
{
interface.setAttr(attrs.getChildName(i), attrs.getChildByIndex(i));
}
// Get relative children from file.
const auto childLocations = fileReader->getChildren(relativeOutputPath);
// Create one child location per entry, with their respective
// attributes. The file reader will be passed as private data.
for (const auto& child : childLocations)
{
interface.createChild(
child,
"CustomFormatIn",
FnAttribute::Attribute(),
Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface::ResetRootAuto,
new PrivateData(fileReader),
PrivateData::Delete);
}
}
};
Private Data Life Cycle¶
The private data passed to an Op is linked to the lifetime of the location data of the location that the Op was involved in creating. Location data is deleted either when the location is evicted, or when the location is re-cooked after having been invalidated.
During a UI session, eviction only takes place when caches are flushed. Therefore, unless the location needs to be re-cooked, private data may live for long periods.
During a render, unless explicit eviction is requested by the renderer (see the
evict parameter present in several functions in Scene Graph Iterators), Geolib will only evict location
data that is not currently in the ancestral path for the location that it is
currently cooking, with the exception of location data that was cooked as a
result of a scattered query.
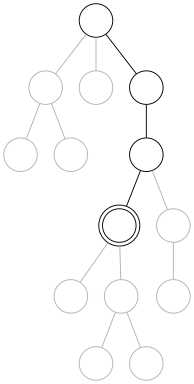
Basic eviction case: After the marked location is cooked, locations that are not in the ancestral path will get their location data evicted, along with the associated Op’s private data that was used to create the location.¶
When private data is used with
Foundry::Katana::GeolibCookInterface::execOp(), its lifetime is short. As
soon as the function completes, the provided deleter function will be invoked
and the private data will be deleted.