흐르는 입자
ParticleBlinkScript 노드로 얻을 수있는 것의 약간 더 관련된 예입니다. 결과적으로 파티클 주위에 파티클이 흐르게됩니다.
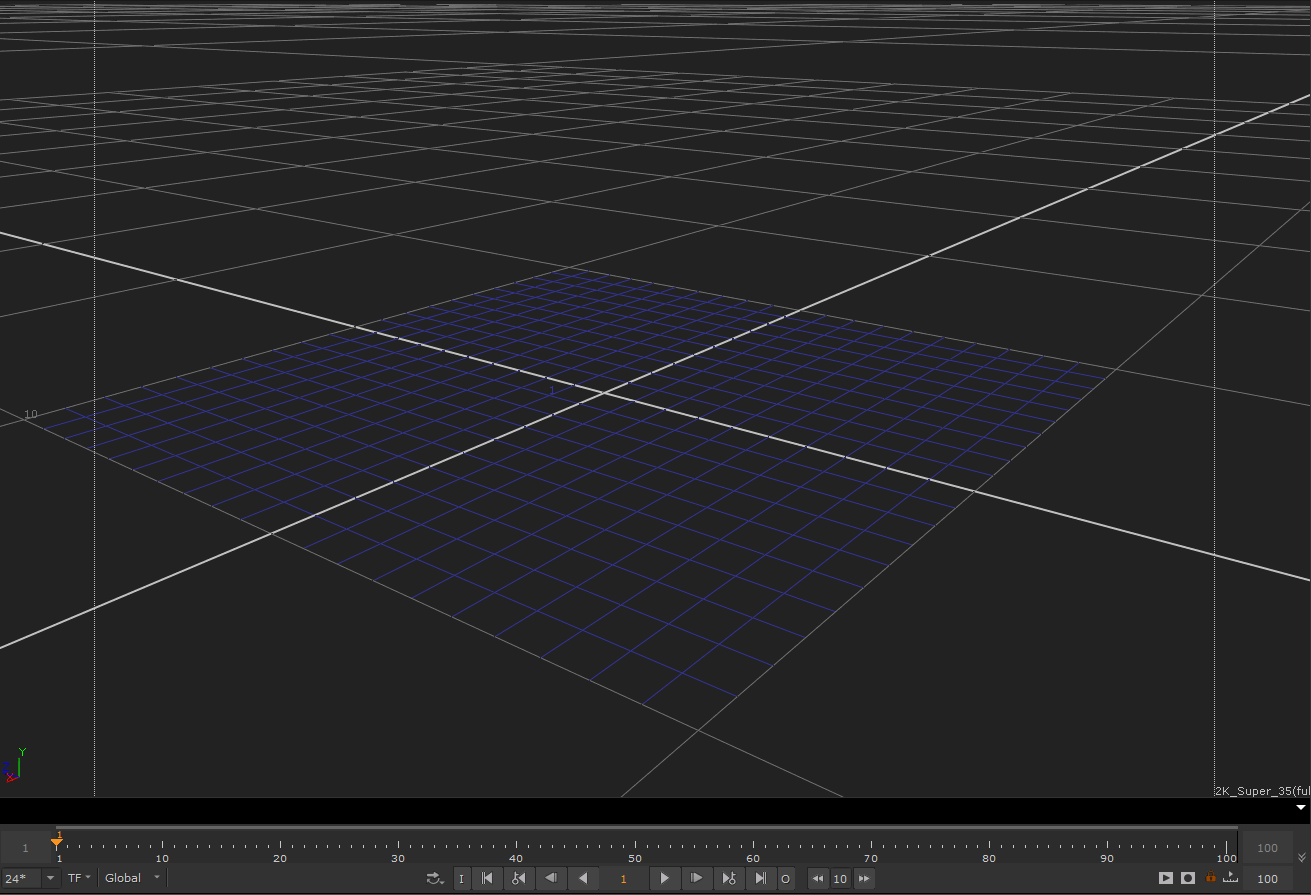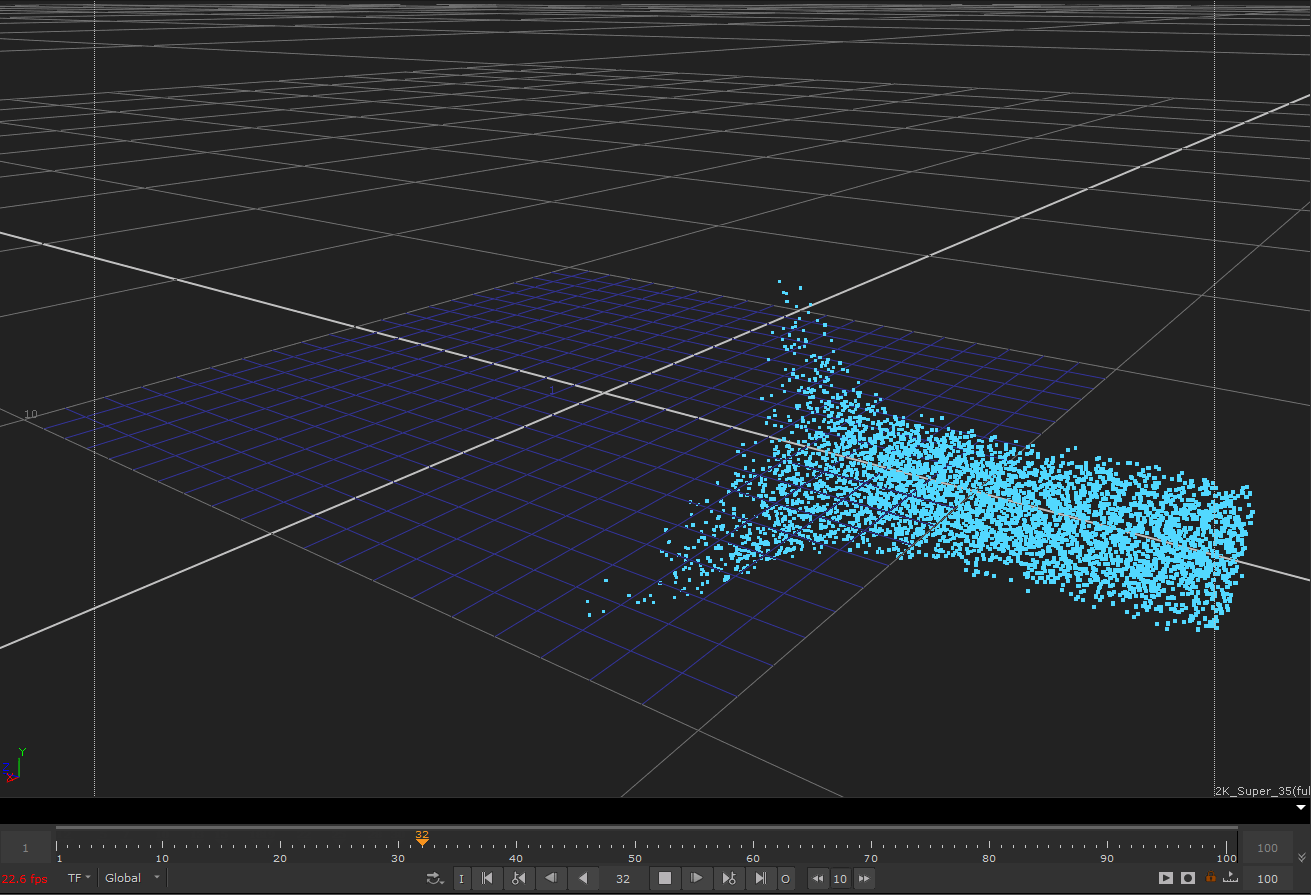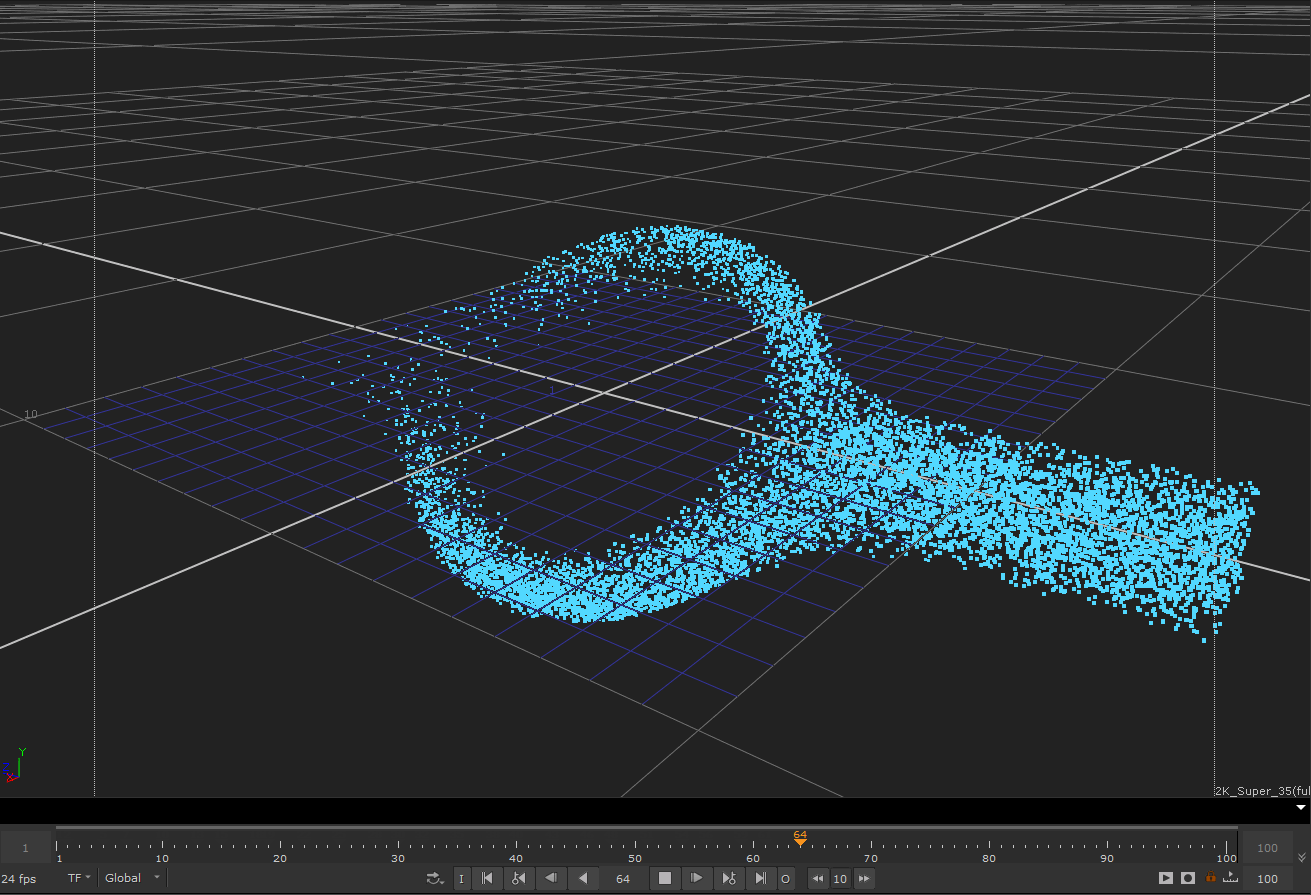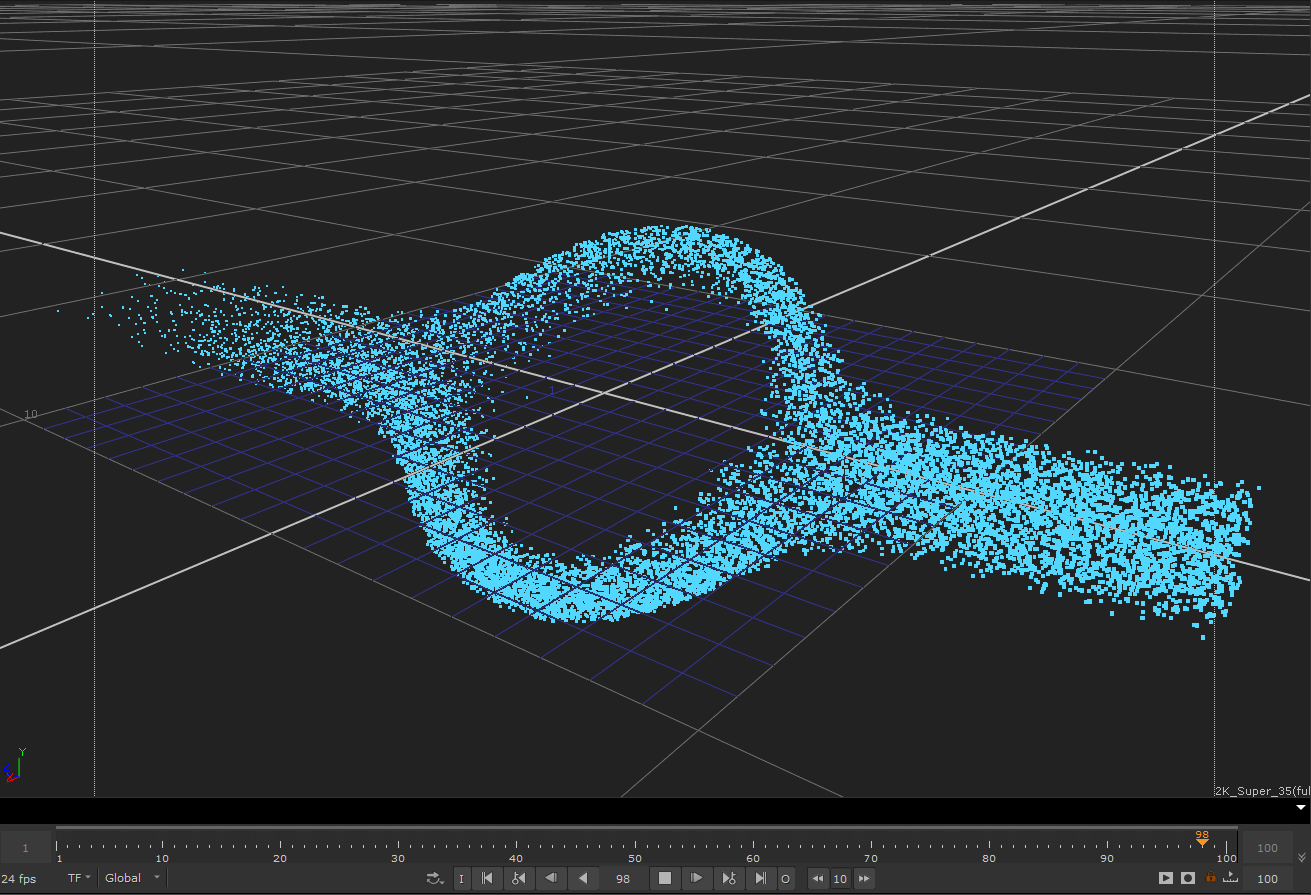
다음 예제 흐르는 입자 커널의 결과 효과
ParticleBlinkScript 노드에서 지오메트리에 액세스 할 수 없으므로 표현식을 translate, rotate 과 scale ParticleBlinkScript 노드의 노브로 translate , rotate 과 scale 의 값 Cylinder 형상 노드. 그만큼 radius 표현식을 사용하여 연결할 수도 있습니다.
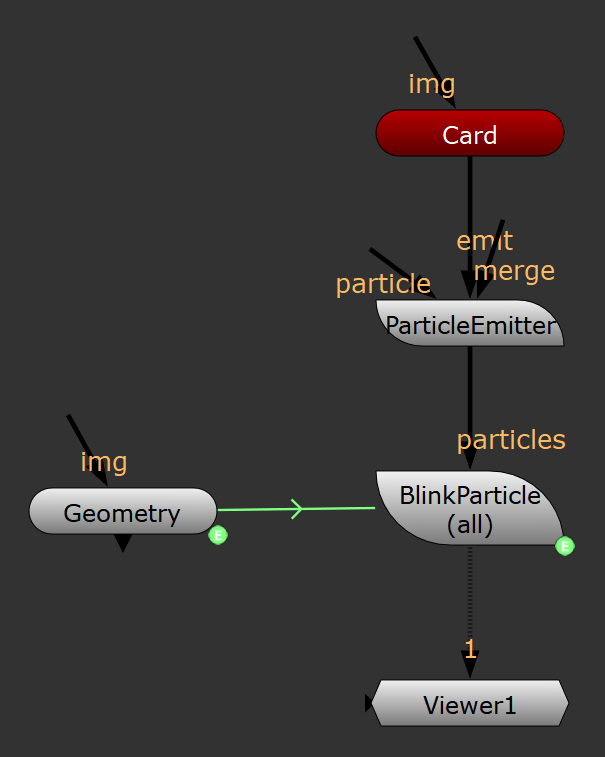
다음 커널에 대한 예제 노드 그래프
이 커널의 기본 원리는 공간의 모든 지점에서 입자의 흐름 방향을 제공하는 벡터 필드를 생성하는 것입니다. 각 입자의 속도 벡터는 흐름 방향을 가리 키도록 변경됩니다.
팁: 물체를 피하는 것은이 예제를 사용할 수있는 방법 중 하나 일 뿐이며, 다른 유동장 기능을 사용하여 다양한 효과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
이것을 구현하는 커널의 관련 부분은 다음과 같습니다. 그만큼 fieldAt 함수는 공간의 한 지점에서 흐름 방향을 반환하고 방법 함수는 각 입자의 속도 벡터를 그 위치의 흐름 벡터를 따라 가리 키도록 방향을 바꿉니다.
|
float3 fieldAt( float3 pos ) { return pos; // A field which just points away from the origin } void process() { float3 p = p_position(); float3 v = p_velocity(); float3 field = fieldAt( p ); field.normalize(); p_velocity() = field*v.length(); } |
다음 예제 커널은 입자가 가상 실린더 주위로 흐르도록하는 기능을 구현합니다.
|
kernel ParticleCylinderFlowKernel : ImageComputationKernel<ePixelWise> { Image<eReadWrite> p_position; Image<eReadWrite> p_velocity; Image<eReadWrite> p_orientation; param: float3 _origin; // Origin of the cylinder float3 _axis; // Axis of the cylinder float _radius; // Radius of the cylinder float3 _flow; // Direction of flow float _strength; // The strength of the interaction with the flow float _falloff; // The speed at which the force falls off with distance from the surface local: float3 _normalizedAxis; void define() { defineParam(_origin, "pa_origin", float3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)); defineParam(_axis, "pa_axis", float3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f)); defineParam(_flow, "pa_flow", float3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)); defineParam(_radius, "pa_radius", 1.0f); defineParam(_strength, "pa_strength", 1.0f); defineParam(_falloff, "pa_falloff", 1.0f); } void init() { _normalizedAxis = normalize(_axis); } float3 mix(float3 a, float3 b, float t ) { return a+t*(b-a); } void process() { float3 p = p_position()-_origin; float l = length(p); if ( l != 0.0f ) { float3 axis = _axis/l; p -= _origin+_normalizedAxis*dot(p, _normalizedAxis); float r = length(p); float3 normal = p; float3 d = cross(normal, _flow); float3 tangent = cross(d, normal); float fall; if ( r >= _radius ) 가을 = exp (-_ falloff * (r-_radius)); else 가을 = 1.0f; float3 force = tangent*_strength; force = mix( _flow, force, fall ); l = length(force); if ( l != 0.0f ) { 힘 = 힘 / l; 흙손 속도 = 길이 (p_velocity ()); p_velocity () = 속도 * 힘; p_orientation () = float4(0.0, force.x, force.y, force.z); } } } }; |
팁: 이 커널을 실험하는 방법은 여러 가지가 있습니다. 유체 시뮬레이션을 사용하여 연기 시뮬레이션을위한 유동장을 생성 해보십시오.
도움이되지 않은 죄송합니다
왜 도움이되지 않습니까? (해당되는 모든 것을 체크하세요)
의견을 보내 주셔서 감사합니다.
찾고있는 것을 찾을 수 없거나 워크 플로 관련 질문이있는 경우 시도해보십시오 파운드리 지원.
학습 내용을 개선 할 수있는 방법에 대한 의견이 있으시면 아래 버튼을 사용하여 설명서 팀에 이메일을 보내십시오.
의견을 보내 주셔서 감사합니다.