Exporting to Maya
Mari can also export data for use in Maya. It does this by exporting textures and creating a custom .ma file that references them. All exported files contain UDIM offsets so that Maya can import and read the UV patches correctly.
To create the .ma file for use in Maya follow the steps below:
|
1.
|
Navigate to Menubar | Python > Examples > Export for Maya. |
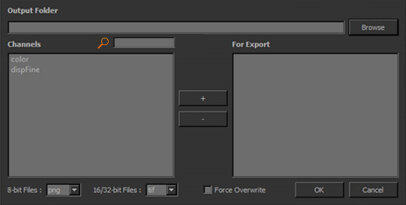
The Mari To Maya Export dialog displays.
|
2.
|
In the Output Folder pane, either enter the filepath or click Browse to find the location to which you would like the files to be exported. |
|
3.
|
From the list in the left pane, select which channels you want to export. |
|
4.
|
Once you have selected the channel and the filepath, click + (plus). |
The selected channel and filepath are added to the For Export pane on the right.
|
5.
|
If you have added a channel by mistake, or want to edit the filepath, simply select the channel from the For Export pane and click - (minus). |
|
6.
|
At the bottom of the dialog, the 8-bit Files and 16/32-bit Files dropdown menus list all of the file formats in which you can export your channels for use in Maya. Before you select OK, make sure you set your desired file format. |
If you have already exported these files to the same file location, you can opt to select the Force Overwrite checkbox to export over and replace them.
Your channel is exported to the selected file location in your choice of file format. The textures, regardless of whether they are diffuse or displacement, are exported as UV patches.
Using Your Textures in Maya
Once the .ma file has been created, you can load your textures into Maya. Follow the simple steps below to set up your textures:
|
1.
|
In your Maya scene, import the .ma file that was created after export from Mari. |
This can be found under the directory you saved the exported file to.
|
2.
|
Navigate to your Hypershade. You should now see that for each channel you exported out of Mari, a Lambert shader was created containing the channel. |
|
3.
|
You can hook up the layered texture element to different parts of your other, independent shader to achieve the desired look. |