Modo Bridge for the Unreal Engine
Modo has the ability to communicate with the Unreal Engine in real-time. To improve the workflow for Game Engine users, you can use a network protocol to share data between Modo and the Unreal Engine. The connection between Modo and Unreal can be on the same machines, across multiple machines on the LAN, or even possibly remotely. An entire scene or selected elements from a scene can bi-directionally be pushed and updated between the client and server. Mesh geometry, normals, UVs, textures, materials, as well as scene hierarchy, lights, and cameras can be synchronize between both applications.
Modo provides an Unreal client, Modo Bridge, as a plug-in for the Unreal Engine Editor. Once downloaded and copied to the appropriate folder, you can start the communication between both applications. You can then push changes made to the connected application.
The benefits of using this tool:
• Transferring mesh items, vertex maps, materials and textures, from Modo to Unreal.
• Transferring static mesh actors and vertex maps from Unreal to Modo.
• Transferring modified selected Polygons, Edges, and Vertices from Modo to Unreal. For more information, see Selecting Items.
• Transferring data changes made in Unreal to Modo. For example, repositioning a mesh.
• Transferring data using a separate server and client computers on the same network.
• Transferring items, materials, and textures from multiple Modo scenes to Unreal.
Installing the Modo Bridge Plug-in
Note: The Modo Bridge plug-ins for the Unreal Engine will soon be available directly from the Epic Game Launcher in the Marketplace but until then you can access them from here for Unreal Engine 4.16 versions.
Installing from Epic Games Launcher
To install the Modo Bridge plug-in for Unreal from the Epic Games Launcher:
| 1. | Start Epic Games Launcher, then click Marketplace and search for Modo Bridge. |
| 2. | On the Content Detail page, click the Free button to download the plug-in, then click Install to Engine to automatically install it to the Unreal Engine. |
Tip: If you currently have an older version of the Epic Game Launcher installed, you can quickly update to the latest Unreal Engine. With the Epic Games Launcher running, on the left panel, click Library and then click Add Versions at the top of the view. Locate the latest version and click Install. 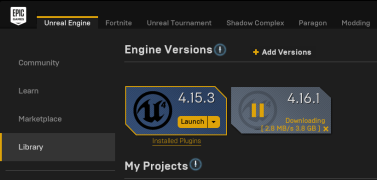
Installing Modo Bridge as a Project Plug-in
This process installs Modo Bridge plug-in as a project plug-in. This means that the plug-in is installed for the current project only, and you need to install it again for each new project you'd like to use it in.
| 1. | Copy the Plugins\ModoBridge folder to the Plugins folder of your Unreal project: <Your Unreal Project>\Plugins\ |
Note: If you don't have a Plugins folder, you need to create one.
For example, for Unreal Engine 4.16 the path looks like this:
Windows:
C:\Users\<user>\Documents\Unreal Projects\MyProject\Plugins\
Mac OS:
/Users/<username>/Documents/Unreal Projects/<Your Unreal Project>/Plugins/
Note: Create the Plugins folder, if it does not exist.
| 2. | When you open the Unreal Editor, the plug-in loads automatically. |
Note: If the plug-in is not loaded automatically, load the project in the Unreal Editor and enable Edit > Plugins > Modo Bridge Plugin.
Note: You need to re-install the plug-in for every new project in which you need it.
Installing Modo Bridge as an Unreal Engine Plug-in
This process installs the Modo Bridge plug-in as an Unreal Engine plug-in, which means that once installed, the plug-in is used in all new projects.
Note: Due to module dependencies used by the Modo Bridge, some constraints in Unreal Engine 4 may prevent the plug-in from working properly. Therefore, if this installation doesn't work for you, please install Modo Bridge as a project plug-in, as described in Installing Modo Bridge as a Project Plug-in.
| 1. | Copy the Plugins\ModoBridge folder to the Plugins folder of the Unreal Engine files: <Unreal4 install location>\Engine\Plugins\ |
For example, for Unreal Engine 4.16 the path looks like this:
Windows:
C:\Program Files\Epic Games\EU_4.16\Engine\Plugins\
Mac OS:
/Users/Shared/Epic Games/UE_4.16/Engine/Plugins/
| 2. | When you open the Unreal Engine 4 editor, the plug-in is loaded automatically. |
Installing Modo Material Importer (Optional)
You can also install the Modo Material Importer plug-in on your Unreal Engine client to transfer material updates.
For more information, see Installing the Material Importer.
Note: If the plug-in is not loaded automatically, load the project in the Unreal Editor and enable Edit > plugins > Modo Material Importer Plugin.
Configuring the Server and Client
Both the Modo server and the Unreal Engine client must use the same address and port number to communicate with each other. The following topics outline the setup and connection process.
Configuring Modo Preferences
To configure Modo:
| 1. | Launch Modo. |
| 2. | Click Systems > Preferences and expand Application on the left panel. |
| 3. | Under Foundry Link Settings, in the Address field, type the TCP server IP address. |
By default the TCP server address is 127.0.0.1. This is the loopback Internet Protocol (IP) address used to point back to your computer's TCP/IP network configuration.
| 4. | In the Port field, type the port number for your TCP connection. |
By default the Port number is 12000.
| 5. | Optional - Enable Search Subfolder and specify the asset ID and naming conventions used. For more information, see Search Subfolder. |
Starting the Communication between Modo and the Unreal Engine Client
Note: You must enable the TCP protocol communication on the Modo server or on the Unreal Engine client.
To enable communication on the Modo server:
| 1. | Launch Modo. |
| 2. | In the Modes section, under the menu bar, click Unreal Bridge. |
The Unreal Bridge options display.

| 3. | Expand Server and click Start. |
The Address and Port information is transmitted to the Unreal Engine client.
To enable communication on the Unreal client:
| 1. | Launch Epic Games and then click Launch Unreal Engine. |

The Projects tab displays MyProjects.
| 2. | On the left panel, click Library and then click MyProjects. |

| 3. | On the top Unreal Engine view, click Modo Bridge and select Settings. |
| 4. | Enable the Connect to Server checkbox. |
The Address and Port information, used by the Modo server, is automatically displayed.
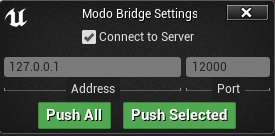
Modo Bridge Settings for Unreal
|
Setting |
Description |
|
Connect to Server |
Connects the Unreal Editor client to the Modo server. For information about how to configure the server, see Configuring the Server and Client. |
|
Push All |
Click to convert all static mesh actors to mesh items and push them to Modo. |
|
Push Selected |
Click to convert selected static mesh actors to mesh items and push them to Modo. |
Using the Modo Bridge Plug-in
Updates made in both applications, Modo and the Unreal Engine client, are transferred simultaneously using the Push functionality. You have the ability to select individual geometry items or selected polygons, edges, or vertices, materials, and textures to transfer them to the other application.
The following procedures provide workflow examples.
Creating Geometry and a Material
First, let's load an example scene containing basic primitives and assigned materials.
| 1. | Launch Modo and open the Model layout. |
| 2. | Load the example scene. |
| 3. | Click Render > Open Preview (alternatively press F8) and click the arrow to render your scene. |
These are the mesh items and the assigned materials that we will use to transfer to the Unreal Engine client.
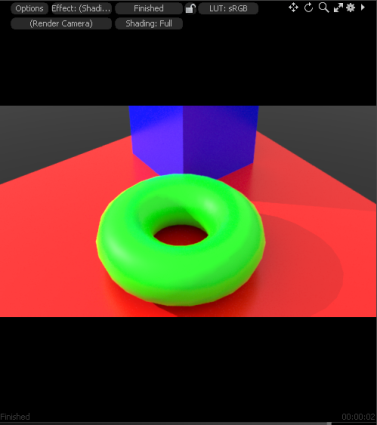
Push the Scene From Modo to the Unreal engine Client
In this procedure, we will walk you through the process of transferring Modo geometry and materials to the Unreal Engine client.
Note: You must complete the steps of Configuring the Server and Client before doing the following procedure.
To push a scene from Modo:
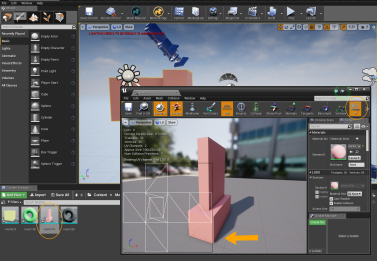
| 1. | In Modo, click  at the top right corner of the interface. at the top right corner of the interface. |
The Modo Bridge Options displays.

| 2. | Under the Push category, enable Items, and click Push All. |
| 3. | Open your Unreal Engine project. |
The Modo geometry is added to your scene.
| 4. | Next, update your materials by enabling Push > Materials and clicking Push All or select the materials you want to update and click Push > Push Selected. |
Note: If the materials are not assigned to geometry, empty materials are created, otherwise it uses existing materials.
All transferred assets are stored on the Unreal Engine client in the Content Browser in the following directories: Meshes, Materials, and Textures. The names for the assets can be auto-generated using unique keys or by a specified name. For more information, see Modo Bridge Options.
Note: Changing their names will disconnect them from sharing between Modo and the Unreal Engine client.
Tip: You can push the Camera from Modo to the Unreal Engine client, if you want to have the same view in both applications.
If you have textures applied to geometry in your scene, enable Push > Textures and then click Push All. The textures are then found and assigned to the appropriate materials.
Push a Transformed Static Mesh from Unreal to Modo
In this procedure, we will walk you through the process of changing the position of one of the mesh items in Unreal and transferring the updates back to Modo.
Note: If you have created new content subfolders, enable the Search Subfolder option in your Modo preferences or from within the Modo Bridge Server > Config settings.
Tip: You can use the Modo Material Importer plug-in to export modified materials made in Unreal and then import them into Modo.
To push a transformed mesh from Unreal:
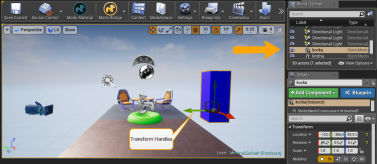
| 1. | With the Unreal Engine Editor open and your project displayed, on the right panel select the Kocka item. |
| 2. | Use the transform handles in the view to move this item to a new location. |
The Kocka item is displayed in a new position in your project scene.
| 3. | On top right corner of the interface, click Save Current. |
| 4. | On the top of the Unreal Engine Editor, click Modo Bridge and click Push Selected. |

| 5. | Open your Modo session to view the updates. |
Push Transformed Polygons from Modo to Unreal
In this procedure, we will walk you through the process of transforming a selection of Polygons in Modo, using the Bevel tool, and transferring the changes to Unreal.
Tip: You can also transform Edges and Vertices on a Mesh item in Modo and push your changes back to the Unreal Engine client.
To push transformed polygons from Modo:
| 1. | In Modo, while in Model layout, click Polygons to change your selection mode. |
| 2. | Select one polygon on the kocka mesh item. |
| 3. | On the Toolbar, located on the left panel, open the Mesh Edit sub-tab and click Bevel. |
| 4. | Click and hold the transform handle and drag. |
The selected polygon is updated.
| 5. | Click File > Save. |
| 6. | From the Modo Bridge options, click Push > All Items. |
| 7. | Open the Unreal Engine client. |
The mesh is updated in the Unreal Engine client.
Push a UV Map from Modo to Unreal
In this procedure, we will walk you through the process of transferring a UV Map from Modo to Unreal.
Note: Modo meshes pushed into the Unreal Engine client have auto generated UVs applied to the Light Map, which always overwrites UV Channel 1. You can disable this behavior by turning off the auto generator for the Light Map in Unreal Engine 4 .
To push a UV map from Modo:
| 1. | In Modo, change your layout to UVEdit. |
| 2. | On the Toolbox, located on the left panel, open the UV sub-tab and select Map > (new). |
The Create New Vertex Map windows displays.
| 3. | Type a name for your Vertex Map, ensure the Vertex Map Type is set to UV Map, and then click OK. |
Tip: You can also use other Vertex Map Types, such as RGB Map and set the Color value. This data can also be pushed to the Unreal Engine client. To see the color specified for the RGB Map in Unreal, open the StaticMesh item in the Content Browser > Meshes directory and click Vert Colors.
| 4. | On Items tab, on the right panel, select kocka and krofna. |
| 5. | On the Toolbox, located on the left panel, click Project. |
| 6. | Click File > Save. Alternatively, press Ctrl/Cmd + S. |
| 7. | In the Modo Bridge options window, click Push > All Items. |
| 8. | Open your Unreal Engine client, in the Content Browser located at the bottom of the view, open Content > Meshes and double-click on a Mesh item. |
| 9. | In the preview window, click UV. |
The UV Map displays.
Modo Bridge Options
The following options are available:
|
Option |
Description |
|
Server |
|
|
Start |
Starts the communication between Modo and the Unreal Engine client using a network protocol. |
|
Stop |
Stops the communication between Modo and the Unreal Engine client. |
|
Config |
Allows you to configure the server IP address and port number and other options. These are the same settings configured in the System > Preferences > Application > Foundry Link Settings category. For more detailed information, see Application. Note: You cannot change the IP address and port information while the Modo Bridge is connected. |
|
Settings |
|
|
Mesh Asset is Item |
Resets the mesh asset at the origin, only applying the transformation at actors. Pushing a static mesh actor from Unreal to Modo creates a mesh item with the transformation. If this option is enabled, a mesh item and an instance item are created. The mesh item is hidden and set at the origin and the instance item has the transformation. The example below demonstrates the workflow. Note: An Unreal mesh actor is always a Modo instance item, whereas an Unreal mesh asset is always a Modo mesh item. Example: In the Unreal Editor client, two static mesh actors, called char1 and char2, reference the same static mesh asset called M_Char. Enabling the Mesh Asset is Item option creates a M_char mesh item, a char1 instance item, and a char2 instance item in Modo. Disabling the Mesh Asset is Item option and pushing the items creates achar1 mesh item and a char2 instance item in Modo. |
|
Reset Mesh Asset |
Resets the transformation of a created mesh. By default, pushing a static mesh actor from Unreal to Modo creates a mesh item with the transformation. If this option is enabled, a mesh item and an instance item are created. The mesh item is hidden and set at the origin and the instance item has the applied transformation. Use this workflow to distinguish mesh actor and mesh asset so that an Unreal mesh actor is always a Modo instance item, whereas an Unreal mesh asset is always a Modo mesh item. Note: You do not have to reconnect the server and client after enabling or disabling this option. Example: In Unreal we have two static mesh actors called char1 and char2, which reference the same static mesh asset called M_Char. By default, enabling Reset Mesh Asset and pushing them in Modo creates a char1 mesh item and a char2 instance item. Modo and Unreal have different coordinate systems. Enabling this option resets the mesh at the origin in Modo based on the transformation for the static mesh actors made in the Unreal Editor client. |
|
Push |
|
|
Selects all mesh items, cameras, lights, and vertex maps (such as UVs used by mesh items) in your scene. All Items pushed are converted to actors in the Unreal Engine client when Push All or Push Selected is clicked. |
|
|
Selects all texture clips (images) used in your scene. Click Push All or Push Selected to push to the Unreal Engine client. Note: Texture assets always use specified Item Name options for asset naming. For more information, see Asset Naming. |
|
|
Selects all materials used in your scene. Click Push All or Push Selected to push to the Unreal Engine client. Note: Material assets always use specified Item Name options for asset naming. For more information, see Asset Naming. Note: |
|
|
Push All |
After specifying which items to push, Items (meshes, cameras, and lights), Textures, and/or Materials, the items are pushed to the Unreal Engine client. All items pushed are converted to actors in the Unreal Engine client. Note: If multiple check boxes are checked, then the order of pushing is always, Items, Textures, and then Materials. |
|
Push Selected |
After specifying which items to push, Items (meshes, cameras, and lights), Textures, and/or Materials, the selected items are pushed to the Unreal Engine client, when these options are enabled. All items pushed are converted to actors in the Unreal Engine client. Tip: You have the ability to select individual geometry items or selected polygons, edges, or vertices, materials, and textures to transfer them. |