Using Selection Modifiers
The following are useful selection commands you can use.
Convert Selection
The Convert Selection command sets a new selection mode specifically, using the content of the current selection to define the new one. You convert between selection types using the Alt key as a modifier. For example, if you have polygons selected in the viewport, pressing the Alt key changes the option buttons on the Modo Modes toolbar to read Convert. Press the Convert button, where Vertices was previously displayed, and the current polygon selection is converted to a vertex selection. This way you can quickly access all the vertices that were part of the original polygon selection. The conversion types are:
• Vertex : edge - selects edges defined by the selected points.
• Vertex : polygon - selects any polygons defined by the currently-selected points.
• Edge : vertex - selects points of all selected edges.
• Edge : polygon - selects polygons that are completely surrounded by selected edges.
• Polygon : vertex - selects points of all selected polygons.
• Polygon : edge - selects all the edges of the currently-selected polygons.
It's also possible to convert from a Material selection to any of the component level selections or the other way around.
Polygon Selection Fill
The Polygon Selection Fill command selects the entire area within an existing enclosed selection. This command is very similar to the select connected option but fills in a selection outline instead of selecting the entire surface. To apply, make a selection that represents the outside perimeter of the desired selection area, and then press the Ctrl+Shift modifiers and double-click inside the desired area to fill. The perimeter area must be fully connected, but it is not necessary that it be perfectly rectangular.
Grow Selection (Shift+Up Arrow)
The Select > Grow command expands, or "grows", the selected elements by selecting all unselected geometry elements directly contiguous with the selection. Grow selection is mapped to Shift+up arrow so you can quickly expand your selection set. This command works with all elements of geometry (Vertices, Edges, and Polygons) and is the functional opposite of the Select > Shrink command.
Shrink Selection (Shift+Down Arrow)
The Select > Shrink command reduces the selection by deselecting elements that are at the "outside" of the currently-selected elements. This has the effect of "shrinking" the selection set to a smaller size. The keyboard equivalent of this tool is mapped to Shift+down arrow. This works with all geometry elements (Vertices, Edges, and Polygons).
Select More/Less (Up/Down Arrows)
Selects the next plausible element. If a polygon was skipped then the next plausible element select would also skip a polygon.
Select Loop (L key)
The Select Loop command selects a continuous span of quadrangular polygons, edges, or vertices, depending on the selection mode. For polygons, select two adjoining polygons to define the loop direction and press the L key to select the entire loop. If not a full loop, selection terminates at non-standard geometry intersections.
For edge selections, a single edge can be selected and then press L to select the entire connected loop. If it is not a connected loop, the selection terminates at a multi-edged intersection. Edge loops can also be automatically selected by double-clicking on the target edge. Pressing Ctrl+Shift+double-click extends the loop beyond multi-edged intersections, based on the angle threshold, resolving toward the direction of the edge that is nearest to parallel with the adjoining edge.
For vertices, a loop can be defined by selecting two consecutive vertices and pressing L to select the loop, terminating in the same way as an edge loop.
Procedural Select Loop
You can take a selection based on a previous selection operation and apply the mesh operation Select Loop. You can apply a previous selection operation in your Mesh Operations list to a polygon, edge, or vertices selection.
Example
| 1. | In Model layout, open the Basic tab on the left panel, and Ctrl/Cmd + click on the |
| 2. | On the right panel, double-click on your mesh item, and name it Polygons. |
| 3. | Under the layout menu bar, click Polygons, and select two polygons on the mesh item. |
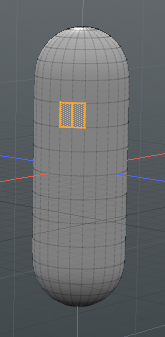
| 4. | On the right panel, click Add Operator, and double-click Mesh Operators > Polygon > Polygon Extrude. |
| 5. | Open the Polygon Extrude tab on the Properties tab and set Extend X to 200 mm. |
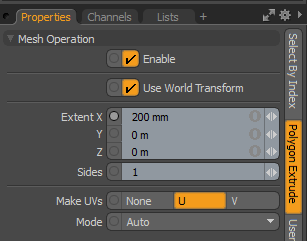
| 6. | Expand the Polygon Extrude, click (Add Selection), and double-click Mesh Operations > Selection > Select Loop. |
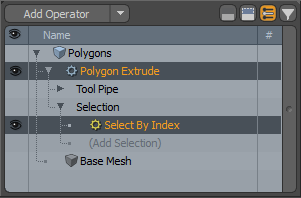
The loop selection is made and the polygons are extruded.

| 7. | Ensure that Polygons selection mode is active and click + drag on the mesh item to select two other polygons. |

| 8. | On the right panel, expand Polygons > Polygon Extrude > Selection, and select the Select by Index. |
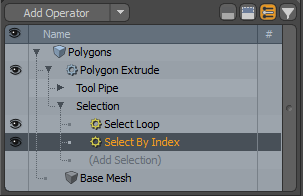
| 9. | In the Properties panel, on the Select By Index tab, and click Add. |
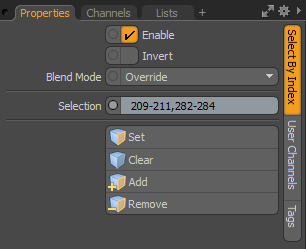
The previous selection operation is applied to your new selection.
Invert Selection ([ key)
Accessed through the Select > Invert menu, this command switches the state of all polygons, edges, or selected vertices. The selected elements become unselected and the unselected become the selected. Toggle the selection using the Invert shortcut key [ (left square bracket).
Select Connected (] key)
The Select Connected command lets you quickly expand geometry selections to include all elements physically contiguous with the selection. This is a very handy workflow for selecting mesh geometry. You simply click to select a single polygon, edge, or vertex, then press ] (right square bracket) and the entire piece of geometry is selected. While in Polygon or Vertex selection mode, you can also simply double-click on a vertex or polygon to select all connected elements.
Select Between (Shift+G)
The Select Between command requires that two polygons or edges are selected prior to triggering the command. Once the command is triggered it completes the selection between the two based on the shortest distance between them. Only a single row is selected, if the initial polygons or edges were on the same loop. Polygons in adjoining rows or columns would create rectangular selection.
Boundary Edges
With polygons selected, this command selects all the edges around the boundary edge of the polygon set. If no polygons are selected, it basically selects all the non-manifold edges of the mesh, which can be useful for finding holes. The mechanism is simply to select all edges bordered by an odd number of selected polygons.
To select a polygon boundary do the following:
| 1. | Select the polygons on the mesh. |
| 2. | Press the Ctrl key. |
Notice the Edge button now is labeled Boundary.
| 3. | Click the Boundary button. |
This command is also available on the Select > Boundary menu or from the Statistics tab of the Info and Statistics form, by expanding the Edges > By Boundary entry.
This command works on both continuous and discontinuous selection sets.
Select Ring (Alt+L)
Geometric selections can be expanded to include all vertices or edges adjacent to the selection across quads. For example, in a sphere, when a single vertical edge is selected, Ring selection highlights all the vertical edges at the same "latitude" around the globe of the geometry. This is the counterpart to Loop selection, which selects all the vertical edges with the same "longitude". Ring selection works with both vertex and edge selections.
Select Close Loop (Shift+])
The Select Close Loop command requires that two polygons are selected prior to triggering the command. Once the command is triggered it completes a loop selection using the two initial polygons to set direction and then selects all polygons on one side of the loop. The selection of the additional polygons is based on which side has fewer total polygons. For example, to select all polygons on a finger from the knuckle to the finger tip, you would select two polygons just above the knuckle, then perform the command. Since the finger itself has fewer polygons than the rest of the hand this is the side that is selected. This is generally the solution you are looking for, however, in the case that it's the opposite side of interest, the Select Close Loop command can simply be followed by Select Invert.
Select Colinear
The Select Colinear command selects any extraneous vertices across a polygon's boundary, making for easy removal. To use, select the command from the menu bar Select > Colinear and a pop-up dialog asks you to define a distance. Click OK to execute the command, resulting in the selection of all colinear vertices.
Select Coplanar
The Select Coplanar command selects the edges between polygons that fall within a flatness range of a selected polygon. To use, select a polygon, and then select the command from the menu bar Select > Coplanar and a dialog box appears, allowing you to specify a flatness limit. Click OK to execute the command, resulting in an edge selection based on your input.
Select Diagonal
The Select Diagonal command selects edges to share triangle pairs. This is useful when you want to convert triangles to quadrangles. You can convert triangles to quadrangles by deleting the selected edges. Here are options for the command:
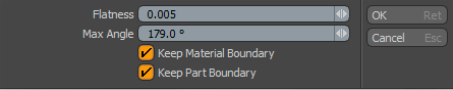
• Flatness - this is the Coplanar flatness threshold between opposing triangle pairs, designating whether the edge is selected or not.
• Max Angle - this is the maximum angle for the corners of a quadrangle from the triangle pair.
• Keep Material Boundary - when this option is enabled, edges that fall along material boundary are not selected.
• Keep Part Boundary - when this option is enabled, edges that fall along a part boundary are not selected.
Select by Info and Statistics
You can also select elements by using the Info and Statistics viewport.