Hybrid
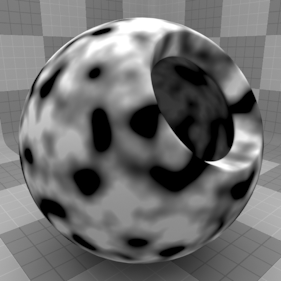
The Hybrid texture is one of the many procedurally generated textures provided with Modo. Procedural textures are mathematically created at render-time and, therefore, have no fixed resolution. They can be magnified almost infinitely with no visual loss in detail. The Hybrid texture can be addressed by its two zones: the Background and Foreground colors. The texture modulates from one zone to the other based on your settings. Each zone can have either a Value or a Color and Alpha. The applied zone is dependent on the Layer Effects to which the texture is applied. For example, if you apply the texture as a Displacement, then Modo uses the Value settings, but if you set the texture effect to Diffuse Color, Modo uses the Color and Alpha settings for the Background and Foreground. This texture is similar to the noisy bumps provided by the FMB (Fractal Brownian Motion) texture, but the Hybrid texture has smoother valleys to make it suitable for craggy mountain tops.
Note: For information about adding and working with Shader Tree item layers, see the Shader Tree topic.
Layer Properties
|
Enable |
Toggles the effect of the layer on and off. This duplicates the functionality of toggling visibility in the Shader Tree. When disabled, the layer has no effect on the shading of the scene. However, Modo saves disabled layers with the scene, and they are persistent across Modo sessions. |
|
Invert |
Inverts the colors (RGB values) for the layer to produce a negative effect. |
|
Blend Mode |
Affects the blending between different layers of the same effect type. With this, you can stack several layers for different effects. For more about blending, see Layer Blend Modes. |
|
Opacity |
Changes the transparency of the current layer. If there are layers below this layer in the Shader Tree, reducing this value increasingly reveals the lower layers. Reducing the value always dims the effect of the layer. |
|
Locator |
Sets the association for the Texture Locator. Most texture layers have a Texture Locator that Modo automatically creates in the Item List. This defines the mapping of the texture (how Modo applies the texture) to the surface. You can specify alternate locators, but this is normally not required. Although you may want multiple texture items to share a single locator. |
|
Projection Type |
Defines how a texture/material is applied to a 3D surface. Types vary significantly in their effects. For a guide to each Projection Type see Projection Type Samples. |
|
Projection Axis |
The texture/material is projected down this axis. This applies to Planar, Cylindrical, Spherical, Cubic, Box, and, Light Probe projection types. |
Hybrid Properties
|
Noise - Hybrid |
|
|
Noise Type |
Specifies the look of the texture distortion, with several noise function types provided: • Perlin • Enhanced Perlin • Gradient • Value • Gradient Value • Impulse • Lattice • Bubble |
|
Noise Seed |
Specifies the initial number Modo uses when generating the procedural values. Different Seed values produce different random variations and can be useful in changing the texture result; however, you need to use the same Seed value when you want items to retain the same variations. |
|
Octaves |
Defines the number of iterations Modo uses to create the texture. As this number increases, Modo generates turbulence by summing noise — with each summed noise being half the magnitude of the previously summed noise. At low values, the turbulence is smoother. It increases in detail as you increase the number of octaves. |
|
Frequency |
Controls the overall frequency or scale of the texture. Increasing this value creates more turbulence to "stir up" the pattern. |
|
Increment |
Controls the scaling of each successive iteration. When you set the control to a low value, the turbulence is tight and crinkled. It becomes increasingly smoother as you increase the value. |
|
Offset |
Controls the detail of the texture. When you set this at a low value, the detail is very sharp. The details become increasingly faded as you increase the value. |
|
Heterogeneous |
When enabled, switches from using the default fractal model to a heterogeneous terrain model. |
|
Output Controls |
|
|
Lower Clip |
Specifies a clip level for the Background Color/Value to truncate values beyond the defined setting. Combined with the Upper Clip value, you can apply this option to extend or contract the total range of values for the texture. |
|
Upper Clip |
Specifies a clip level for the Foreground Color/Value to truncate values beyond the defined setting. Combined with the Lower Clip value, you can apply this option to extend or contract the total range of values for the texture. |
|
Bias |
Determines whether the texture favors the foreground or background color. Increasing this value causes the texture to favor the foreground color; decreasing the value favors the background color. |
|
Gain |
Determines the falloff effect for the texture. This is similar to a gamma control that affects the falloff of the gradient ramp between the two color values. Setting the Gain to 100% creates a sharp falloff effect; setting the value to 0% creates a plateau around the value (or color mid-point) with a sharp falloff at either gradient extreme. |
|
Output Regions |
When enabled, outputs random gray shades per region rather than outlines for tiles. This adds random variety to the procedurally created texture. You can further control the amount of variation using the Regional HSV process layer. |
|
Background Color/Value |
Specifies the Color (or Value) of the texture's background area, which ramps toward the Foreground Color/Value. |
|
Background Alpha |
Specifies the Alpha transparency of the Background Color. |
|
Background - Use Last Layer |
When enabled, makes the Background Color area completely transparent to reveal the shading results of lower layers. |
|
Foreground Color/Value |
Specifies the Color (or Value) of the texture's foreground area, which ramps toward the Background Color/Value. |
|
Foreground Alpha |
Specifies the Alpha transparency of the Foreground Color. |
|
Foreground - Use Last Layer |
When enabled, makes the Foreground Color area completely transparent to reveal the shading results of lower layers. |