Bridge
The Bridge tool creates polygons to span the area between selected edges or polygons. The Bridge tool has several options to control how Modo generates the spanning polygons to connect the two locations.
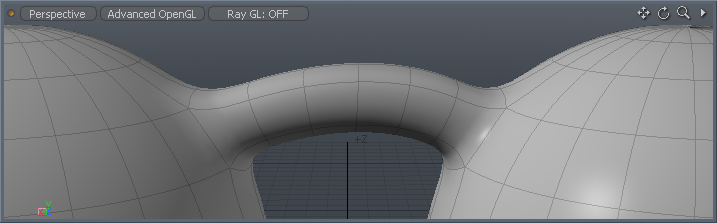
The Bridge tool is found in the Model layout Toolbox, under the Duplicate, Edge, and Polygon sub-tabs. It is also found in the Topology layout Tools sub-tab. In addition, you can also activate it by choosing Geometry > Duplicate > Bridge.
Prior to activating the tool, you must select at least two polygons that do not share any edges. The first polygon (or cluster of polygons) selected connects with the second polygon (or cluster of polygons). Make sure each cluster (or individual polygon) does not share any edges with the first selection for Modo to determine how to bridge from one location to the next.
Note: You can use Edge selections as well — as long as they don't share any vertices between the two or more selections.
Once you specify the selection, clicking the Bridge tool icon activates the tool. Clicking again in the 3D viewport enables the interactive mode for you to drag and interactively adjust the number of segments between the polygon clusters.
Bridge Tool Properties
You can adjust additional options in the tool's Properties panel.
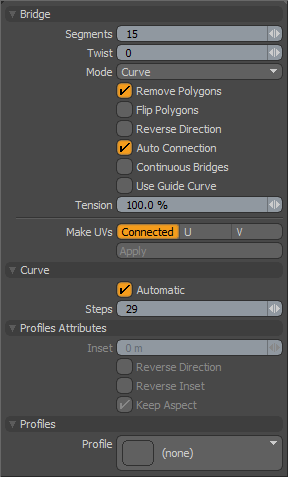
Bridge Properties
Segments: Determines the number of polygons that Modo creates across the length of the bridge. You can set this value interactively by dragging in the 3D viewport while the tool is active or numerically in the Properties panel. For curved bridge spans or those modulated by a profile, having more segments produces smoother results.
Twist: Rotates the bridge polygons between the original connection points when set to a non-zero number. This is useful to clean up bridges between disparate polygon selections where the bridge can become overlapped. By specifying the Twist value you may be able to untangle the bridge manually.
Mode: Sets the interpolation style of the generated bridge polygons.
Linear- Creates a bridge in a straight line between the original selection.
Curve- Creates an arc between the original selection points. You can further refine the curve by adjusting the Tension setting.
Smooth- Creates an "ease in/ease out" blend between the original selection sections.
Remove Polygons: When enabled, removes the originally selected polygons used to create the bridge if you selected polygons prior to activating the tool. This is enabled by default and is the preferred behavior.
Flip Polygons: When enabled, flips the normals of the newly created polygons in the bridge. Use when a negative bridge action causes the resulting polygons to appear inside-out.
Reverse Direction: When enabled, reverses the normal direction of the target polygon cluster when bridging. This can help resolve a skewed bridge span that can't be resolved by adjusting the Twist value alone.
Auto Connection: When enabled, adds segments automatically, connects them to adjoining boundary edges when bridging opposing edges within the same surface, and attempts to retain the surrounding curvature.
The video shows the edge selection prior to activating the tool, then the tool activated on the selection bridging between the two clusters, and finally with Auto Connection enabled, Modo adds additional spans automatically and connects them to the border edges.
Continuous Bridge: When enabled, bridges successive clusters of polygons or edges into a continuous length or tube with the spans evenly divided between each individual span. Selection order determines the order in which Modo bridges the spans.
Use Guide Curve: When enabled, uses a guide curve to determine a single continuous edge along the final bridged span that may eliminate a twisting issue. When using the Bridge tool to connect consecutive curves created with the Contour tool, twisting may occur in the resulting geometry. You can select a single vertex from each curve and press Shift+O on the keyboard to create an open curve to serve as a guide curve. Then switch to Polygon selection mode and select all the curves in order, with the guide curve last. Do this before activating the Bridge Tool and enabling Use Guide Curve.
Tension: Provides additional control over the bridge path used when Curve mode is active. Increasing this percentage value accentuates the curved effect and decreasing it mutes the effect toward the linear path.
Make UVs: Determines how Modo generates a UV map automatically for the resulting geometry.
Connected- Connects the edges between existing UV values as a straight line.
U/V- Fills the entire UV map 1-0 area with the resulting bridged geometry in the specified orientation.
Curve Properties
It is possible to bridge between selections of two curves or, by enabling Continuous Bridge, a series of successive curves. You can control the smoothness of the bridging in these cases by adjusting the Segments between spans and the Steps across the curve. The Tension setting controls how smoothly one span blends into the next.
Automatic: When enabled, determines automatically the Steps value by subdividing the curve based on the Mesh Item layer's Curve Refinement Angle setting.
Steps: Determines the the number of curve subdivisions when Automatic is disabled. Larger values produce smoother surfaces; smaller values produce more faceted surfaces.
Profile Attributes Properties
Inset: Specifies the X direction offset amount of 1D profile.
Reverse Direction: When enabled, evaluates the 1D profile from top to bottom.
Reverse Inset: When enabled, reverses the Inset value to mirror the profile.
Keep Aspect: Sets the Inset value automatically based on the aspect ratio of the profile.
Profiles: Provides a list (essentially a mini Preset Browser) for viewing various profiles. This works the same as the standard Preset Browser.