

You can create vertices one at a time by specifying their location in 3D space. To do so, choose Geometry > Vertex > Create.
To create an individual vertex:
| 1. | In the Viewport Shading list select Visibility Options > Show Vertices. |
| 2. | Choose Geometry > Vertex > Create. |
| 3. | in the Create New Vertex dialog, specify the X, Y, and Z coordinates for the vertex's location. |
| 4. | Click OK. |
The vertex is visible in the 3D model view.
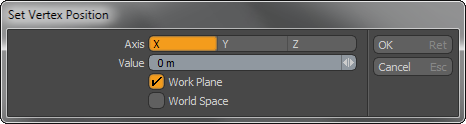
With the Set Position command you can reposition an existing vertex (or many) to a specific position by typing new coordinates. With this command, you can center an entire loop of vertices on the zero position for a mirror operation. You access the Set Position command from the Vertex sub-tab of the Modo toolbox (under Commands) or choose Geometry > Vertex > Set Position. Prior to invoking the command select a number of vertices.
Axis: Determines the plane with which to position the vertices.
Value: Determines the position to assign to the selected vertices.
Work Plane/World Space: Assigns the position value based off the World Space or the Work Plane position.
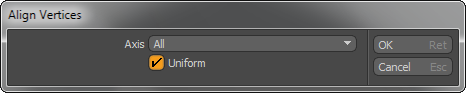
With the Align command you can align a selection of vertices into a straight row (in a line between the first and last vertices selected).
Axis: Confines the movement of the repositioned vertices to one or All axes. You can also select an axial plane (XY, YZ, or ZX).
Uniform: When enabled, spaces the vertices evenly (uniformly) along the span.
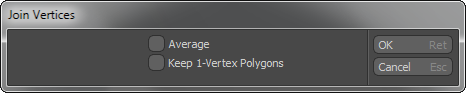
The Join command welds the selected vertices to the last vertex selected and then moves them all to the position of the last selected vertex.
You access the Join command on the Vertex tab of the Modo Tools toolbar.
Average: When enabled, welds the selected vertices into a single vertex positioned at an average distance between the selected points.
Keep 1-Vertex Polygons: When enabled, allows single vertices to exist after the join operation. When disabled, Modo automatically deletes 1-vertex polygons.
The Join Average command welds two (or more) vertices together at a central position between the two vertices.
To join multiple vertices:
| 1. | Select the vertices to join together. |
| 2. | On the Modo Tools toolbar, click the Vertex tab. |
| 3. | In the Commands section, click Join Averaged. |
| 4. | In the Join Vertices dialog, read the message indicating how many vertices were joined into one. |
| 5. | Click OK. |
The Geometry Remove command deletes the selected vertices, edges, or polygons from the 3D model view.
You can use the Remove command from the Vertex or Edges tab of the Modo Tools toolbar or choose Geometry > Remove. Also, you can use the Backspace or Delete key to remove vertices, edges, or polygons. Geometry Remove works on individual or multiple selected vertices, edges, or vertices.
The Collapse command removes the selected element without destroying the integrity of the geometry. You can delete any selected polygon, edge, or vertex but, with this command, no hole is left behind. Instead, Modo heals the mesh to close any gaps by merging neighboring elements together.
You access the Collapse command in several places:
• Vertex: On the Vertex tab of the Modo Tools toolbar click Commands > Collapse.
• Edge: On the Edge tab of the Modo Tools toolbar click Commands > Collapse Edges.
• Polygons: On the Polygons tab of the Modo Tools toolbar click Commands > Reduce > Collapse.
• You can also select whatever geometry to collapse and then choose Geometry > Collapse.
The Split command for vertices is the opposite of the Join command. Instead of combining multiple vertices into a single vertex, this command takes a single vertex and creates multiple vertices in the same location based on the number of polygons that share the point.
Unlike the Join command, the Split command creates the multiple vertices in their original location. It doesn't move them apart. Select any polygon or edge and move it to separate the split vertices.
You can find the Split command on the Vertex tab of the Modo Tools toolbar in the Commands section. Also, you can select the vertices and then choose Geometry > Vertex > Split.
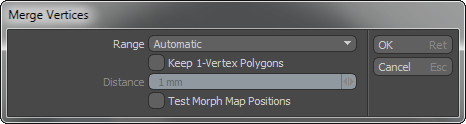
The Merge Vertices command measures the distance between vertices in the currently selected geometry to see if any fall within a specific distance threshold to one another. If any vertices are within that range, Modo combines them into a single vertex. It positions the resulting vertex at the site of the most recently selected vertex of the merged vertices.
The Merge command is on the Vertex tab of the Modo Tools toolbar in the Tools section.
Range: Specifies when to merge vertices. By default, the Merge Vertices command uses a Range setting of Automatic.
Automatic: Merges only vertices that share the exact location on all three axes.
Fixed: Provides a way to specify a distance threshold. Select to increase the distance allowed between two vertices to be merged. After selecting Fixed, you can set a threshold value for the Distance.
Distance: Specifies the distance threshold if you selected Fixed as the Range. For example, if the Distance is set to one meter, Modo merges any points that fall within one meter of another point.
Keep 1-Vertex Polygons: When enabled, leaves behind any 1-vertex polygons from merging vertices. Often when merging vertices within a certain threshold, polygons become flattened into only one vertex. In this case they become 1-vertex polygons. These 1-vertex polygons can cause rendering anomalies and other issues in the model file when exporting to other systems. When disabled (by default), Modo removes these 1-vertex polygons. However, there are some cases where you may want to keep the resulting 1-vertex polygons.