Particle Step Modifier
The particle step modifier applies any or all of the three basic transforms (Move, Scale and Rotate) to a procedurally generated particle source, in additive steps. Meaning each subsequent element inherits the transform of its predecessor and then applies the transform again, generating progressively positioned, scaled or rotated elements. The resulting effect on the particles is based on point order, so the transforms are applied in that order. Generally meant for use with the Particle Generator, they can also be applied to the Particle Cloud and the Surface Particle Generator items.
Adding a Particle Step Modifier
You can add a particle step modifier item by using the Add Item function of the Items List. Click the button to open the menu, then under Particles > Modifiers, double-click Particle Step Modifier option.
Once added, you need to specify the point source that you wish to affect. Once the originating point source is defined, you also need to specify the particle step modifier item as the source in the final item. If thought of like a chain, the originating particle generation is defined as the source in the step modifier, and then the modified values are fed into the final effect, such as a Replicator, Blob, Volume or Sprite. The source must be defined in this order so as to produce the intended result.
When applying the step modifier to an active particle simulation, you need to connect the modifier in the proper order within the Schematic viewport. For existing networks, simply select the connector between the simulation item and the target and add the modifier. The step modifier is found in the Schematic view in the Add... menu under Particles > Modifiers > Particle Step Modifier. When selected, the following attributes are available in the Properties panel.
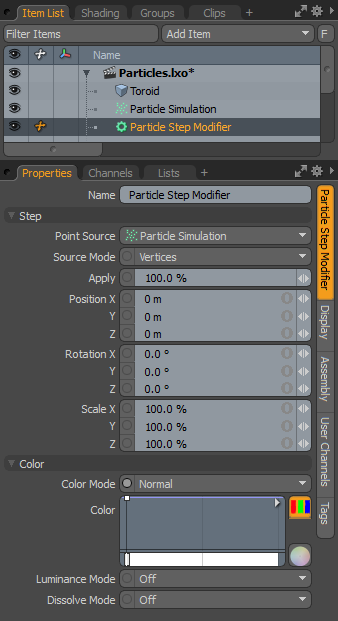
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Point Source |
Defines the source of the particles that are affected by the modifier. |
|
Source Mode |
Specifies the way the particle modifier affects the source. Vertices uses the point positions, Polygons uses the polygon centers, and Detached Vertices uses the point positions of vertices that are not part of polygons. |
|
Apply |
Acts as a multiplier, controlling the overall strength of the transforms applied to the source particles. |
|
PositionX/Y/Z |
Determines a position offset value for the initial particle for each individual axis. Subsequent particles inherit this values and then apply it again, producing a progressive type effect. |
|
RotationX/Y/Z |
Determines a rotation offset value for the initial particle for each individual axis. Subsequent particles inherit this values and then apply it again, producing a progressive type effect. |
|
Scale X/Y/Z |
Determines a size increase/decrease for the initial particle for each individual axis. Subsequent particles inherit this values and then apply it again, producing a stepped or progressive type effect. |
|
Color |
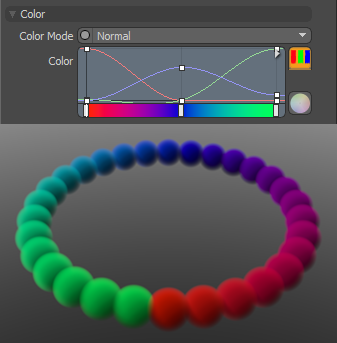
Allows you to use mini gradient editors to assign and control different attributes for the resulting particles. These attributes are then passed along to the final effect, working with both volumes and sprites. The gradient values are generated sequentially, dividing the gradient itself into the number of generated particles it is assigned to, each receiving the value for that position along the gradient. For example, a red to blue gradient assigned to a linear array of particles produces one red particle at the start. The particle colors then fade toward the blue color in even increments along the length of the array. There are three different settings that can be applied to their associated surface attributes. Any of these functions are enabled by selecting any option other than Off (the default value that disabled the function). The selected Mode determines the blending of the gradient with the base setting of the target element. |
|
Color Mode |
Determines how the resulting gradient applies, defining the blending mode of the colors as they apply to the base particle coloring. The Color gradient editor that opens allows you to define the actual gradient values that are applied. |
|
Luminance Mode |
Determines how the resulting gradient applies, defining the blending mode of the luminosity value as it applies to the base particle luminosity. The Luminosity gradient editor that opens allows you to define the actual gradient values that are applied. |
|
Dissolve Mode |
Determines how the resulting gradient applies, defining the blending mode of the colors as they apply to the base particle transparency. The Dissolve gradient editor that opens allows you to define the actual gradient values that are determine the transparent amount.
A Normal color mode gradient applied to a particle generator's radial array |