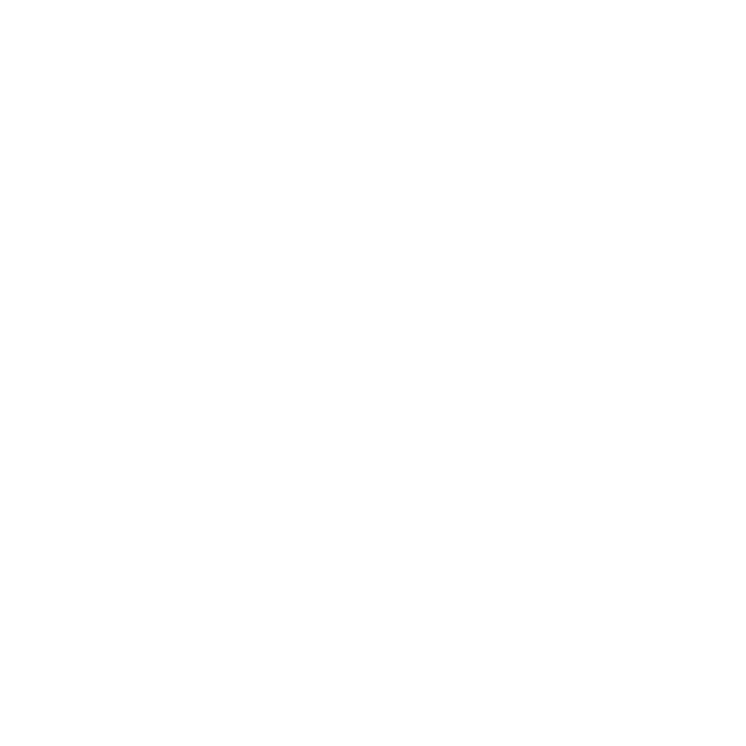
Gabor Noise
The Gabor Noise texture is one of Modo's procedurally generated textures. Procedural textures are mathematically created at render-time, and therefore have no fixed resolution; they can be magnified nearly infinitely with no visual loss in detail. Gabor Noise is a simple procedural noise texture that generates patterns which can be stretched and rotated, like brush strokes. It also offers direct control over the frequency characteristics of the pattern, meaning that you can specify the feature density and smoothness very easily.
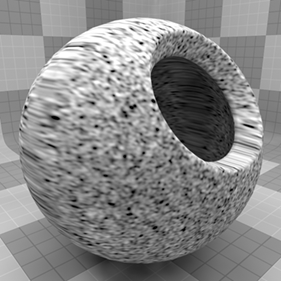
The texture has two zones, the Color/Value 1 and Color/Value 2. The texture modulates between the two based on the particular algorithm and settings. Essentially there are pseudo-random points created in 3D space and the texture blends from one value to the next, based on the proximity of one sample point to the next. Each zone can have a value, color and alpha value. Which of these are used is dependent on the Effect channel to which the texture is applied. For instance, if the texture is to be used as a displacement, the Value settings would be utilized whereas setting the texture Effect to Luminous Color uses the Color and Alpha settings for Value/Color 1 and Value/Color 2.
For information regarding adding and working with Shader Tree Items Layers, see Shader Tree.
Layer Properties
>
|
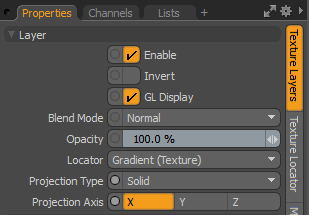
Enable |
Toggles the effect of the layer on and off. This duplicates the functionality of toggling visibility in the Shader Tree. When disabled, the layer has no effect on the shading of the scene. However, Modo saves disabled layers with the scene, and they are persistent across Modo sessions. |
|
Invert |
Inverts the colors (RGB values) for the layer to produce a negative effect. |
|
Blend Mode |
Affects the blending between different layers of the same effect type. With this, you can stack several layers for different effects. For more about blending, see Layer Blend Modes. |
|
Opacity |
Changes the transparency of the current layer. If there are layers below this layer in the Shader Tree, reducing this value increasingly reveals the lower layers. Reducing the value always dims the effect of the layer. |
|
Locator |
Sets the association for the Texture Locator. Most texture layers have a Texture Locator that Modo automatically creates in the Item List. This defines the mapping of the texture (how Modo applies the texture) to the surface. You can specify alternate locators, but this is normally not required. Although you may want multiple texture items to share a single locator. |
|
Projection Type |
Defines how a texture/material is applied to a 3D surface. Types vary significantly in their effects. For a guide to each Projection Type see Projection Type Samples. |
|
Projection Axis |
The texture/material is projected down this axis. This applies to Planar, Cylindrical, Spherical, Cubic, Box, and, Light Probe projection types. |
Gabor Noise Properties
|
Gabor Noise |
|
|
Orientation |
Controls the rotation of the striped/stretched sections of the Gabor Noise, essentially rotating the noise around the defined axis (as set in the Texture Locator). |
|
Frequency |
Controls the rate of modulation of the noise features. |
|
Bandwidth |
Controls the frequency spread between the two different values, low values preserve the striped appearance, while higher values increasingly randomize the look of the pattern. |
|
Random Offset |
Shifts the location of the noise across the surface. |
|
Brightness |
Adjusts the apparent lightness to darkness intensity, modifying the fade between the Value/Color 1 setting and the Value/Color 2 setting. |
|
Contrast |
Adjust the apparent light to dark ratio, modifying the fade abruptness between the Value/Color 1 setting and the Value/Color 2 setting. |
|
Value/Color/Alpha (1 and 2) |
Depending on the defined Effect type, Modo either looks for a Value input such as for a Bump Map or a Color input for a Diffuse Color setting. The two separate values attenuate between each other, modified by the Brightness and Contrast settings. The Alpha Values define opacity of the values allowing underlying Shader Tree layers to show through. Note: You can adjust the Alpha value using the Color Picker. |