About Clips and Shots
The interface sorts your clips into three broad categories: Audio and Video, Audio Only, and Video Only. Clips are displayed differently depending on their content, location, and in the case of the Viewer, the current mode.
Note: The timeline Viewer currently treats all alpha channels as premultiplied, which can result in the Viewer background being "added" to the image. If you’re working with un-premultiplied images, set the Viewer background to Black.
Note: There is currently no QuickTime audio support on Linux. Support for audio is scheduled for a later release.
Source Clips
Source clips are representations of files on disk. Shots on the timeline refer to source clips, so making changes to a clip in a bin affects all shots that refer to that source clip.
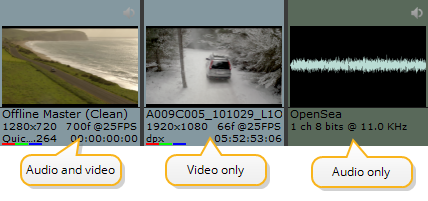
Note: The colored bars under the thumbnail represent the layers available in the clip, in this case color. Other layers include alpha, depth, and motion, similar to Nuke.
Shots
Shots are representations of source clips, they are not saved on disk. Making changes to a shot only affects that instance. See Managing Timelines for more information.

A Source Clip Opened in the Timeline View
Opening a source clip in the timeline view allows you to control its output and add soft effects to the source clip. Clips opened as timelines always contain all available frames, but you can adjust their output using the original range controls in the clip's properties or in and out points. See Using In and Out Markers and Soft Effects for more information.