Train Neural Networks to Replicate Effects Using Machine Learning
The CopyCat node (NukeX and Nuke Studio only) copies sequence-specific effects, such as garbage matting, beauty repairs, or deblurring, from a small number of frames in a sequence and then trains a network using machine learning to replicate this effect on a full sequence. CopyCat outputs a trained network in a .cat file ready for the Inference node to apply your effect.
Note: NVIDIA CUDA is not supported on macOS so training defaults to the CPU, which may result in longer training times.
For more details on Machine Learning with CopyCat in NukeX, see https://learn.foundry.com/nuke#machine-learning-compositing-in-nuke.
CopyCat ingests any number of image pairs called Input and Ground Truth images, which are referred to as the data set. The data set is used to train a neural network using machine learning to manipulate the Input images to replicate the Ground Truth. For example, a data set could be six frames from a sequence that you want to garbage matte and six manually roto'd masks, as shown in the image.
Note: CopyCat can ingest sequential formats, such as .jpg and .exr, and container formats, such as .mov and .mxf, but the set up is slightly different in each case.
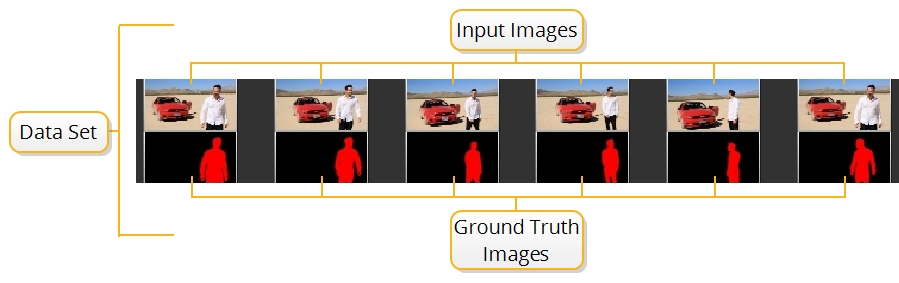
As the network learns, it creates .cat files in the Data Directory, which can then be used by an Inference node to reproduce the effect learned from a few frames across the whole sequence.
Creating a Data Set for Training
Learn how to create a data set to train a network to perform a specific task.
Training and Monitoring the Network
Train your network using the data set to replicate the desired effect.
Applying and Improving the Results
Apply a trained network to a sequence using the Inference node.
Training on Multiple GPUs Simultaneously
Machines with multiple GPUs can leverage the extra processing power in two ways:
• Train a single network using all GPUs up to 30% faster than with a single GPU. See Train the Network to Perform a Task for more details.
• Run different training sessions on each GPU, allowing you to train multiple models at the same time. See Train Networks from the Command Line for more information.
AIR Nodes on Ampere GPUs
Training using the CopyCat node requires an NVIDIA GPU, with compute capability 3.0 (Kepler) or above.
Note: If an appropriate GPU is not available, Inference and other machine learning plug-ins can run on the CPU with significantly degraded performance.
To use CopyCat, Deblur, Inference, or Upscale on Ampere GPUs in Nuke 13.2, the CUDA kernels need to compile the first time you use them. This process is only necessary once and should take about half an hour. The compiled kernels are stored in the CUDA cache which requires between 2147483648 bytes (2 GB) and 4294967296 bytes (4 GB) of storage.
Nuke automatically sets the cache size to 2 GB in a directory called NukeComputeCache in the default location for NVIDIA caches on your operating system:
Windows
%APPDATA%\NVIDIA\NukeComputeCache
macOS
$HOME/Library/Application Support/NVIDIA/NukeComputeCache
Linux
~/.nv/NukeComputeCache
The location and size can be overridden using the CUDA_CACHE_PATH and CUDA_CACHE_MAXSIZE environment variables respectively.
Warning: CUDA_CACHE_MAXSIZE must be set in bytes between 2147483648 and 4294967296 bytes.