 button.
button.This section pulls together and organizes the Nuke (.nk) scripts available to you throughout the help to ensure you can access them easily.
The links allow you to load the scripts into Nuke directly, but there are a few setup steps. If you just want to display a script to copy/paste it into Nuke manually, click the  button.
button.
NOTE: Loading example scripts only works if you launched the help from Nuke and have set documentation source to local in the Behaviors > Documentation tab of the Preferences.
See Using Script Links for more information.
The auto-links for the scripts in this help only work when Nuke and the help files are linked by the helpCommandRequestHander. To enable the links:
| 1. | Launch Nuke. |
| 2. | Navigate to the Preferences > Behaviors > Documentation tab and select source > local. |
| 3. | Add a node to the Node Graph and click the ? in the node's Properties panel. |
The help available for that node displays.
| 4. | Navigate to Example Nuke Scripts in the help table of contents on the left of the screen. |
| 5. | Click the required link to auto-load the script into the Nuke session. |
NOTE: If you close Nuke or the help, that session link is broken and must be re-established.
Bouncing particles off a sphere 
Using a curve to adjust particle size over time 

Applying a directional force to particles in a particular channel only 

Using the world position value as the color for each particle 
Adjusting the color, opacity, size, and position of particles using expressions 

Adjusting the color and opacity of particles using expressions 
Making each particle look towards a moving 3D point 

Realigning particles along their direction of motion 
Repelling particles from a point in 3D space 
Applying noise to the particle movement 

Creating a whirlpool of particles 
Simulating a wind blowing on the particles 
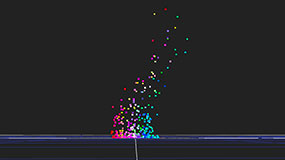
Using particles to simulate fireworks 

Using particles to simulate smoke 

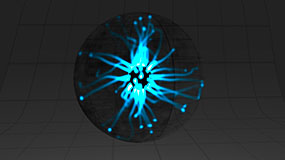
Using particles to simulate an electricity ball 
Using particles to simulate a blue light trail 

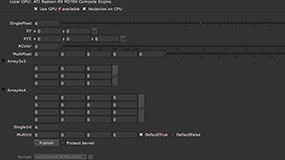
Examples of all the knob types that can be added to Kernel Parameters 
A balloon-like effect that uses random access and bilinear interpolation 

A weighted blur where the weights are taken from a second input 

A rippling curtain effect that uses 1D-ranged access 
A simple lens flare generator that requires no inputs 

A 5x5 average that uses Blink's median function 

A swirl effect that uses random access, trigonometric functions and bilinear interpolation 

A two-pass resize implemented with two Blink kernels chained together 

|
|