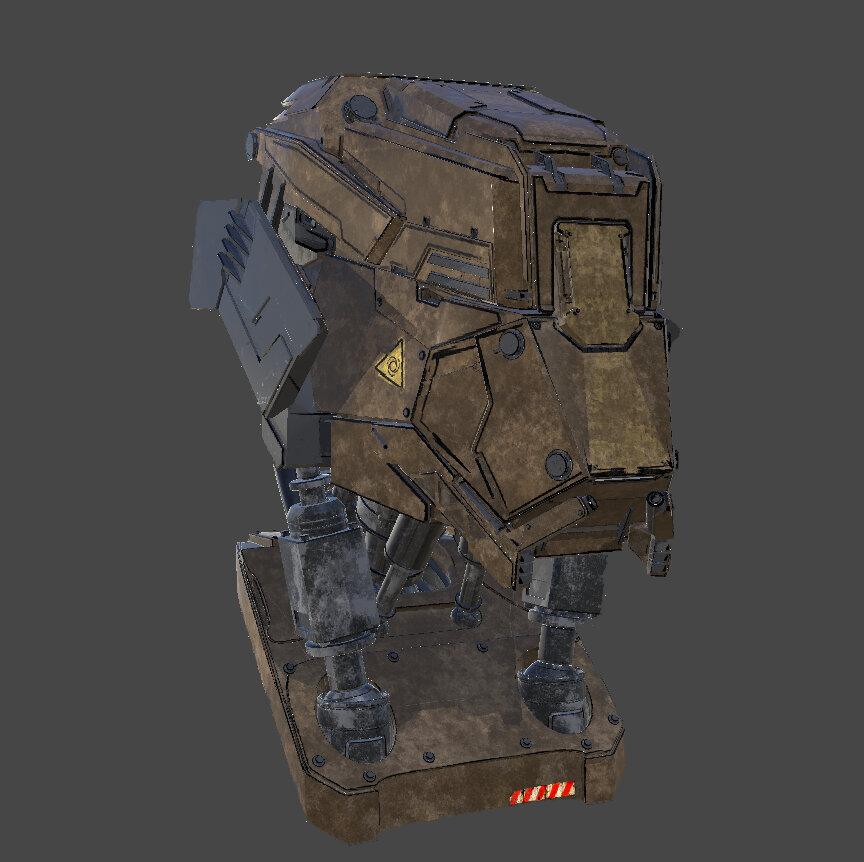
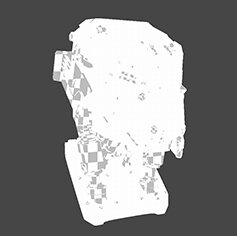
Shader Types and Examples
Below are descriptions and examples of the different shaders available in the Shaders palette.
Note: The project the illustrative image is taken from has three channels: diffuse, specular, and bump. For certain shaders, such as Flat, not all of these channels are hooked up to the input fields. Other shaders, such as the BRDF shader, have many other inputs that affect the shader output, but these may not be demonstrated from the three channels that are hooked into the shader.
Experiment: The illustrative image displays the Example Project model that's shipped with Mari. Try adding channels or layers to the Example Project in order to experiment with all the inputs and controls of the shaders in the table below.
Don't forget to adjust the sliders in the shader controls in order to modify the effect of the shader on the channel that you are trying out.
Note: The example images for each shader are highly dependent on how the controls have been adjusted for each shader. For the purposes of this table, most of the shaders are shown with default or near default settings unless otherwise specified.
|
Shader, Description, and Settings |
Example |
|
Current Channel A default shader that displays only the output of the selected channel. In the example shader, the diffuse channel is the currently selected channel. Settings: Adjust the sliders for the: Diffuse, Specular, and Specular Roughness amounts. |
|
|
Current Layer and Below A default shader that displays only the output of your selected sub-stack (such as a mask or adjustment stack) up to the selected layer. If you don’t have a sub-stack selected, it shows the parent stack up to the selected layer. Settings: Adjust the sliders for the: Diffuse, Specular, and Specular Roughness amounts. |
|
|
Current Layer A default shader that displays only the output of the current layer with the mask of the layer applied. Settings: Adjust the sliders for the: Diffuse, Specular, and Specular Roughness amounts. Specify whether the View is set to Primary or Secondary in the dropdown menu. |
|
|
Current Paint Target A default shader that displays only the selected component of the selected layer, for instance the paint, procedural, adjustment, or mask; whichever is selected on the selected layer. In the example shader, a procedural layer in a "dirt" mask stack is the current selected paint target. Settings: Adjust the sliders for the: Diffuse, Specular, and Specular Roughness amounts. |
|
|
Shader, Description, and Settings |
Example |
|
A physically-based shading model that includes Fresnel effects. The BRDF shader defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface from both direct and indirect light sources. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Diffuse Color Specular Color Glossiness Reflectance Ambient Occlusion Emissive Color Normal Bump Vector Displacement The amount of each of these inputs can be adjusted in the respectively named sliders. |
|
|
A shader that emulates the VRayMtl material shader, which allows physically-correct illumination and convenient reflection and refraction parameters. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Diffuse Color Diffuse Amount Opacity Map Roughness Amount Self-Illumination Reflection Color Reflection Amount Reflection Glossiness Fresnel IOR GGX Tail Falloff Metalness Anisotropy Anisotropy Rotation Refraction Color Refraction Amount Refraction Glossiness Refraction IOR Fog Color Translucency Color Normal Bump Vector Displacement Map The amount of each of these inputs can be adjusted in the respectively named sliders. |
|
|
A physically-based shading model for PBR (physically-based rendering) that follows a set of principles to make BRDF shader control more intuitive, less complex, and artist friendly. For more information, see https://disney-animation.s3.amazonaws.com/library/s2012_pbs_disney_brdf_notes_v2.pdf. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Base Color Metallic Subsurface Specular Roughness Specular Tint Anisotropic Sheen Sheen Tint Clearcoat Clearcoat Gloss Ambient Occlusion Emissive Color Normal Bump Vector Displacement The amount of each of these inputs can be adjusted in the respectively named sliders. |
|
|
3Delight Principled (See 3Delight Principled section in the Mari Reference Guide) The 3Delight Principled material is 3Delight's interpretation of the Principled BRDF shader. For more information, see https://www.3delight.com/documentation/display/sfrp/3delight+principled. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Base Color Base Roughness Base Specular Level Metallic Anisotropy Anisotropy Direction Opacity Coat Thickness Coat Color Coat Roughness Coat Specular Level Subsurface Weight Subsurface Color Subsurface Scale Incandescence Color Incandescence Intensity Normal Bump Normal Intensity Vector Displacement |
|
|
The Arnold Standard Surface shader is a physically-based shader capable of producing many types of materials. It includes a diffuse layer, a specular layer with complex Fresnel for metals, specular transmission for glass, subsurface scattering for skin, thin scattering for water and ice, a secondary specular coat, and light emission. The non-active inputs (highlighted in gray) help drive the shaders but have no effects on the canvas. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Diffuse Weight Diffuse Color Diffuse Roughness Metalness Specular Weight Specular Color Specular Roughness Specular IOR Anisotropy Anisotropy Rotation Transmission Weight Transmission Color Transmission Depth Transmission Scatter Transmission Scatter Anisotropy Transmission Dispersion Transmission Extra Roughness Subsurface Weight Subsurface Color Subsurface Radius Subsurface Scale Clearcoat Weight Clearcoat Color Clearcoat Roughness Clearcoat IOR Sheen Weight Sheen Color Sheen Roughness Thin Film Thickness Thin Film IOR Emission Weight Emission Color Opacity Normal Map Bump Map Vector Map Displacement Map Note: Displacement Map is toggled off by default. The amount of each of these inputs can be adjusted in the respectively named sliders. |
|
|
A physically-based material shader for assigning textures and materials that match what would be seen in the Unreal Engine 4. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Base Color Roughness Metallic Specular Ambient Occlusion Normal Bump Emissive Color Vector Displacement |
|
|
This shader approximates the look of Pixar's UsdPreviewSurface. This shader can be used in tandem with your primary render vendor’s shader or Mari’s BRDF. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Diffuse Color Emissive Color Use Specular Workflow Specular Color Metallic Roughness Clearcoat Clearcoat Roughness Opacity Opacity Threshold Index of Refraction Normal Occlusion Bump Vector Displacement |
|
|
Creates a flat shader with a special channel that allows other shaders to be added as layers. Shader layers can be masked, grouped, and largely treated as layers in the Layers palette. The Layered shader lets you apply different shading models to create different material effects. Settings: Set the channel used for the following inputs: Vector Displacement The amount of displacement can be adjusted with the Displacement sliders. |
|