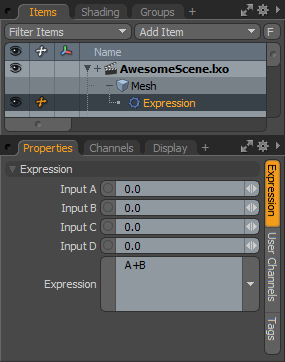
Expression

With the Expression Channel Modifier you use various mathematical and logical operators to define an output value based on input values. Expressions are especially useful in creating complex animations that don't require keyframes, and they are easy to adjust and update. The Expression modifier uses the muParser expression engine.
Input A/Input B/Input C/Input D: These are the user-defined input variables. Each is a floating-point value and is referred to in an expression by its variable name: A, B, C, or D.
Expression: This is the expression that Modo executes based on the defined inputs. For example, A passes the value coming in on the Input A channel to the output channel, or C+D adds the values coming in on the Input C and Input D channels and sets the sum to the output channel. You can also use built-in functions. For example, sin(A) outputs the sine value of Input A to the output. You can also use conditional statements. For example, with A>B?C:D Modo sends the value in Input C to the output if Input A is greater than Input B; if not, Modo sends the value in Input D.
Output: The output value is the value returned by the user-defined expression.
User-Defined Channels: You can use any User Channel that you have defined in the expression string. For example, if you add a floating-point channel called test, you can use test in an expression such as sin(test).
By default, Modo with the muParser expression engine includes the following functions. The table lists the function names and a brief description of each with the number of arguments, if applicable.
|
Name |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
sin |
sine function |
|
cos |
cosine function |
|
tan |
tangens function |
|
asin |
arcus sine function |
|
acos |
arcus cosine function |
|
atan |
arcus tangens function |
|
sinh |
hyperbolic sine function |
|
cosh |
hyperbolic cosine |
|
tanh |
hyperbolic tangens function |
|
asinh |
hyperbolic arcus sine function |
|
acosh |
hyperbolic arcus tangens function |
|
atanh |
hyperbolic arcur tangens function |
|
log2 |
logarithm to the base 2 |
|
log10 |
logarithm to the base 10 |
|
log |
logarithm to the base 10 |
|
ln |
logarithm to base e (2.71828...) |
|
exp |
e raised to the power of x |
|
sqrt |
square root of a value |
|
sign |
-1 if x is less than 0; 1 if x greater than 0 |
|
rint |
round to nearest integer |
|
abs |
absolute value |
|
min |
min of all arguments |
|
max |
max of all arguments |
|
sum |
sum of all arguments |
|
avg |
mean value of all arguments |
|
noise |
noise value takes 1-3 arguments |
|
floor(x) |
gives the integer value of x (For example, 3.5 becomes 3.) |
|
ceil(x) |
rounds up to the next integer value of x (For example, 3.5 becomes 4.) |
|
mod(a,b) |
returns the remainder of a divided by b |
|
clamp(a, min, max) |
given a value a, if a is less then min, min is returned. If greater then max, max is returned. If in between min and max, a is returned. |
By default, Modo with the muParser expression engine includes the following binary operators. The table lists the operator, a brief description, and the priority assigned to each operator.
|
Operator |
Meaning |
Priority |
|---|---|---|
|
= |
assignment * |
-1 |
|
&& |
logical and |
1 |
|
|| |
logical or |
2 |
|
< = |
less or equal |
4 |
|
>= |
greater or equal |
4 |
|
!= |
not equal |
4 |
|
== |
equal |
4 |
|
> |
greater than |
4 |
|
< |
less than |
4 |
|
+ |
addition |
5 |
|
- |
subtraction |
5 |
|
* |
multiplication |
6 |
|
/ |
division |
6 |
|
^ |
raise x to the power of y |
7 |
*The assignment operator is special because it changes one of its arguments. You can only apply it to variables.
The muParser expression engine has built-in support for the if/then/else operator. It uses a 'lazy' evaluation to make sure only the necessary branch of the expression is evaluated.
|
Operator |
Meaning |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
|
?: |
if then else operator |
C/C++ style syntax |