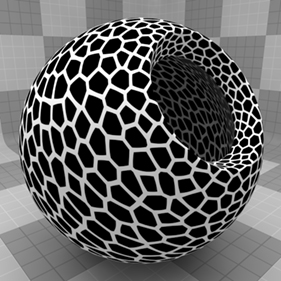

The Poisson Cells texture is one of the many procedurally generated textures provided with Modo. Procedural textures are mathematically created at render-time and, therefore, have no fixed resolution. They can be magnified almost infinitely with no visual loss in detail. The Poisson Cells texture can be addressed by its two zones: the Cell and Filler values. The texture modulates from one zone to the other based on your settings. Each zone can have either a Value setting or Color and Alpha. The applied zone is dependent on the Layer Effects to which the texture is applied. For example, if you apply the texture as a Displacement, then Modo uses the Value settings, but if you set the texture effect to Diffuse Color, Modo uses the Color and Alpha settings for the Cell and Filler values.
The Poisson Cells texture is very similar to the standard Cellular texture in many ways, but it produces a more regular distribution of cells across a surface. You can achieve the best results when you apply the texture to a surface with a UV map or one of the planar projection types. By doing this, the texture can seamlessly tile outside of the defined boundary.
NOTE: For information about adding and working with Shader Tree item layers, see the Shader Tree topic.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Layer |
|
|
Enable |
Toggles the effect of the layer on and off to duplicate the functionality of toggling visibility in the Shader Tree. When disabled, the layer has no effect on the shading of the scene. However, Modo saves disabled layers with the scene, and they are persistent across Modo sessions. |
|
Invert |
Inverts the colors (RGB values) for the layer to produce a photonegative effect. |
|
Blend Mode |
Affects the blending between different layers of the same effect type. With this, you can stack several layers for different effects. For more about blending, see the Layer Blend Modes topic. |
|
Opacity |
Changes the transparency of the current layer. Reducing this value increasingly reveals lower layers in the Shader Tree, if present, or dims the effect of the layer, itself, on the surface. |
|
Locator |
Sets the association for the Texture Locator. Most texture layers have a Texture Locator that Modo automatically creates in the Item List. This defines the mapping of the texture (how Modo applies the texture) to the surface. You can specify alternate locators, but the need to do so is rare. Still, you may want multiple texture items to share a single locator. |
|
Poisson Cell |
|
|
Cell Value |
Determines the magnitude of the texture where the cell is most concentrated. This value ramps to the Filler Value. You only use the Cell Value option when you set the texture layer to an effect that does not require color. |
|
Cell Color R |
Determines the color of the texture where the cell is most concentrated. This color ramps to the Filler Color R. You only use the Cell Color R option when you set the texture layer to an effect that requires color. |
|
Cell Alpha |
Determines the opacity of the Cell Color R value. When the value is below 100%, underlying Shader Tree layers show through attenuating to fully transparent at 0%. |
|
Filler Value |
Determines the magnitude between the cells. This value ramps to the Filler Value. You only use the Filler Value option when you set the texture layer to an effect that does not require color. |
|
Filler Color R |
Determines the color of the texture between the cells. This color ramps to the Filler Color R. You only use the Filler Color R option when you set the texture layer to an effect that requires color. |
|
Filler Alpha |
Determines the opacity of the Filler Color R value. When the value is below 100%, underlying Shader Tree layers show through attenuating to fully transparent at 0%. |
|
Type |
Specifies the style of the Poisson Cell texture. These options determine how the texture interpolates between its sample points. Click to view examples of the various Type options.
|
|
Cell Width |
Determines the maximum scale of the texture's features. At 100% the maximum scale of any single detail in the texture is equal to the texture size as set on the Texture Locator tab. To change the scale of the details of the texture, use this value. To set the overall scale of the texture, modify the texture scale on the Texture Locator tab. Click to view examples of various Cell Width settings. |
|
Transition Width |
Controls the amount of gradient falloff around each of the texture details. Setting this value over 100% can yield interesting effects. Click to view examples of various Transition Width settings. |
|
Cell Density |
Controls the cell size by determining the amount of coverage for each cell within the defined grid area. Outside the grid area, the Poisson cells tile infinitely, so increasing the density makes more cells within a single tile. Click to view examples of various Cell Density settings. |
|
Level |
Defines the number of cells in a given solution. Each increase doubles the number of cells from the previous level. Click to view examples of various Level settings. |
|
Solid 3D Cells |
When enabled, allows you to apply a non-planar solid projection on the target surface. Doing this, loses the tiling functionality, and the corners of some cells may intersect with the surface causing non-uniform cells to work more like the regular cellular texture. Normally, the Poisson Cells texture applies a planar-type projection to a surface, where curved glancing angle areas stretch the texture. By applying the texture as a 3D solid, the target surface carves out the texturing from the 3D volume. |
|
Brightness |
Determines whether the texture favors the Cell values or the Filler values. Increasing this value causes the texture to favor the Cell values over the Filler values. Decreasing the value causes Modo to favor the Filler values. Click to view examples of various Brightness settings. |
|
Contrast |
Affects the falloff of the gradient ramp between the Cell and Filler values, which is similar to a gamma control. Setting the Contrast to 100% creates a very sharp falloff effect; setting the value to 0% creates a plateau around the value (or color mid-point) with sharp falloff on either extreme of the gradient. Click to view examples of various Contrast settings. |
|
Hue Variation |
Varies the hue (or color) of each individual cell randomly. Higher numbers increase the color differences between cells; lower values create fewer color variations. Click to view examples of various Hue Variation settings. |
|
Saturation Variation |
Varies the color saturation of each individual cell randomly. Higher numbers increase the color differences between cells; lower values create fewer saturation variations. Click to view examples of various Saturation Variation settings. |
|
Value Variation |
Varies the brightness (or luminosity) of each individual cell randomly. Higher numbers increase the differences between cells; lower values create fewer brightness variations. Click to view examples of various Value Variation settings. |
|
Use Profile Gradient |
When enabled, uses the embedded gradient control to get extra control over the appearance of the cells. This gradient replaces the smooth linear transition between the Cell and Filler values specified by the Transition Width setting. When you enable this, you make the embedded gradient profile visible. |
|
Type Angular |
Type Round |
|
Cell Width 0% |
Cell Width 25% |
Cell Width 50% |
Cell Width 75% |
Cell Width 100% |
|
Transition Width 0% |
Transition Width 25% |
Transition Width 50% |
Transition Width 75% |
Transition Width 100% |
|
Cell Density 0% |
Cell Density 25% |
Cell Density 50% |
Cell Density 75% |
Cell Density 100% |
|
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Level 4 |
Level 5 |
|
Brightness 0% |
Brightness 25% |
Brightness 50% |
Brightness 75% |
Brightness 100% |
|
Contrast 0% |
Contrast 25% |
Contrast 50% |
Contrast 75% |
Contrast 100% |
|
Hue 0% |
Hue 25% |
Hue 50% |
Hue 75% |
Hue 100% |
|
Saturation 0% |
Saturation 25% |
Saturation 50% |
Saturation 75% |
Saturation 100% |
|
Value 0% |
Value 25% |
Value 50% |
Value 75% |
Value 100% |