You use the Vertex Paint tool to define and adjust vertex color maps and vertex Weight Maps interactively. By using the familiar painting workflow already established for creating bitmap-based textures, you can select the Vertex Paint tool and paint directly onto the surface in the 3D Viewport with either a tablet-based input or a mouse.
The Vertex Paint tool is in the Paint interface tab on the Vertex Map Tools sub-tab of the toolbox. To use the Vertex Paint tool, you first need to select a target Mesh Item layer in the Item List. You also need to create and select a vertex color map or a Weight Map in the Vertex Map list viewport. See the Working with Vertex Maps topic for information about creating Vertex Maps.
After selecting the tool, its attributes appear in its Properties viewport. When you first select the tool, it has Smooth Brush as the default brush tip. You can select an alternate brush tip before proceeding or right-click in the 3D Viewport to scale the brush size. Drag in the viewport to apply the specified values to the designated map. Pressing Ctrl reduces the values applied to Weight Maps (instead of increasing them). Pressing Shift applies the Smooth Vertex Map function.
Paintbrush

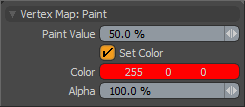
Paint Value: Determines the strength of the painting action. Higher values saturate the canvas more quickly than lower values. Set this to 100% to quickly overlay an area, or set to 5% or less to make subtle adjustments.
Set Color: Enabled automatically when applying values to a vertex color map. Once enabled, you can then define a Color value and apply it to the target map.
Color: Defines an RGB value to apply to the target vertex color map.
Alpha: Determines the opacity of the color applied to the RGBA vertex color map.
TIP: Modo stores the Vertex Map values for the vertices themselves of the mesh's surface. Therefore, it is not possible to resolve any finer detail than the resolution of the target geometry (un-subdivided). If you don't want to subdivide the mesh, then using a bitmap-based texture may be a better option to assign colors to the surface.