You can use the Copy command with the Paste command to take information from one Vertex Map and apply it to another.
You can access the Copy and Paste commands by choosing Vertex Map > Copy or Vertex Map > Paste. You can also select the map in the Vertex Map list and then right-click the map and choose Copy. Then, select a different map in the same list, right-click again and choose Paste to complete the operation.

Vertex Map Type: For proper results, make sure when copying values with the Vertex Map > Copy command that the proper Vertex Map type is defined for both maps.
You can use the Paste command with the Copy command to take information from one Vertex Map and apply it to another.
You can access the Copy and Paste commands by choosing Vertex Map > Copy or Vertex Map > Paste. You can also select the map in the Vertex Map list and then right-click the map and choose Copy. Then, select a different map in the same list, right-click again and choose Paste to complete the operation.
Vertex Map Type: For proper results, make sure when copying values with the Vertex Map > Copy command that the proper Vertex Map type is defined for both maps.
Choosing Vertex Map > Clear resets the values of any Vertex Map edits. For example, if you make changes to a Weight Map and then click Clear or use the menu command, those values are discarded and Modo returns the Weight Map to its initial state. You can also right-click the map's name in the Vertex Map list and choose Clear.
To completely remove a Vertex Map from the Vertex Map list and the current Modo session, select the map in the list, and then use the Delete command. You can right-click the entry in the list and choose Delete or choose Vertex Map > Delete.
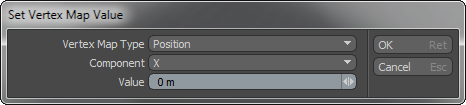
Use the Set Value tool to quickly and accurately set the value of a particular Vertex Map or a group of selected Vertex Maps. Because Modo stores much of the data in a 3D model as a Vertex Map, this is a powerful tool. Vertex maps are typically referred to when discussing things such as morph maps, Weight Maps, or UV data, but Vertex Maps are also used for storing the basic positional information for all vertices in a mesh. When using the Set Value tool, Modo changes the dialog to reflect current conditions. For example, if there are no selected RGBA maps, then there is no RGBA choice available. Also, the contents of the Component list changes to match the type of the selected Vertex Map.
To use the Set Value tool, select the desired Vertex Map class in the Type list. (The contents of this list change depending on what types of Vertex Maps are active in the currently selected data.) Now, in the Component list specify the setting to change. Finally, specify a Value for the Vertex Map.
With this tool you can manage many different aspects of your model's data quickly. For example, you could quickly set the UV coordinates to U = 0 for an entire set of selected vertices so that they snap to an edge. Alternatively, you could use the tool to quickly set the selected vertices' Weight Map to 100%. You could even use this tool to set all the selected vertices to an absolute location such as X = 0.

With the Set Vertex command you can define precise values for individual vertices in a Vertex Map. In the Set Vertex Value dialog you can specify these options:
Component: Specifies which component Modo sets. Some Vertex Maps have multiple components. For example, a UV Vertex Map has two components U and V; an RGB map has three components R, G, and B; and a Weight Map has only a single component: the weights value. Using the Set Vertex command on a UV map with the Component set to 0, sets the value on the U component of the map. Using a value of 1 as the Component, sets the V value.
Index: Specifies which vertex is to be affected. If you turn on Show Indices under Visibility Options, you can see the vertex indices in the viewport.
Value: Determines the numeric value for the vertex.
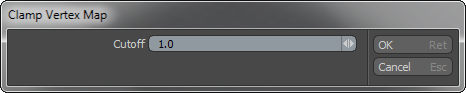
Vertex Map Clamp command limits the values in a Vertex Map based on the Cutoff value.
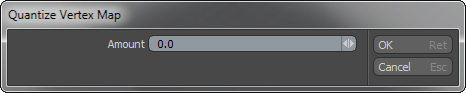
The Vertex Map Quantize tool reduces the Vertex Map selection values mathematically. Modo evaluates all the selected components and simplifies them based on the Amount value set in the Quantize Vertex Map dialog. Increasing the Amount results in fewer diverse values in the Vertex Map. To apply this command, choose Vertex Map > Quantize.
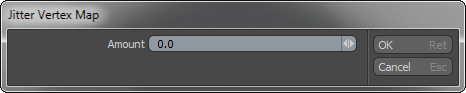
The Vertex Map Jitter tool procedurally affects selected Vertex Map values based on an Amount value. This tool makes the placement of the vertices in the Vertex Map random. To apply this command, choose Vertex Map > Jitter.
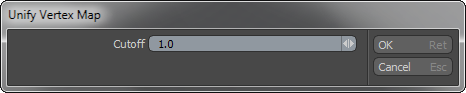
A discontinuous Vertex Map is one where a single vertex has multiple UV map values. The Vertex Map Unify command merges continuous and discontinuous Vertex Map values if their difference is below the threshold given as the Cutoff value. Modo computes the difference from the largest component value difference (as opposed to the difference of the magnitude of the entire vector). One way to visualize this operation is to make some discontinuous UVs that are very close to similar continuous UVs. Then use the command to close the seam.
The Cull command removes extra Vertex Map values. It clears the values below the Cutoff setting. If you select the Hollow Area checkbox, then Modo removes only values that have non-culled neighbors and limits culling to isolated values or values that are below the threshold and are not connected to any vertices with values above the threshold.

The Mirror command creates mirrored Vertex Map values across the user-defined Symmetry axis. The target geometry with the Vertex Map must be symmetrical, itself, and you must select the Symmetry checkbox before running the command. In the dialog, specify a source map and a Destination map. If the source and destination are the same map (have the same name), then Modo mirrors the values from one side to the opposite side. If the destination map is different from the Source map, then Modo creates a new map (or assigns the mirrored values to an existing map).
Source Map: Lists the active Vertex Maps on the current Mesh Item layer(s). Select the source map for the mirroring operation from the list.
Destination Map: Specifies the name of the target map for the mirrored vertex values. Type the name of the destination map. If the name is the same as the source map, then Modo mirrors the values across the designated symmetry axis in the same Vertex Map to create a symmetrical map (if it wasn't symmetrical to begin with). If the name is different from the source map, then Modo creates the resulting map as a mirrored version of the source map (not symmetrical).