Soft Move
Soft Move is a tool preset that consists of the Transform tool with Radial falloff. With this tool preset, you can select vertices, edges, or polygons and move them.
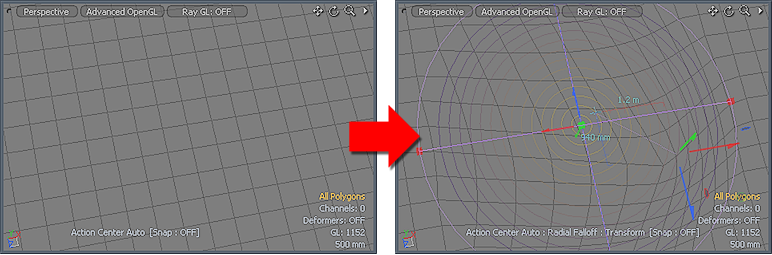
Using Soft Move
| 1. | You can find the tool in the Model layout's Deform sub-tab, or in the menu bar, under Edit > Deform > Soft Drag. |
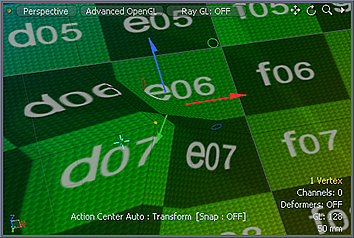
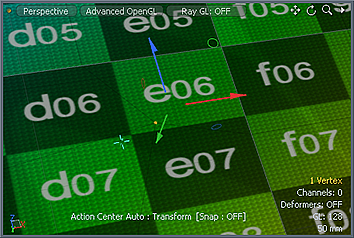
| 2. | Click in the 3D viewport to display the transform handles and the Radial Falloff. |
| 3. | Adjust the handles by clicking and dragging in the viewport. |
Modo attenuates the amount of movement to neighboring items based on the size of the Radial Falloff. This produces a soft, organic deformation. You can define the Radial Falloff interactively.
The following options are available for Soft Move:
|
Transform |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Position X/Y/Z |
Applies specific offset distances (calculated from the position the object was in when you activated the tool). When adjusting an object interactively in the viewport, the Position values display the current offset distance. |
|||
|
Pivot |
Disabled for the Soft Move tool. |
|||
|
Gimbal |
Disabled for the Soft Move tool. |
|||
|
Child Compensate |
(Only available in Items mode) When enabled, ignores any transform values for child items. When disabled, passes along transform values to any child items of the current selection. |
|||
|
Slip UVs |
(Only available in Component modes) When enabled, edits applied to the geometry do not change the existing UV map. UV values are generally fixed to specific vertices; therefore, further edits to the geometry may warp, deform, or otherwise distort the UV values in undesirable ways. When this happens, you may need to adjust the map or to redo it altogether. To avoid this undesirable result, you enable Slip UVs so as to not disturb any existing UV mapping applied to the geometry.
|
|||
|
Morph |
(Only available in Component modes) Determines how Modo treats stored morphing information when applying transforms (such as the Move, Rotate, or Scale transforms) to geometry. There are three options for controlling how Modo deals with the morph map vertex data when applying any transforms. • None - Transforms selected (visible) morphs independent of their source, but does not affect unselected morph data.
• Transform - Transforms morph data along with the base mesh.
• Keep Positions - Converts morph data into an absolute morph map. All vertices retain their pre-transformed positions. Note: In previous versions of Modo, to transform a morph along with its base, you needed to select it in the Vertex Map list. If you didn't, when Modo recalled the relative morph map data, it would produce distorted, undesirable results; therefore, it was easy to accidentally spoil a model. To remedy this problem, current versions of Modo have three options to deal with the morph map vertex data. |
|||
|
Snapping |
See the Applying Snapping topic for details about this feature. |
|||
|
Radial Falloff |
||||
|
Center X/Y/Z |
Defines the center of influence, which is where the strength of the falloff is the greatest (100%). The strength of the falloff attenuates toward the outer bounds of the spherical volume. The area outside the volume receives no tool influence (0%). |
|||
|
Size X/Y/Z |
Defines the radius of a perfect circle from the Center position and determines the outer area of the falloff where there is no effect. |
|||
|
Auto Size |
Adjusts the falloff's Center and Size values automatically to match the bounding box of the current selection. |
|||
|
Shape Preset |
Controls the strength of the falloff's influence along the extent by using a shape preset. • Linear - Attenuates the falloff evenly across its range.
• Ease-In - Strengthens the falloff toward the start position.
• Ease-Out - Strengthens the falloff toward the end position.
• Smooth - Strengthens the falloff toward the center of the falloff.
• Custom - Fine tunes the strength of the falloff based on the In and Out values. |
|||
|
In/Out |
Determines the strength of the falloff nearer to the start or end position. |
|||
|
Mix Mode |
Defines how each falloff interacts with the other(s) in instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (by using Add in the Falloff menu). |
|||