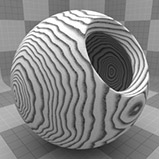
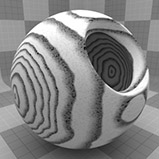
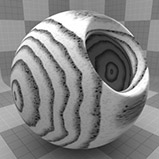
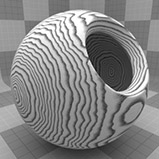
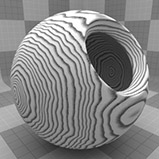
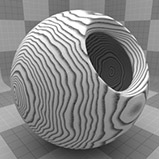
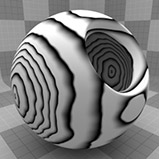
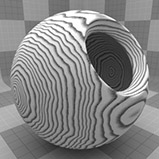
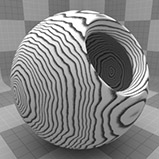
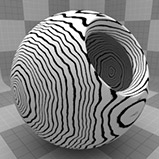
Wood Procedural

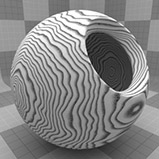
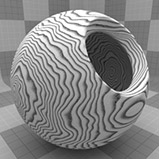
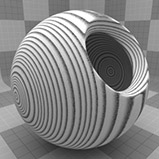
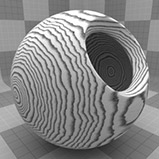
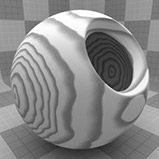
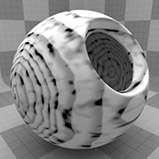
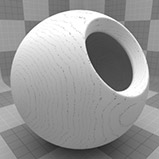
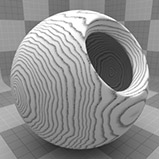
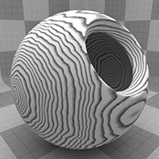
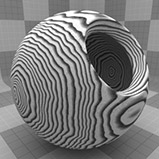
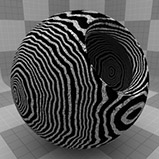
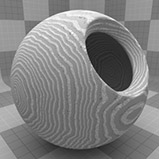
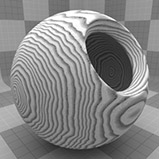
The Wood procedural texture is a powerful texture that is designed to simulate wood grain. Of course, you can use the Wood texture for effects other than wood. Modo creates procedural textures mathematically at render time and, therefore, they have no fixed resolution. You can magnify procedural textures almost infinitely with no visual loss in detail. This texture has rings, which are distorted by waves and a layer of noise, that simulate wood grain.
Note: For information about adding and working with Shader Tree item layers, see the Shader Tree topic.
Layer Properties
>
|
Enable |
Toggles the effect of the layer on and off. This duplicates the functionality of toggling visibility in the Shader Tree. When disabled, the layer has no effect on the shading of the scene. However, Modo saves disabled layers with the scene, and they are persistent across Modo sessions. |
|
Invert |
Inverts the colors (RGB values) for the layer to produce a negative effect. |
|
Blend Mode |
Affects the blending between different layers of the same effect type. With this, you can stack several layers for different effects. For more about blending, see Layer Blend Modes. |
|
Opacity |
Changes the transparency of the current layer. If there are layers below this layer in the Shader Tree, reducing this value increasingly reveals the lower layers. Reducing the value always dims the effect of the layer. |
|
Locator |
Sets the association for the Texture Locator. Most texture layers have a Texture Locator that Modo automatically creates in the Item List. This defines the mapping of the texture (how Modo applies the texture) to the surface. You can specify alternate locators, but this is normally not required. Although you may want multiple texture items to share a single locator. |
|
Projection Type |
Defines how a texture/material is applied to a 3D surface. Types vary significantly in their effects. For a guide to each Projection Type see Projection Type Samples. |
|
Projection Axis |
The texture/material is projected down this axis. This applies to Planar, Cylindrical, Spherical, Cubic, Box, and, Light Probe projection types. |
Wood Properties
|
Wood |
|
|
Ring Value |
Determines the magnitude of the texture where the ring pattern occurs. This value ramps to the Filler Value. This is only available when the texture layer is set to a non-color attribute. |
|
Ring Color |
Specifies the RGB color value of the texture where the ring pattern occurs. This color ramps to the Filler Color. This is only available when the texture layer is set to an effect that requires color. |
|
Alpha |
The opacity of the Ring Color. Note: You can adjust the Alpha value using the Color Picker. |
|
Filler Value |
Determines the magnitude of the texture where the filler pattern occurs. This is only available when the texture layer is set to a non-color attribute. |
|
Filler Color |
Specifies the RGB color value of the texture where the filler pattern occurs. This is only available when the texture layer is set to an effect that requires color. |
|
Alpha |
Determines how transparent the Filler Color is. |
|
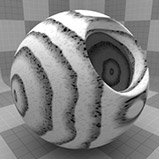
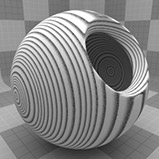
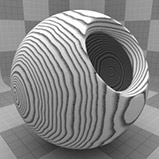
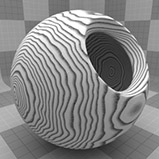
Ring Scale |
Determines the size of the rings in the texture. Click to view examples of various Ring Scale settings. |
|
Waviness |
Controls the amount of distortion that Modo applies to the rings in the texture. Click to view examples of various Waviness settings. |
|
Wave Scale |
Sets the size of the wave distortion that deforms the rings in the texture. Click to view examples of various Wave Scale settings. |
|
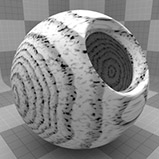
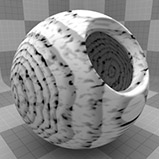
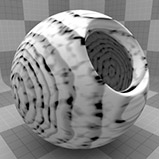
Graininess |
Determines how visible the grain effect is when it is combined with the ring texture. Decreasing this value creates a more subtle grain appearance. Click to view examples of various Graininess settings. |
|
Grain Scale |
Determines how large the grain spots are. Click to view examples of various Grain Scale settings. |
|
Bias |
Determines whether the texture favors the Ring Color (or Ring Value) over the Filler Color (or Filler Value). Increasing this value causes the texture to favor the Ring Color (or Ring Value); decreasing the value favors the Filler Color (or Filler Value). Click to view examples of various Bias settings. |
|
Gain |
Determines the falloff effect for the texture. This is similar to a gamma control that affects the falloff of the gradient ramp between the ring and filler values. Setting the Gain to 100% creates a sharp falloff effect; setting the value to 0% creates a plateau around the value (or color mid-point) with a sharp falloff at either gradient extreme. Click to view examples of various Gain settings. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ring Scale 0.1% |
Ring Scale 25% |
Ring Scale 50% |
Ring Scale 75% |
Ring Scale 100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Waviness 0% |
Waviness 25% |
Waviness 50% |
Waviness 75% |
Waviness 100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wave Scale 0.1% |
Wave Scale 25% |
Wave Scale 50% |
Wave Scale 75% |
Wave Scale 100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Graininess 0% |
Graininess 25% |
Graininess 50% |
Graininess 75% |
Graininess 100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grain Scale 0.1% |
Grain Scale 25% |
Grain Scale 50% |
Grain Scale 75% |
Grain Scale 100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bias 0% |
Bias 25% |
Bias 50% |
Bias 75% |
Bias 100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gain 0% |
Gain 25% |
Gain 50% |
Gain 75% |
Gain 100% |