Search is based on keyword.
Ex: "Procedures"
Do not search with natural language
Ex: "How do I write a new procedure?"
Contact Support
Localizing Files for Better Performance
You may find that sometimes loading files from a remote server slows down processing. Nuke has the facility to cache files locally, either individually or by setting an automatically localized folder (NUKE_TEMP_DIR/localize, by default), to help guarantee playback stability. Local caching is controlled initially in the Preferences dialog, then on a file-by-file basis.
Setting Localization Preferences
| 1. | Press Shift+S to open the Preferences dialog and navigate to Performance > Localization. |
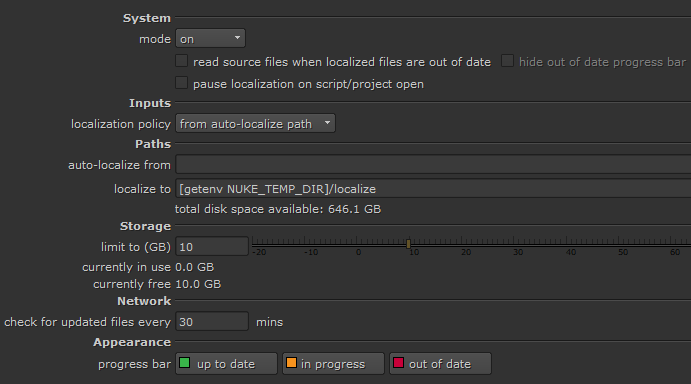
| 2. | Set the required localization mode: |
• on - checks for updates to source clips for all localization policies, and localizes those files set to On or From auto-localize path automatically. On demand source clips must always be localized manually.
• manual - checks for updates to localized source clips and prompts you to update them manually. Only those with the policy set to off are not updated.
• off - no source clips are localized, regardless of the their localization policy.
Note: The current localization mode is displayed in the status bar at the bottom-right of the interface.
| 3. | Set the default localization policy for new Read nodes using the dropdown: |
Note: The localization policy for existing Read nodes in the script must be set individually. See Managing Localization for more information.
• on - always localize Read nodes with this policy.
• from auto-localize path - localize these Read nodes automatically if they reside in the auto-localize from directory.
• on demand - only localize these Read nodes when you manually update them. See Updating On Demand Clips for more information.
• off - never localize these Read nodes.
| 4. | Enter a file path for auto-localize from, if required. |
Any files that reside in this directory are automatically cached when brought into Nuke, providing that the Read node'slocalization policy is set to from auto-localize path.
Note: Localization in both the timeline and Node Graph is paused during compositing Viewer playback so that performance is not affected.
| 5. | Enter a file path for localize to. Leaving this field as the default creates a sub-directory in the Temp Directory as the local cache. |
Note: On Windows, files saved to the localize to directory replace \\ (double back slashes) and : (colon drive signifiers) with underscores so that the file path works as expected between operating systems. For example:
\\windowspath\to\my\network\file.dpx is saved as __windowspath\to\my\network\file.dpx
t:\my\network\path\file.dpx is saved as t_\my\network\path\file.dpx
| 6. | Enter a value for limit to (GB) to control how much disk space is available in the cache directory. |
Note: Negative values in this field reserve the specified amount of space at all times. For example, -2 stops 2 GB of memory being used for caching.
| 7. | You can specify the time interval (in minutes) before localized files are checked for updates using the check for updated files every ## mins control. |
The default setting checks for new versions of files every 30 minutes, but you can set this control to any value. Any Read nodes that have changed since the last update check are flagged red in the Node Graph.
Tip: You can change the default localization indicators using the Appearance controls.

If read source files when localized files are out of date is enabled, Read nodes referencing cached files that have changed since they were localized revert to reading the source files. Read nodes that are reading from the source files are marked with a striped red bar on the Read node.
Enabling hide out of date progress bar hides the localization state of out of date files so that the Read node appears the same as regular Read nodes.
Note: The out of date localized files are not discarded, disabling read source files when localized files are out of date picks up the out of date files instead of reading the source files.
Managing Localization
As well as the overall Preferences for when new Read nodes should be localized, you can set localization on a file-by-file basis. The localization policy for any existing Read nodes in your project must be managed individually.
Tip: If you find that localization is slow to copy files, you can increase the number of threads that Nuke uses to process jobs. Set the NUKE_LOCALIZATION_NUMWATCHERS environment variable to the number of threads you want to use. See Environment Variables for more information.
| 1. | Open the Read or ReadGeo node's Properties panel. |
| 2. | Set the localization policy dropdown to one of the following options: |
• On - the files are localized, regardless of location, as long as the limit to (GB) limit is not breached.
• From auto-localize path - the files are localized if they reside in the auto-localize from directory, as long as the limit to (GB) limit is not breached.
• On Demand - the files are only localized when you update them manually. See <XREF> for more information.
• Off - the files are never localized, regardless of location.
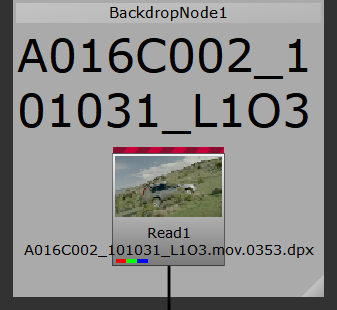
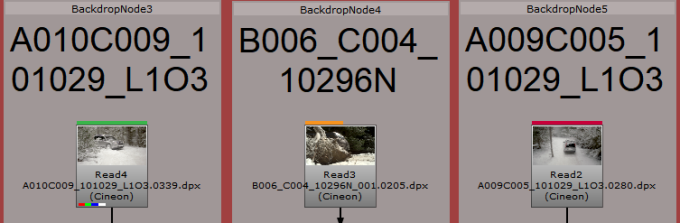
As Read nodes are localized, an amber progress bar displays in the thumbnail. Fully cached clips are marked with a green bar at the top of the thumbnail and out-of-date clips are marked in red.
Note: Container formats, such as .mov and .r3d, do not display progress bars during localization. The Read node only shows the green indicator once the entire file is localized successfully.
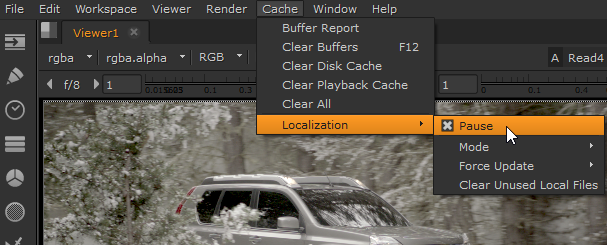
| 3. | If you need to pause localization temporarily, navigate to Cache > Localization and select Pause. |
| 4. | If you find that your cache is filling up regularly, you can: |
• increase the amount of available space for localization by raising the limit to (GB) preference,
• navigate to Cache > Localization > Delete Unused Local Files (see Clearing Localized Files), or
• manually clear files from the cache directory in NUKE_TEMP_DIR/localize, by default.
| 5. | You can force Nuke to check for updated source files, rather than waiting for the check for updated files every interval to expire, by selecting Force Update for All files, just Selected Read nodes, or On Demand only. |
Note: Each file has its own update time, which is reset whenever the source files are checked.
The following table is a quick reference guide to when and how Read nodes are localized, where:
• green - Read nodes are localized automatically.
• amber - Read nodes are localized when updated manually.
• red - Read nodes are not localized.
|
System Preference |
Read Node Preference |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
on |
auto-path |
on demand |
off |
|
|
on |
|
|
|
|
|
manual |
|
|
|
|
|
off |
|
|
|
|
Updating On Demand Clips
Read nodes with their localization policy set to on demand are polled to check for updates at the interval set in the Preferences. If the file has changed, the Read node is marked with a red bar to show it is out of date.
To update a single on demand Read node:
| 1. | Double-click the Read node in the Node Graph to display its Properties. |
| 2. | Click Update. |
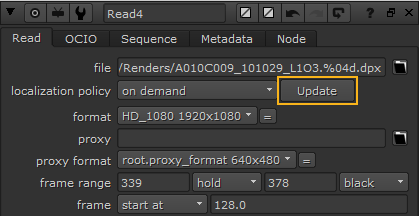
Note: If a Read node's localization policy is set to on demand and it hasn't been localized previously, clicking the Update button localizes the file.
The local copy of the files is updated from the remote source files.
To update all on demand Read nodes:
| 1. | Navigate to Localization > Force Update. |
| 2. | Click On demand only. |

The local copy of all on demand Read nodes is updated from the remote source files.
Clearing Localized Files
Localizing a large amount of files can fill up the localization cache quite quickly if you leave the limit to (GB) preference at the default 10 GB. When the cache runs out of space, a Failed to Localize File dialog displays and localization pauses.
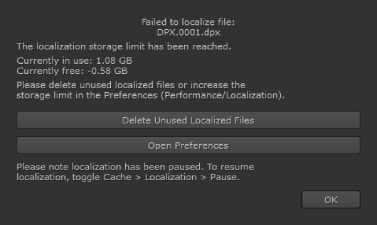
You can delete localized files by clicking Delete Unused Local Files (or by navigating to Cache > Localization > Clear Unused Local Files). Nuke displays a dialog containing all the files that are marked for delete.
Tip: You can also open the Preferences from this dialog to adjust the localization behavior, such as increasing the limit to (GB) preference.
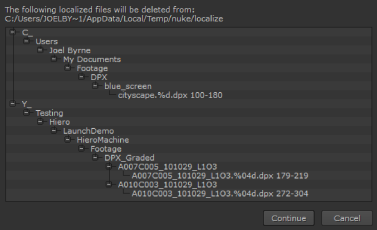
Click Continue to delete the localized files or Cancel to keep the cached files.