Manipulating Geometry Data
Using GeoDisplace
You can use displacement to quickly add detail to geometry. The GeoDisplace node moves each vertex along the normal to the surface according to channels in a texture map connected to the displace input.
For example, you can create a bumpy surface on a GeoCard:
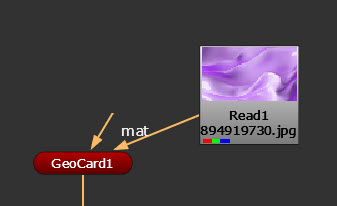
| 1. | Add geometry to your scene using GeoCard node. |
| 2. | Connect a texture image to your GeoCard using the Read node and its mat input. |
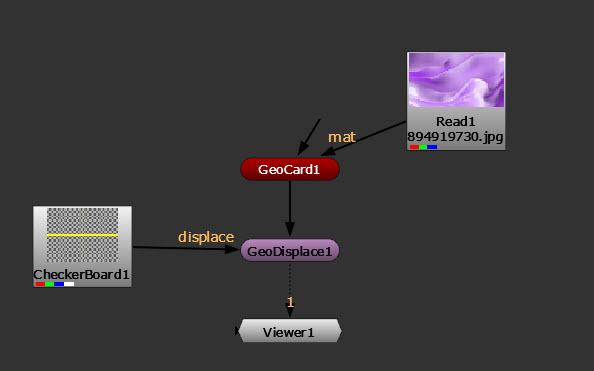
| 3. | Add a GeoDisplace node downstream of your GeoCard node. |
| 4. | Add a CheckerBoard node connected to the GeoDisplace nodes’ displace input. |
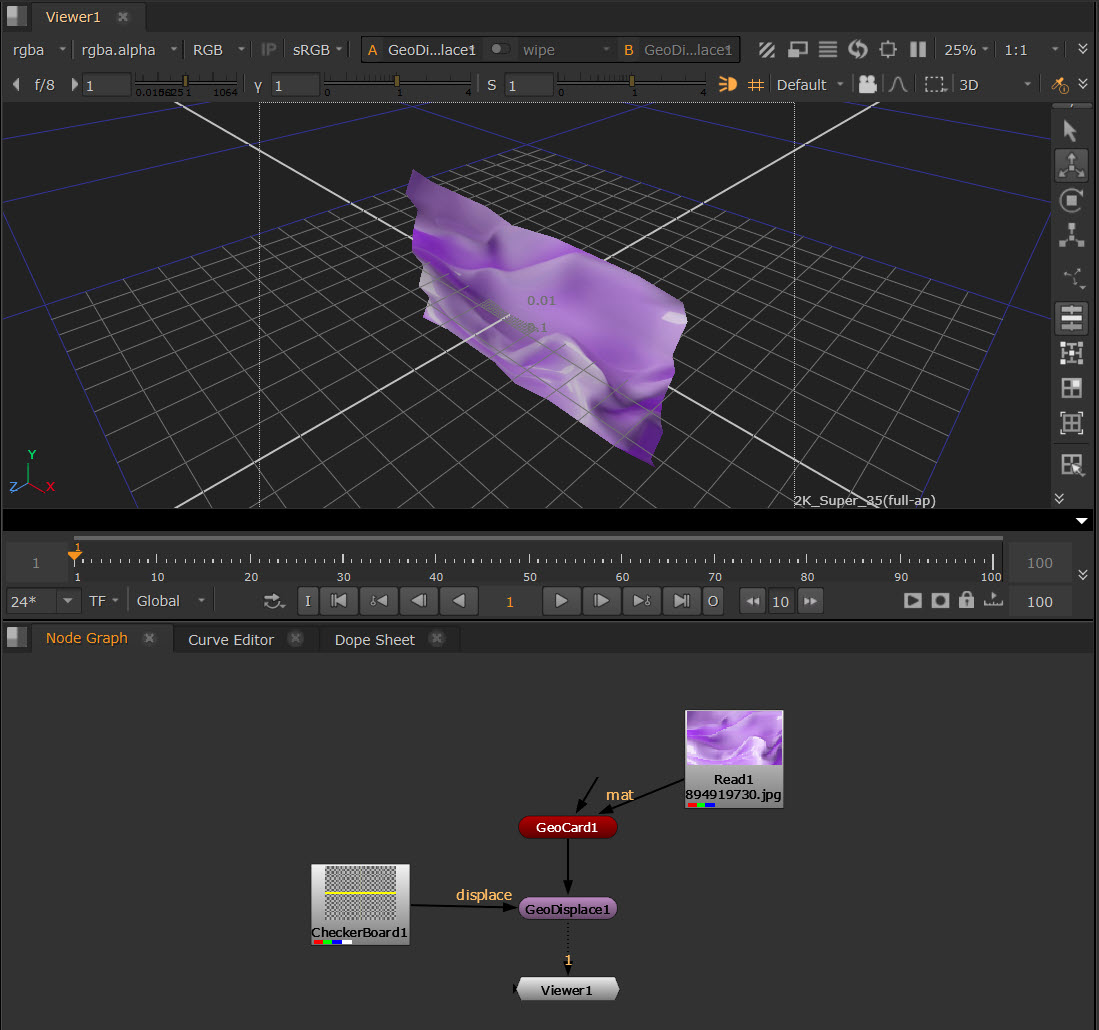
| 5. | Now you can view the displaced geometry in the Viewer and edit the GeoDisplace node Properties to refine the effect. See GeoDisplace in the Node Reference Guide to learn about the controls. |
Using GeoNoise
The GeoNoise node warps meshes using a Perlin noise function that creates seemingly random noise. For example, you could use this node to generate terrain from a card.
Using the same example as the above, this time we are using GeoNoise downstream of the GeoCard.
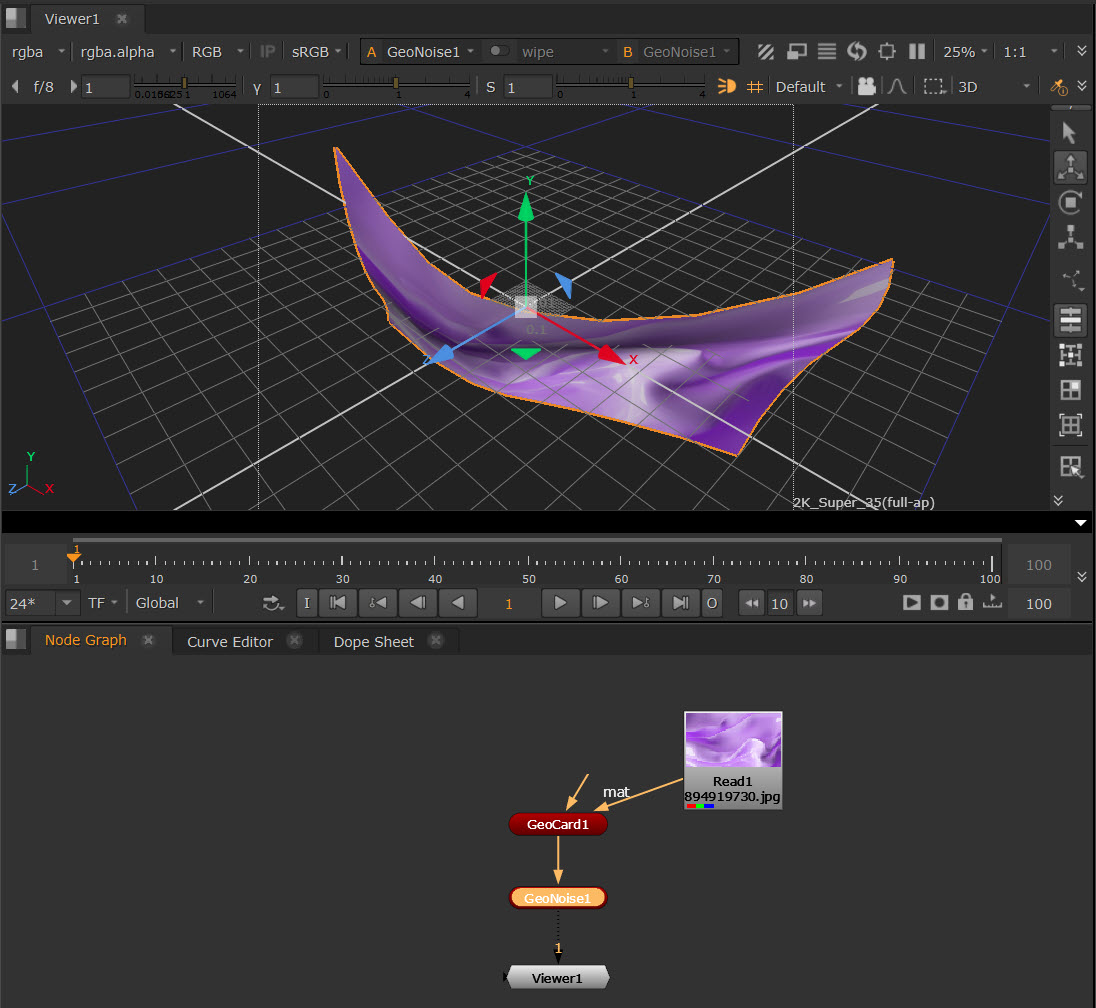
• You can use the transformation handles in the Viewer to refine its shape.
• Edit the knobs in the Node Properties, such as Noise Type and Time, to adjust the effect. See GeoNoise in the Node Reference Guide to learn about the controls.
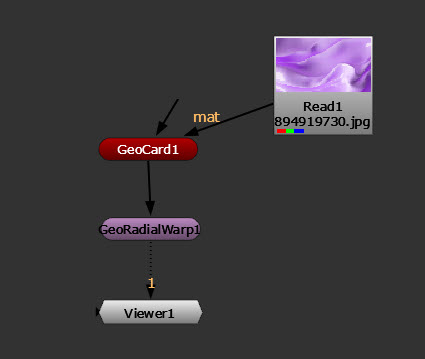
Using GeoRadial Warp
The GeoRadialWarp node warps meshes away from a center point.
| 1. | Connect a GeoRadialWarp node downstream of your geometry. |
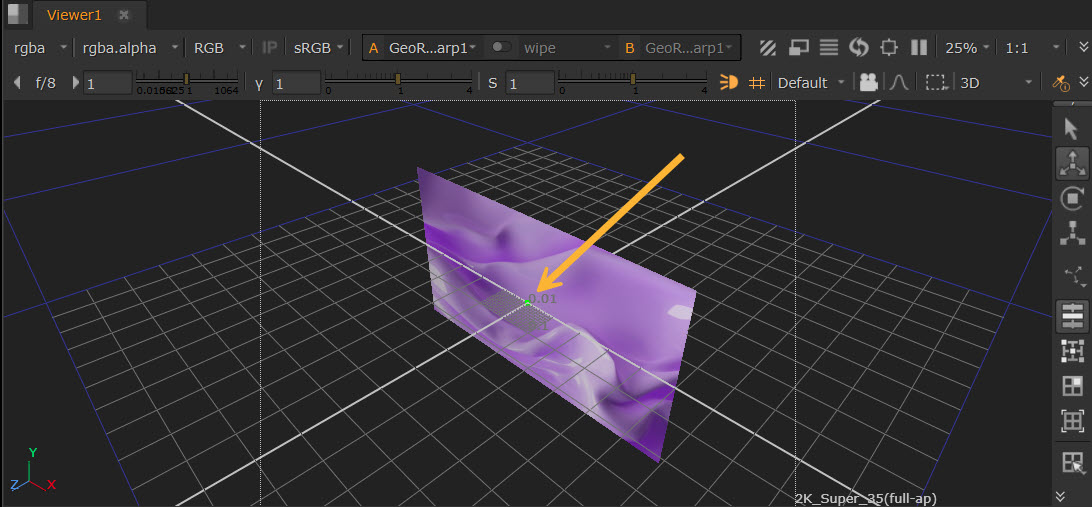
| 2. | You can use the Rotation Center control in the Properties to set the location of the warp center. Or you can drag the center widget around in the Viewer as below. The center widget is the green dot here. |
Using GeoTrilinearWarp
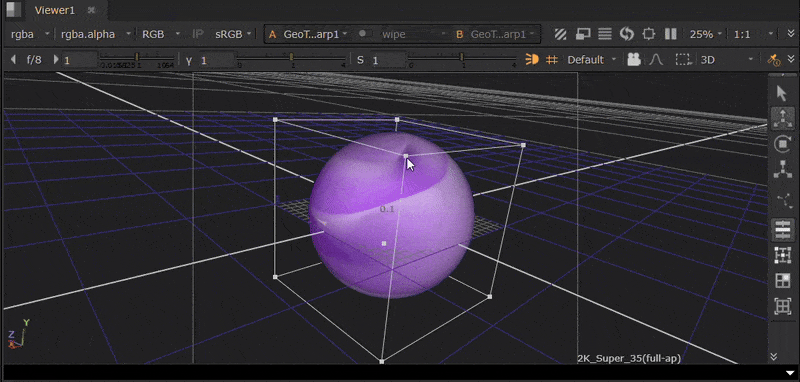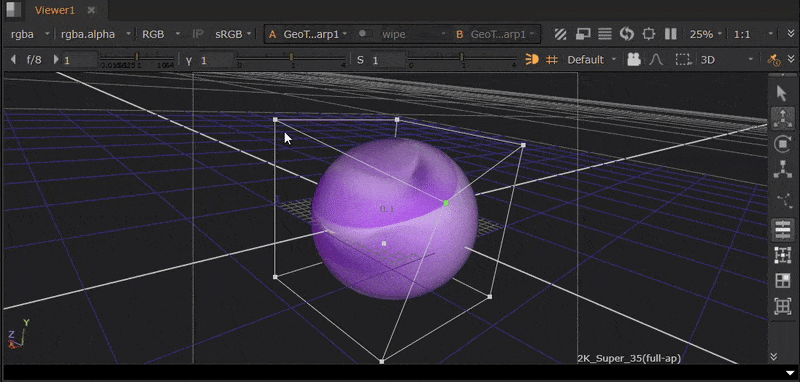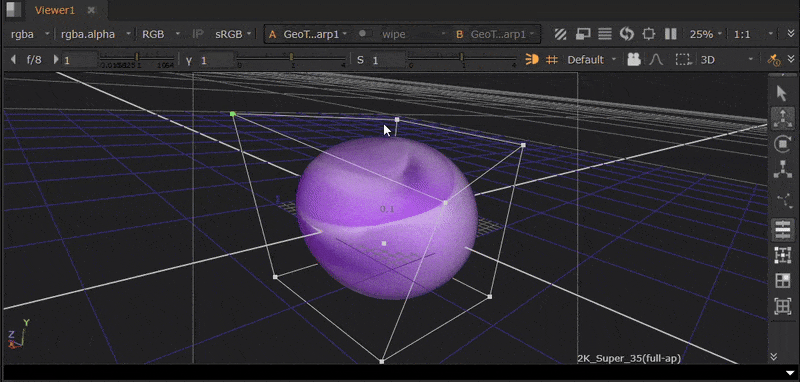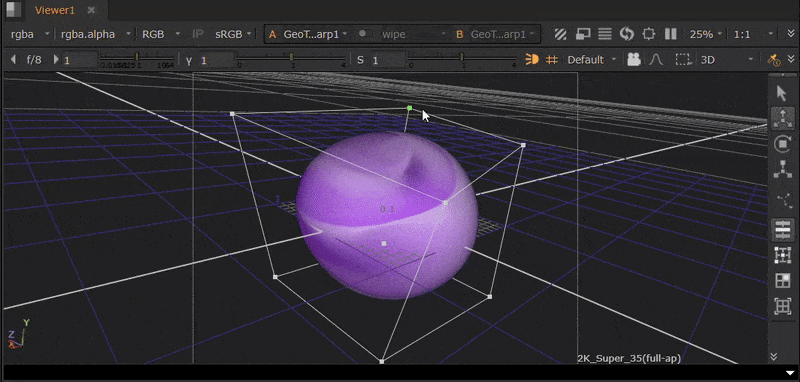
The GeoTrilinearWarp node warps meshes by moving the corners of its bounding box separately to create the warp.
For this example, we will use a GeoSphere node so that the bounding box is visibly distinct.
| 1. | Connect a GeoTrilinearWarp node downstream of your geometry. The bounding box will then be visible in the Viewer. |
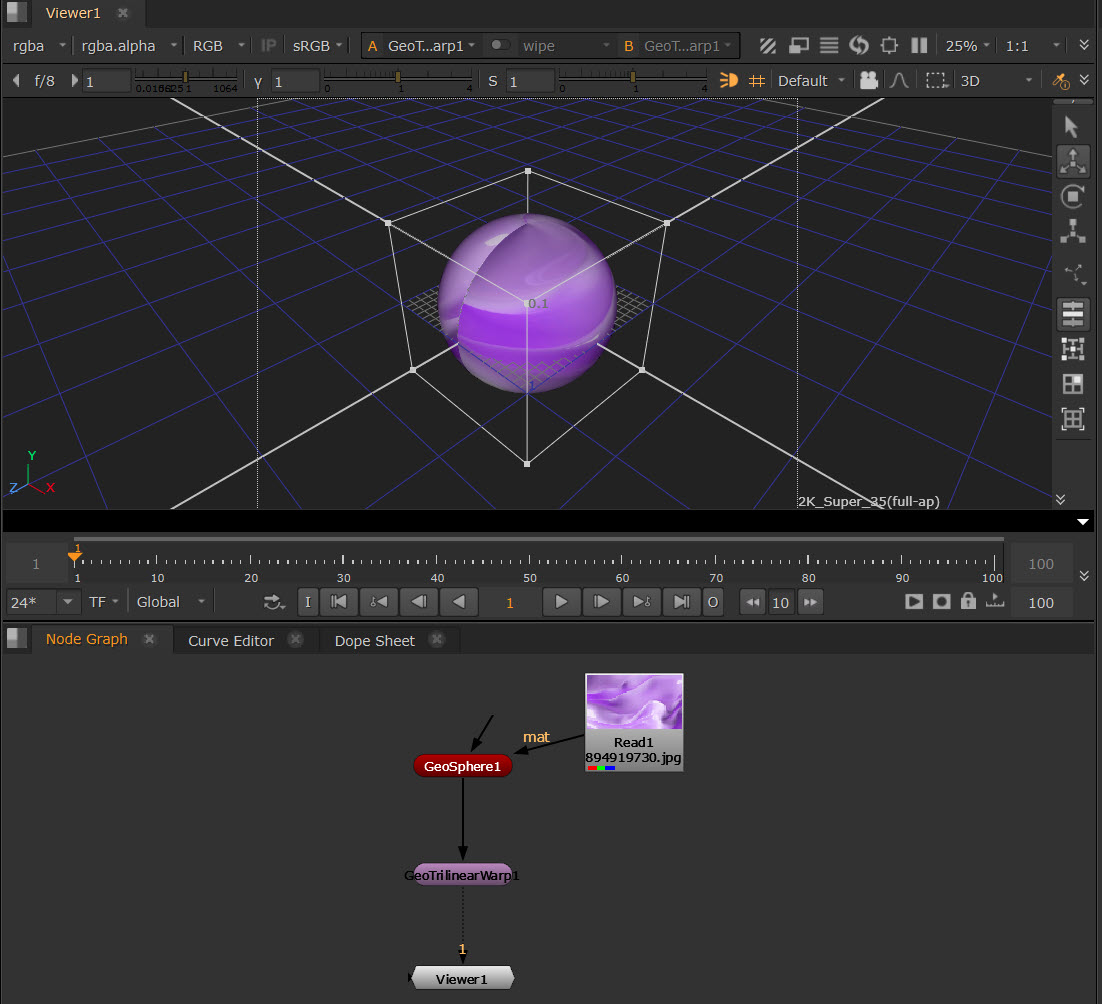
| 2. | Click and drag the corners of the bounding box in the Viewer to warp the mesh. |