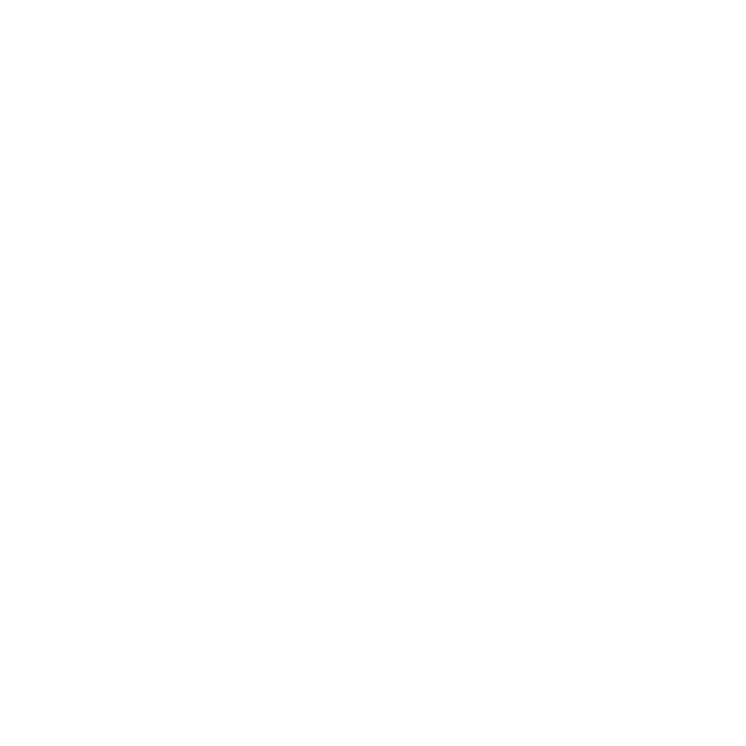
Project Settings
A good place to start work is by defining default Project Settings before importing sequences, particularly in the case of EDLs as they may not contain frame rate information. Project Settings only apply to the current project and override Preferences settings.
Note: You can modify Project Settings later on, for example, when you’re ingesting media.
Tip: You can create templates for Hiero or Nuke Studio by creating .hrox files in the .nuke/Templates folder. This helps if you have particular Project Settings, such as Colorspaces, footage, and folder structures, that you wish to reuse across multiple projects. See Creating and Using Project Templates.
To define Project Settings:
| 1. | Navigate to Project > Edit Settings. |
The Project Settings dialog displays.
| 2. | Click the General sub-menu to set the project Name. |
| 3. | Enter a Project Directory if required. This is the location of the .hrox project file and can be used as the root of the project if you want to use relative paths to source clips. See About Clips and Shots for more information. |
If you want this setting to apply to all new projects, use the Preferences > Project Defaults > General panel settings.
Tip: Click Hrox Directory to automatically enter an expression that evaluates to the .hrox location.
| 4. | Set the Poster Frame used by Project bin clips or use the default First frame. See Setting Poster Frames for more information. |
| 5. | Click the Sequence sub-menu to set the default Output Resolution, Frame Rate, and Start Timecode for new timelines in the current project, and set clip formatting when new clips are added to the timeline. |
| 6. | Click the Views sub-menu to set up multi-view or stereo projects. See Stereoscopic and Multi-View Projects for more information. |
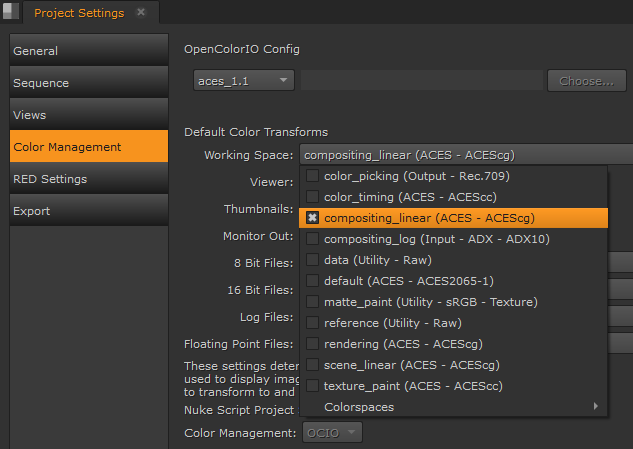
| 7. | Click the Color Management sub-menu to manage the display and file colorspaces for this project. |
See Color Management Settings for more information.
Tip: Use the options in Preferences > Project Defaults > Color Management to apply them to all new projects.
| 8. | Click the RED Settings sub-menu to define the Default Video Decode Mode for new R3D files in the current project. This setting overrides the Preferences > Behaviors > File Handling > default red clip video decode mode control for existing projects. See Preferences for more information. |
Note: Changing this setting does not change the decode setting for R3D media that has already been imported.
The dropdown contains a sliding resolution scale from FullPremium to SixteenthGood, but bear in mind that higher resolutions are slower to decode.
| 9. | Lastly, click the Export/Roundtrip sub-menu to select: |
• External Media Track Name - sets the default name of the track created when exported media is brought back into Hiero.
• Export Directory - sets whether the Project Directory, if specified, or a custom directory is used for exports. If no Project Directory is specified, the project root in the Export dialog is used.
If you want this setting to apply to all new projects, use the Preferences > Project Defaults > General panel settings.
• Custom Export Directory - when Export Directory is set to custom, enter the required custom export directory.
• Shot Preset - sets the default preset to use when exporting.
Color Management Settings
Hiero uses OpenColorIO for color management. All of the colorspaces in Hiero, whether those shipped with the application or custom colorspaces are defined in OCIO config files.
Depending on the OCIO config file that you are working with, there are a number of colorspace options and roles (aliases to colorspaces) that you can set in Hiero. There are also default options, which change depending on what file type you are working with. When the default option is selected, the colorspace that Hiero has set for it is listed in brackets.
Tip: Use the options in Preferences > Project Defaults > Color Management to apply them to all new projects.
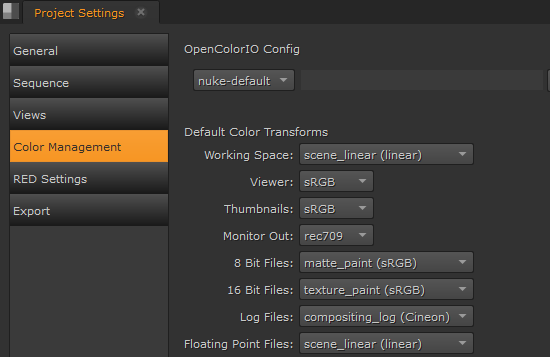
| 1. | Set the OpenColorIO Config you want to use for this project. |
Hiero ships with a number of default configurations, but you can:
• use a custom OCIO config file by selecting custom from the OpenColorIO Config dropdown and then entering the file path, or
• add your own config to your .nuke file. See Adding OCIO Configurations for more information.
Changing the configuration updates the Default Color Transforms accordingly. If the selected configuration is invalid for certain transforms, a warning displays. For example, if you choose the shipped iff configuration, the 8-bit and 16-bit transforms are not compatible.
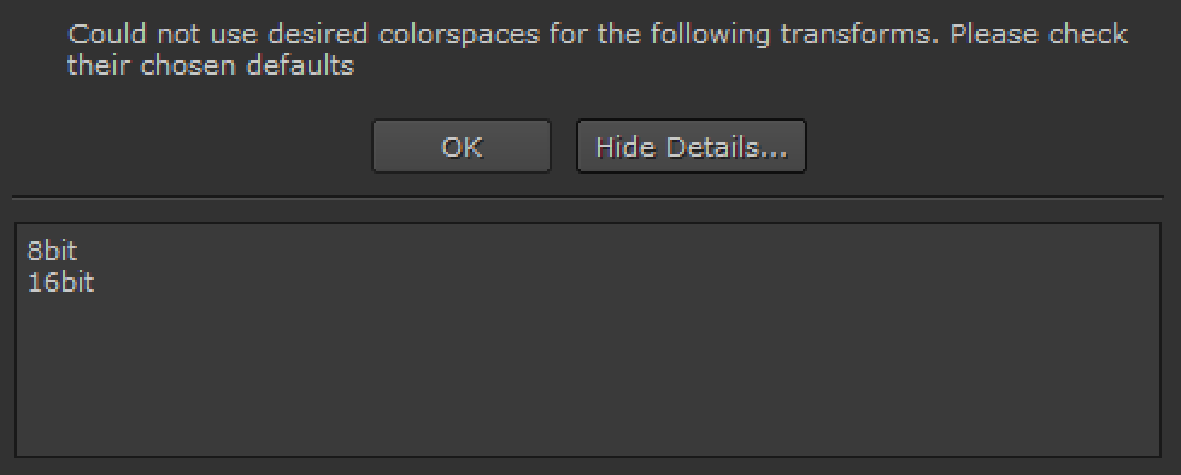
In this case, the non-compatible transforms are set to the raw colorspace.
| 2. | The Working Space transform determines what colorspace files should be converted to, on import, and from, during export - it's the colorspace used by Hiero under the hood. |
Note: In earlier releases of Hiero, this colorspace was hidden because linear was always chosen as the Working Space. You may find that some operations work better in colorspaces other than linear. For example, some transforms work better in the CLog colorspace.
| 3. | You can use Default Color Transforms dropdown menus to override how clips in the Viewer, thumbnails, and so on are converted to and from the Working Space. |
| 4. | The Nuke Script Project Settings dropdown determines whether Hiero uses the LUTs read from the configuration specified or the Nuke native LUTs during export. Selecting OCIO makes the relevant OCIO LUTs available to the Read and Write nodes in scripts on a per project basis. |
All configurations except nuke-default automatically switch this control to OCIO.
When the Nuke is selected, Reads and Writes work the same as in previous versions of Hiero, with no integrated OCIO transforms. When OCIO is selected:
• Reads and Writes use OCIO transforms, with no Hiero built-in LUTs applied to the image.
• Read and Write colorspace controls are populated with the list of colorspaces defined in your currently selected OCIO config.
• The default LUT settings dropdowns are also populated with the list of colorspaces or display transforms defined in your OCIO config. The default value for each menu match the defaults in a Hiero project with the same config. These defaults can be overridden using Python callbacks. See the following path for the default implementation that ships with Hiero:
<install_dir>/plugins/nuke/colorspaces.py
• The working space dropdown allows you to change the colorspace that Nuke uses internally for its image processing. This automatically sets the in colorspace of Write nodes and Viewer Processes, and the out colorspace for Read nodes. This defaults to the scene linear role defined in your OCIO config.
• Hiero-created comps no longer contain automatically injected OCIOColorspace nodes. Instead, OCIO Color Management is automatically set in the comp’s Project Settings, and the correct OCIO colorspace is set directly into the Read and Write nodes.
Adding OCIO Configurations
You can add your own OCIO configurations to Hiero as they become available, such as new versions of ACES. You can also add legacy configs for backward compatibility.
| 1. | Navigate to the location of your .nuke file as shown by platform. You may have to create a .nuke folder if it doesn't exist. |
• Linux: /users/login name/.nuke
• Mac: /Users/login name/.nuke
• Windows: ~\.nuke
Note: On Windows, the .nuke folder can be found under the directory pointed to by the HOME environment variable. If this variable is not set (which is common), the .nuke directory is under the folder specified by the USERPROFILE environment variable - which is generally of the form drive letter:\Documents and Settings\login name\ or drive letter:\Users\login name\
To find out if the HOME and USERPROFILE environment variables are set and where they are pointing at, enter %HOME% or %USERPROFILE% into the address bar in Windows Explorer. If the environment variable is set, the folder it’s pointing at is opened.
| 2. | Recreate the following structure within your .nuke folder: |
~/plugins/OCIOConfigs/configs/<config name>
| 3. | Copy the contents of the config into the config name named folder. There should be a luts folder and .ocio file at the bare minimum. |
| 4. | If Hiero is already running, relaunch the application to apply the change. |
| 5. | You can now select your configuration from the Project Settings > Color Management > OpenColorIO Config dropdown. |
Adding OCIO Roles
OCIO roles allow you to set custom role names for different colorspaces to make it easier for artists to instinctively know which LUT to use for any shot. For instance, if an element is coming from your matte painting department and should always be brought into Nuke as sRGB, you can create a matte painting role, which is associated with the sRGB colorspace for your artist to select.
OCIO roles are the primary method for selecting colorspaces. All of the colorspaces in the OCIO config file are still accessible, but they have been grouped together into a Colorspaces menu under the roles.
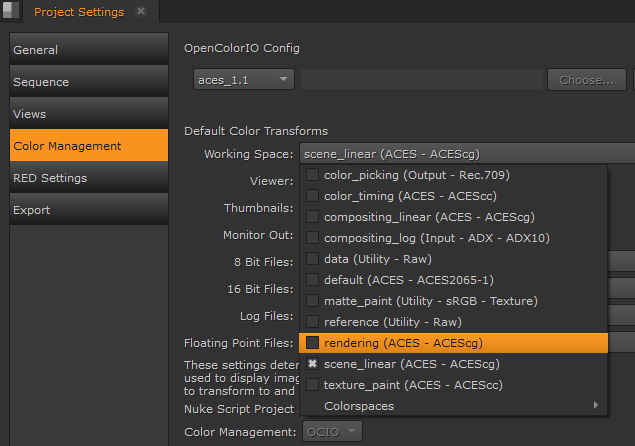
OCIO roles are stored in config files, some of which ship with Nuke in the following directory:
<install_dir>/plugins/OCIOConfigs/configs/
For example, the aces_1.1 config file includes the following roles:
roles:
color_picking: Output - Rec.709
matte_paint: Utility - sRGB - Texture
scene_linear: ACES - ACEScg
texture_paint: ACES - ACEScc
The first part of the role defines the name of the role displayed in Nuke and second part describes colorspace family and name. The family and name define which colorspace is associated with the role. For example:
- !<ColorSpace>
name: ACES - ACEScg
family: ACES
equalitygroup: ""
bitdepth: 32f
description: |
The ACEScg color space
ACES Transform ID : ACEScsc.ACEScg_to_ACES
isdata: false
allocation: lg2
allocationvars: [-8, 5, 0.00390625]
to_reference: !<MatrixTransform> {matrix: [0.695452, 0.140679, 0.163869, 0, 0.0447946, 0.859671, 0.0955343, 0,
-0.00552588, 0.00402521, 1.0015, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]}
Note: The LUT specified must exist in the luts directory in the same location as config file for the role to pick up the required colorspace.
You can edit these files to add roles or create your own custom config and then point Nuke to the file using the Project Settings > Color Management > OpenColorIO Config field.
To add a role to a config file:
| 1. | Open the required config file or create a custom config. |
| 2. | Enter the role , family, and name of the role under the roles: line. For example: |
compositing_linear: ACES - ACEScg
| 3. | Save the file and open Nuke. |
| 4. | Open the Project Settings and click the Color Management tab. |
| 5. | You can now pick your role from the default LUT settings. For example, you can set the working space to compositing_linear if you want to work in the ACEScg colorspace. |
Define Color Space Mappings Using OCIO Aliases
Hiero supports the use of aliases in an OCIO config and checks these when attempting to set the input transform for a given image or sequence. The aliases feature in OCIO allows config authors to define a set of alternate names for a color space, which can then be used in place of the primary color space name. For example, it may be useful to define a more suitable name for file paths, or a color space name might have changed between versions of a config, so it may be necessary to add an alias for the older version of the name for backwards compatibility. Additionally if an application tries to set defaults based on a specific name then aliases can be used to ensure a suitable color space is found.
Below is part of a ColorSpace definition from an ACES 1.3 OCIO config.
- !<ColorSpace>
name: ARRI LogC3 (EI800)
aliases: [arri_logc3_ei800, Input - ARRI - V3 LogC (EI800) - Wide Gamut, logc3ei800_alexawide]
family: Input/ARRI
equalitygroup: ""
bitdepth: 32f
description: |
Convert ARRI LogC3 (EI800) to ACES2065-1
Here you can see the name: attribute is defined as ARRI LogC3 (EI800). This is the primary name for the color space.
Directly below is the aliases: attribute. This is where the alternate names are defined, in this case:
-
arri_logc3_ei800
-
Input - ARRI - V3 LogC (EI800) - Wide Gamut
-
Logc3ei800_alexawide
The first and third aliases (arri_logc3_ei800 and logc3ei800_alexawide) could be an example of a suitable name for including in a file path.
The second alias (Input - ARRI - V3 LogC (EI800) - Wide Gamut) is the name that was used for this color space in ACES 1.2. This is useful when switching from an ACES 1.2 config to ACES 1.3. The Hiero script will likely reference the older name but the alias means the input transform should be set correctly without any user intervention required.
Adding an alias to a color space in an OCIO config can be as simple as appending it to the end of the comma separated list. For example:
- !<ColorSpace>
name: ARRI LogC3 (EI800)
aliases: [arri_logc3_ei800, Input - ARRI - V3 LogC (EI800) - Wide Gamut, logc3ei800_alexawide, AlexaV3LogC]
...
Here we’ve added the alias AlexaV3LogC. This is the color space name that Hiero looks for in the first instance when it detects an ARRI V3 LogC file.
Note: In versions of Hiero prior to 14.1 the example above would typically result in an error, because there isn’t a matching color space name in the ACES config.
From Hiero 14.1, the following aliases are included in our ACES 1.3 configs:
- Aliases (Nuke > ACES):
AlexaV3LogC > ARRI LogC3 (EI800)
ARRILogC4 > ARRI LogC4
Blackmagic Film Generation 5 > BMDFilm WideGamut Gen5
Log3G10 > Log3G10 REDWideGamutRGB
SLog3 > S-Log3 S-Gamut3
Gamma1.8 > Gamma 1.8 Rec.709 - Texture
Gamma2.2 > Gamma 2.2 Rec.709 - Texture
Gamma2.4 > Gamma 2.4 Rec.709 - Texture
The color space names that Hiero currently looks for can be seen in the nuke-default OCIO config.
For more information on aliases and authoring configs please see the official OCIO documentation.