Curvature Falloff
The Curvature falloff is defined by surface variation. Computing the same type of effect as the RT Curvature, the Curvature falloff is used to generate a falloff that attenuates across changes in surface topology, especially noticeable in areas of abrupt change or protrusion (producing an effect sometimes called an accumulation or dirt shader). Adjust the Scale value to apply the effect to concave or convex areas of the surface.
Note: The curvature is sampled based on continuous surfaces, intersecting surfaces are calculated independently. Also, surfaces with little topological variation (smooth surfaces) likely appear to produce little to no results.
|
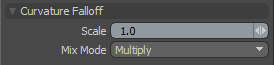
Scale |
This value determines the attenuation amount from one area to the next across topological changes. Reducing the scale tends to bias the effect toward concave areas, increasing it biases it outward from them. Setting the scale to negative values inverts the effect where the convex areas get masked by the falloff and the concave areas are affected. |
|
Mix Mode |
In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (by using the Add option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each falloff interacts with the other. |