Training Networks to Replicate Effects
The CopyCat node (NukeX and Nuke Studio only) copies sequence-specific effects, such as garbage matting, beauty repairs, or deblurring, from a small number of frames in a sequence and then trains a network using machine learning to replicate this effect on a full sequence. CopyCat outputs a trained network in a .cat file ready for the Inference node to apply your effect.
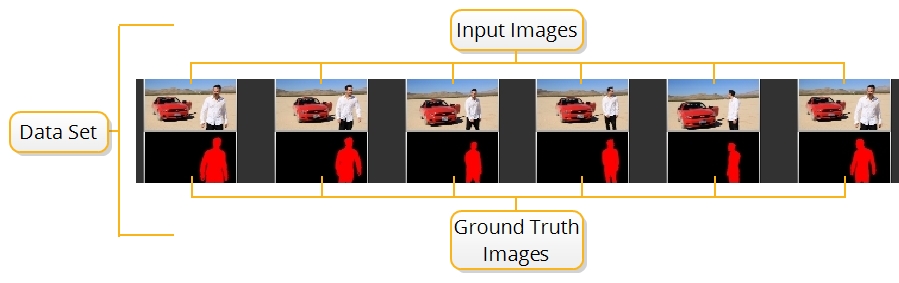
CopyCat ingests any number of image pairs called Input and Ground Truth images, which are referred to as the data set. The data set is used to train a neural network using machine learning to manipulate the Input images to replicate the Ground Truth. For example, a data set could be six frames from a sequence that you want to garbage matte and six manually roto'd masks, as shown in the image.
Note: CopyCat can ingest sequential formats, such as .jpg and .exr, and container formats, such as .mov and .mxf, but the set up is slightly different in each case. See Training Networks to Replicate Effects for more information.
As the network learns, it creates .cat files in the Data Directory, which can then be used by an Inference node to reproduce the effect learned from a few frames across the whole sequence.
Creating a Data Set for Training
Learn how to create a data set to train a network to perform a specific task.
Training and Monitoring the Network
Train your network using the data set to replicate the desired effect.
Applying and Improving the Results
Apply a trained network to a sequence using the Inference node.
AIR Nodes on Ampere GPUs
To use CopyCat, Deblur, Inference, or Upscale on Ampere GPUs in Nuke 13.0, you must set a global environment variable CUDA_CACHE_MAXSIZE to a value between 2147483648 (2 GB) and 4294967296 (4 GB). This is because the AIR plug-ins need to compile CUDA kernels in order to run on these GPUs. This process is only necessary once and should take about 30 minutes.
Note: We recommend setting the CUDA_CACHE_MAXSIZE variable globally where possible, otherwise running Nuke under a user account where it is not set may invalidate the cache.
- Set the CUDA_CACHE_MAXSIZE environment variable to an appropriate size in bytes.
- Launch Nuke.
- Add a Checkerboard and an AIR node to the Node Graph.
- Connect a Viewer to the AIR node.
See Environment Variables for more information on setting variables on different operating systems.
The kernel starts compiling and writing to the CUDA cache. A progress bar is displayed during compilation, which takes about 30 minutes.
Note: Deblur, Inference, and Upscale nodes start compiling immediately, but CopyCat only begins when you click Start Training.
The compiled kernels are stored in the CUDA cache and require about 2 GB of space, so the environment variable CUDA_CACHE_MAXSIZE must be set accordingly.
The cache is stored in different default locations by OS:
Windows
%APPDATA%/NVIDIA/ComputeCache
Linux
~/nv/ComputeCache
The location can be changed by setting the environment variable CUDA_CACHE_PATH.