Using Nuke Lights
There are four Nuke light nodes in Nuke’s New 3D System. You can create and fully edit these lights inside Nuke. Their node parameters are based on USD values to make sure they align across your pipelines, but this involves some conversion, as explained below.
| Light Node | USD Equivalent |
| DirectLight | DistantLight |
| EnvironmentLight | DomeLight |
| PointLight | SphereLight |
| SpotLight | DiskLight |
How does the conversion work?
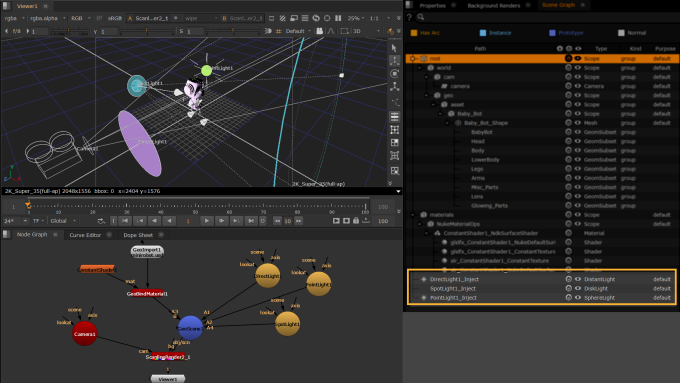
The lights are converted to the USD stage to the location in the Output Prim Path knob. You can set the prim path where the light will be created, or this is done automatically once you connect them to a GeoScene node. By default, the converted light will appear in your scene graph as {nodename}_Inject. The converted light will update dynamically when you make changes if Live Read is enabled (it is enabled by default). Turning Live Read off resets the knobs to their local state.
This process essentially converts the light from a Nuke shader light to a USD light prim for use in other DCCs, which values matching as close as possible, but note these won’t necessarily be 1:1. See details about each light below.
Tip: If you want to avoid conversions to USD, you can create and edit USD-native lights directly, see Using USD Lights.
Note: Learn more about the different types of light at Light Your Scene.
Adding Lights to Your Scene
• To add a new light, add any of the light nodes to your node graph and connect it to the GeoScene node that is downstream of your geometry. Or if you wish to import an existing light, go to the Import/ Export tab and use the Source Prim (to pick from your scene) or Import From File (to use an external file) options.
• Ensure Live Read is enabled to have your changes update live.
• In the Import/ Export tab, if the Output Prim Path is left blank , the lights will then be added to the Scene Graph automatically under {nodename}_Inject. Or if you wish to adjust the prim path, edit the Output Prim Path.
• In this example, we have added three of the Nuke lights: DirectLight, PointLight and SpotLight. (We have also changed the Color of each of them in the Node Properties).
• The scene is then connected to a ScanlineRender node and the Viewer in order to view it. The Position tab includes Constrain and Xform options, and the Display tab allows you to change how the lights look in the Viewer. You can then use the transformation handles to transform the lights interactively in the Viewer. See more about how you can use the Viewer at Lights in the Viewer.
Adjusting Light Properties
All lights have Basic, Refine, ScanlineRender Options, Position, Import/Export, and Display options listed here. Light-specific knobs are outlined in the sections below.
Basic
• You can set the Intensity of the light, which scales the power of the light linearly.
• You can also set an Exposure value which scales the power of the light exponentially as a power of 2, similar to an FStop control.
• You can enable the Normalize checkbox to keep the power of the light constant when the size of the light is altered. This makes it easier to independently adjust the intensity/exposure and size of the light because the total illumination provided will not vary with the area or angular size of the light. May not be respected by all light shader implementations.
• Use the Color wheel to set the color of the light.
• Use the Color Temperature checkbox to enable color temperature. In degrees Kelvin, this represents the white point of the light. When enabled the rgb converted result multiplies against the ‘Color’ control. The default is a common white point 6500k, or D65. Lower values are warmer and higher values are cooler with a valid range from 1000k to 10000k.
Refine
• The Diffuse Amount knob is a multiplier for the effect this light has on diffuse response of materials, so changing this essentially makes a diffuse shader respond differently to the light.
• The Specular Amount knob does the same for the specular response of materials.
ScanlineRender Options
• You can set an Illumination Mask and Receive Shadow Mask if you want the light to cast shadows on other objects. See Lights and Shadows to learn more about the workflow.
Position
• Each light has the usual transformation options, plus Constrain and Xform options. Learn more about these at Using Transformation Tools, Constraining Prims, and Xform Extract Options.
Import/Export
• Live Read allows your changes to update live.
• If you wish to import an existing light, use the Source Prim (to pick from your scene) or Import From File (to use an external file) options.
• If the Output Prim Path is left blank , the lights will then be added to the Scene Graph automatically under {nodename}_Inject. Or if you wish to adjust the prim path, edit the Output Prim Path.
Display
• The Display tab allows you to change how the lights look in the Viewer, including locator size and color.
DirectLight
This is a directional light which can be transformed to shine in the direction of your choice in your scene, equivalent to the USD DistantLight.
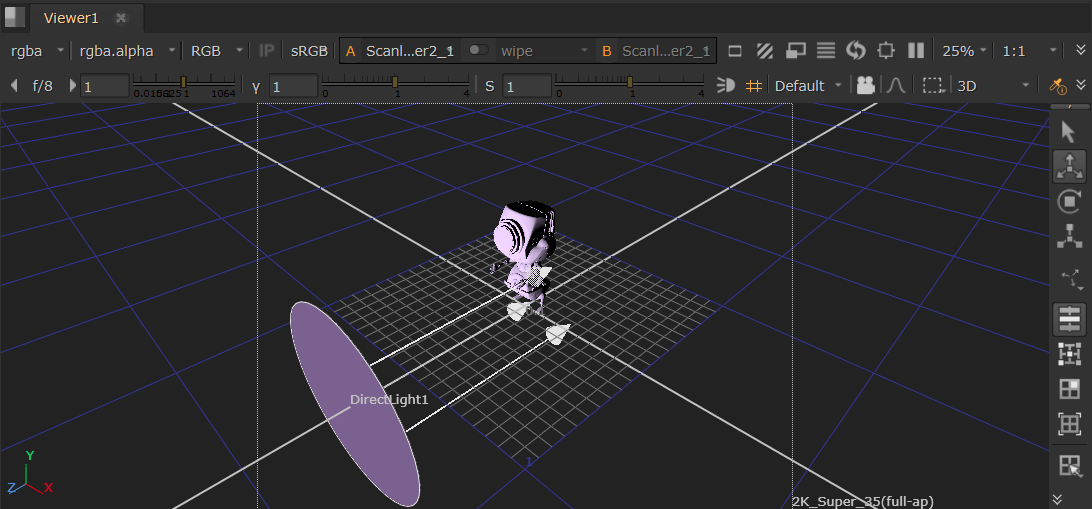
• Spread Angle lets you edit the angular diameter of the light in degrees.
Note: All controls are listed in the Node Reference Guide - DirectLight.
EnvironmentLight
The EnvironmentLight is there to produce a mesh’s specular color, so essentially anything plugged into the map input of the environment light will show up in the reflections of a mesh. This is equivalent to the USD DomeLight.
The easiest way to set this up is to connect a Read node with your image into the EnvironmentLight's map input.
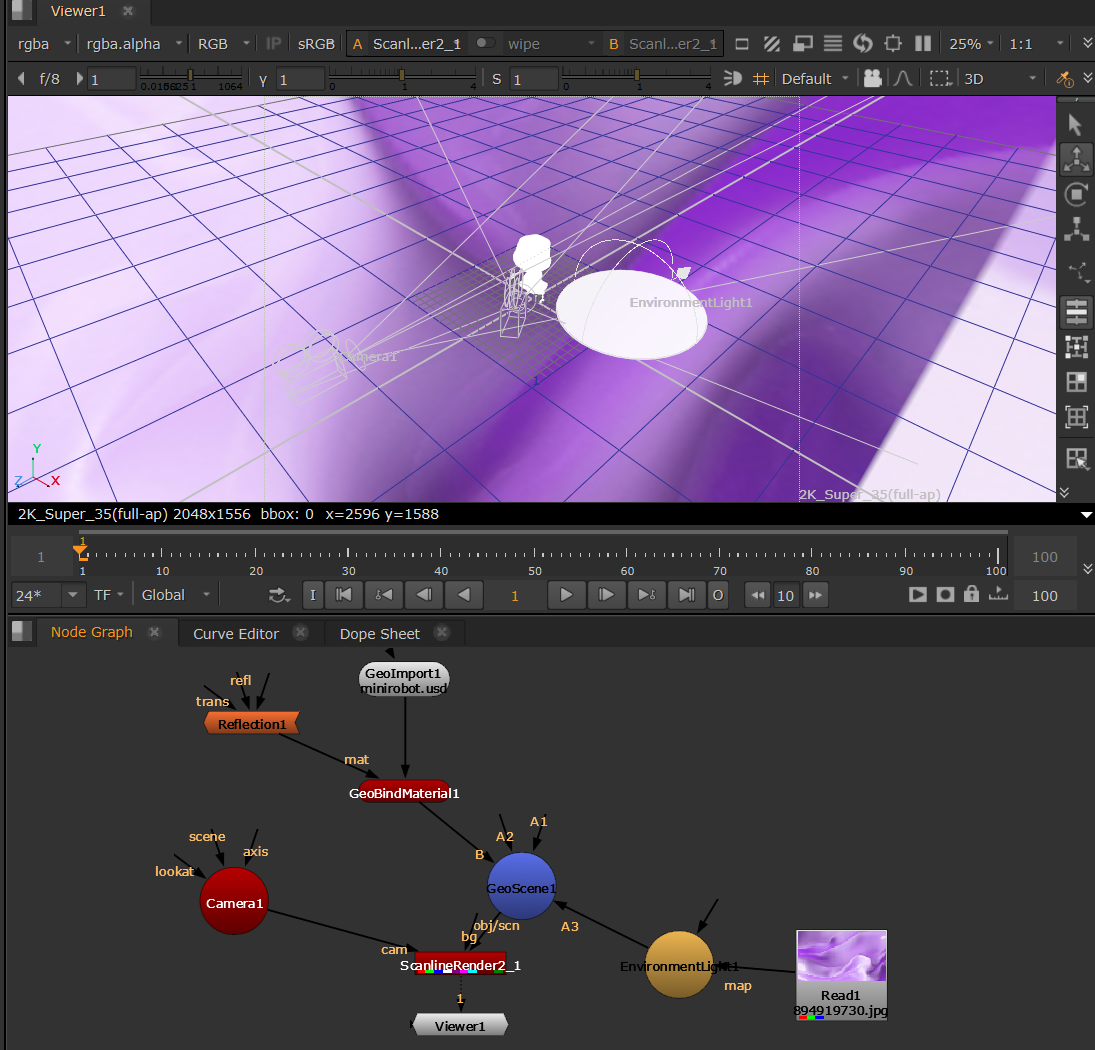
• Guide Radius is intended to scale the locator in the Viewer. See Lights in the Viewer.
• ScanlineRender Options: These changes will not be visible in the 3D viewport via HDStorm as HDStorm doesn’t provide controls for these yet, but will be visible in your ScanlineRender output. Blur Size allows you to set how much you want to blur the image you are mapping to the light, and Mirror X and Mirror Y will let you flip and flop the image being mapped. You can always opt to create a blur or mirror nodes to do this in the node graph also.
Note: All controls are listed in the Node Reference Guide - EnvironmentLight.
PointLight
This creates a point in 3D space that emits light in every direction, equivalent of the USD SphereLight but with a small radius.
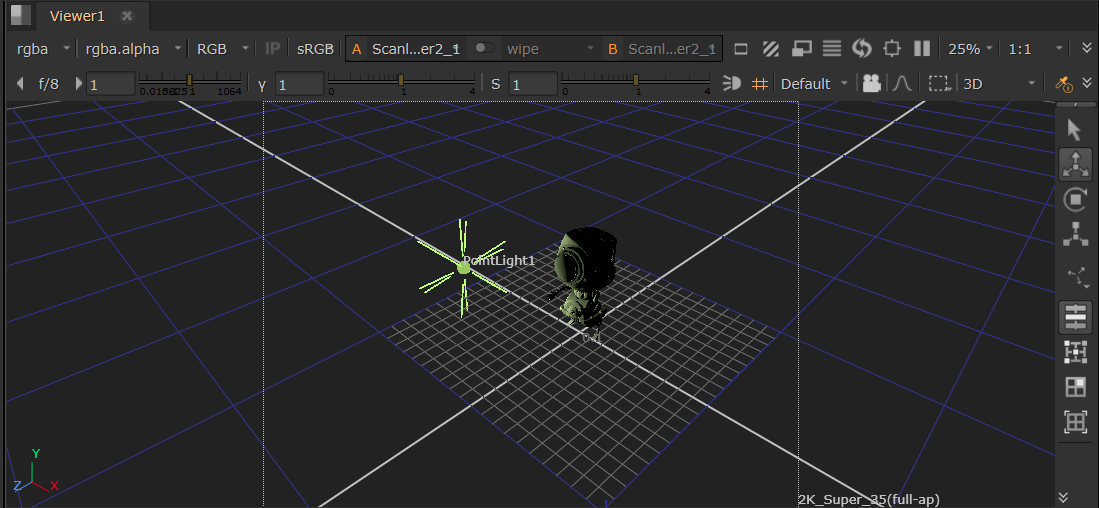
• The Radius knob controls the radius of the light, where a larger radius increases the overall reach of the light.
• The Treat As Point checkbox essentially reduces the radius to the equivalent size of a point. The Radius knob is greyed out when this Treat As Point is active as you have no need to change the radius in that case.
• ScanlineRender Options: These changes will not be visible in the 3D viewport via HDStorm as HDStorm doesn’t provide controls for these yet, but will be visible in your ScanlineRender output. Falloff Type controls how much light the object gets from the light source. It is based on the distance between the light source and the object. A Linear type will diminish the light at a fixed rate as it travels from the object. Quadratic and Cubic types will diminish the light at an exponential rate. FallOff Amount also affects the scale of this.
Note: The Output Prim Path will export a Sphere Light to the USD stage. So this would convert the light from a Nuke shader light to a USD light prim for use in other DCC’s, which values matching as close as possible, but note these won’t necessarily be 1:1. For the PointLight for instance there is no equivalent USD light, so the best approximation is a SphereLight with a radius set to an extremely small amount.
Note: All controls are listed in the Node Reference Guide - PointLight.
SpotLight
The SpotLight node creates a point in 3D space that emits a cone-shaped light, equivalent to the USD DiskLight.
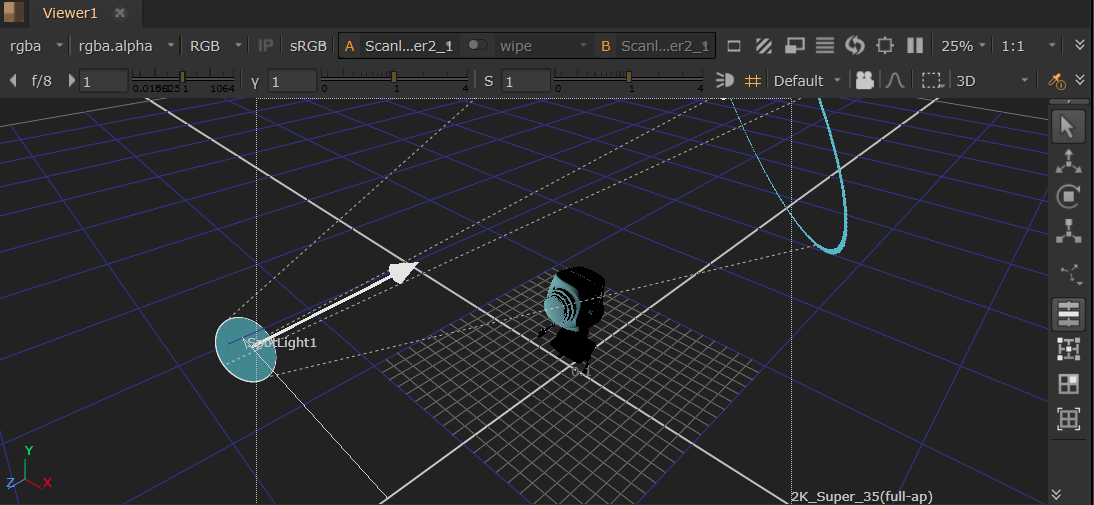
• The Radius knob controls the radius of the light. A larger radius increases the overall reach of the light.
• The Cone Angle controls the angular diameter of the light in degrees. The light will be cone shaped at smaller angles and behave more like a spotlight.
• The Cone Softness is the softness of the cone angle; typically a value of 1 is used for a soft gradation, while 0 would give the cone angle a hard cut-off. Values greater than 1 can be used to further soften the gradation.
• Focus affects the spread of the light. The greater the value the more focused the light is. Lower values result in a diffused effect.
• Focus Tint changes the color tint of the light in the falloff region determined by the focus property.
• ScanlineRender Options: These changes will not be visible in the 3D viewport via HDStorm as HDStorm doesn’t provide controls for these yet, but will be visible in your ScanlineRender output. Falloff Type controls how much light the object gets from the light source. It is based on the distance between the light source and the object. A Linear type will diminish the light at a fixed rate as it travels from the object. Quadratic and Cubic types will diminish the light at an exponential rate. FallOff Amount also affects the scale of this.
Note: The Output Prim Path will export a DiskLight to the USD stage. So this would convert the light from a Nuke shader light to a USD light prim for use in other DCC’s, which values matching as close as possible, but note these won’t necessarily be 1:1.
Note: All controls are listed in the Node Reference Guide - SpotLight.