 in the Viewer you want to flipbook.
in the Viewer you want to flipbook. Flipbooking a sequence refers to rendering out a range of images (typically at proxy resolution), then playing them back in order to accurately access the motion characteristics of added effects.
You have a few options for flipbooking within Nuke:
• You can enable automatic disk caching of rendered frames, then play these frames back using Nuke’s native Viewer. This option does not let you define a specific playback rate.
• You can render out temporary image sequences to FrameCycler, a RAM-buffering playback utility, which is automatically installed with your copy of Nuke and plays back sequences at the defined frame rate.
• You can also set up an external flipbooking application in Nuke using Python. For more information, see the Nuke Python documentation (Help > Documentation).
The Nuke Viewer automatically saves to disk a version of every frame it displays. When you play through sequences in the Viewer, it reads, where possible, from this cache of pre-rendered images, making real-time play back possible (depending, of course, on image resolution and your hardware configuration). You can define the location and size of the Viewer cache in the Preferences.
Depending on what viewer buffer bit depth has been set to in the Viewer settings, the cache can contain 8-bit (byte), 16-bit (half-float), or 32-bit (float) image data. This offers a trade-off between speed and quality. Half-float and float modes provide higher precision than byte but are also slower to process.
| 1. | Click Edit > Preferences to display the Preferences dialog. |
| 2. | In the disk cache field, enter the path name of the directory in which you want to store the flipbook images (for example, c:/temp). |
| 3. | Using the disk cache size control, select the number of gigabytes you want to allow the image cache to consume. |
| 4. | Click the Save Prefs button to update preferences and then restart Nuke. |
The Viewer now caches each frame it displays in the directory specified. When you click the playback buttons on the Viewer, or drag on the scrub bar, Nuke reads in images from this cache.
Note that the cached images have unique names reflecting their point of output location in the script. This means that you can cache images from multiple nodes in the script without overwriting previously cached images.
To flipbook an image sequence inside FrameCycler, do the following.
| 1. | Select the node whose output you wish to see flipbooked. |
NOTE: If you select a Write node in the step above, you must first click its Render button in order to manually render its output to the destination defined in the file field. This step is necessary only in the case of Write nodes.
| 2. | Select Render > Flipbook selected (or press Alt+F). Alternatively you can click the Flipbook this Viewer button  in the Viewer you want to flipbook. in the Viewer you want to flipbook. |
A Flipbook dialog opens.
| 3. | Check that your settings are correct in the dialog. The default values are copied from the Viewer you currently have active. You can change them if necessary: |
• Flipbook - set the flipbooking application you want to use.
• Take settings from - set which Viewer should be used to draw default values from.
• Enable ROI - Check to define your region of interest.
• Channels - select which layer to display in the flipbook result.
• Frame range - set the frame range you want to flipbook.
• Use proxy - check to use proxy mode.
• Render in background - check to render in the background. If you check this, you can also set #CPU limit and Memory limit controls. The former limits the number of threads that Nuke uses in the background and the latter limits the amount of cache memory that Nuke uses.
NOTE: If you’re rendering multiple sequences in the background, this can take up more than the total RAM on your machine. When running background renders of any type, you need to make sure they don't require more RAM all together than what's available on the machine, otherwise you may experience problems such as hanging.
• Continue on error - check to keep rendering even if an error occurs during the process.
• Delete existing temporary files - Check to delete any existing temporary files with the same file name before flipbooking.
• LUT - select the LUT appropriate for viewing. By default, the flipbook renders your files with a linear colorspace and attempt to pass a LUT file to the flipbook.
• Burn in the LUT - If you check this box the flipbook files are rendered with the LUT applied. If you uncheck it, the flipbook is displayed using it's equivalent LUT (based on the LUT’s name). If you have an equivalent LUT available in the flipbook program, then it's better not to check the Burn in the LUT box. This way, when you measure pixel values in the flipbook application they match what you get in the Nuke Viewer.
• Audio - if you want to flipbook an audio file with your clip, select the AudioRead node you need in this dropdown. For more information on audio files in Nuke, see Audio in Nuke.
• Continue on error - check this if you want to continue flipbooking when FrameCycler encounters an error.
• Views - set which stereo views to include.
| 4. | Click OK. |
Nuke renders as a temporary sequence the output of the selected node using the frame range and resolution defined in the script’s settings. This may take a few moments.
| 5. | Once the render is complete, Nuke launches FrameCycler and loads in the temporary sequence. You can play it back and view it using FrameCycler’s media controls. |
NOTE: FrameCycler comes packed with many features to complement flipbooking. You can, for example, attach sound files to the image sequence, cut it, or splice it together with other image sequences. Surf to www.iridas.com for more information.
You can capture the contents of the Viewer for a quick real-time flipbook, also known as a playblast, and save the content out to .jpg for review. This is very useful for quickly checking the animation in your 3D scene in real-time without having to do a full scanline render. Playblast flipbooks the Viewer 'as is', including 2D and 3D scenes, handle and transform overlays (such as roto shape outlines), wipes, and so on.

|
|
The contents of a Viewer containing 3D and 2D information, including the wipe handle, captured in .jpg format. |
To flipbook the Viewer contents:
| 1. | Click the Capture button under the Viewer, to the right of the flipbook button. |
The Capture dialog displays.
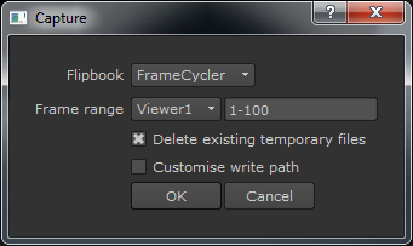
| 2. | Select the required Flipbook tool using the dropdown. |
| 3. | If you have more than one Viewer in the script, select the required Viewer |
| 4. | Set the Frame range to preview. |
| 5. | Disable Delete existing temporary files if you want to retain previously cached files. |
| 6. | Click OK to flipbook the contents of the Viewer. |
The frames are cached to the cache directory specified in the Preferences.
To capture the Viewer contents:
| 1. | Click the Capture button under the Viewer, to the right of the flipbook button. |
The Capture dialog displays.
| 2. | Select the requried Flipbook tool using the dropdown. |
| 3. | If you have more than one Viewer in the script, select the required Viewer |
| 4. | Set the Frame range to preview. |
| 5. | Enable Customize write path and enter a Write path or click the folder icon and browse to the required location. |
NOTE: Nuke only captures sequences using the .jpg format. Don't forget to include printf or hash frame padding, such as %4d or ####.
| 6. | Enable No flipbook if you don't require the selected flipbooking tool to display the frame range. |
| 7. | Click OK to capture the contents of the Viewer. |
The frame range is cached as .jpgs to the directory specified in the Write path control.